This document provides an overview and analysis of a study area located along the Bhairab River in Bangladesh. Key findings from the document include:
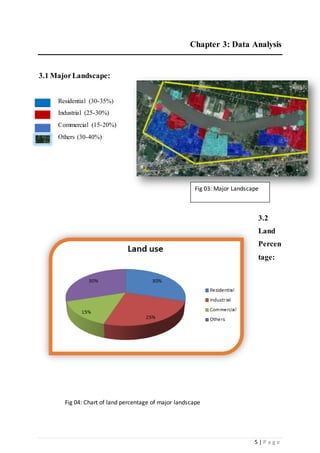
1) The study area consists of residential, industrial, commercial and other land uses including infrastructure like roads, drainage systems and utilities.
2) An analysis of the land use patterns found residential areas make up 30-35% of the area, industries 25-30%, and commercial 15-20%. Major industries included several jute mills and presses.
3) Issues identified include poor road and drainage infrastructure, lack of utilities like water supply, and economic dependence on the jute industry. The river was also found to be polluted with reduced flows.