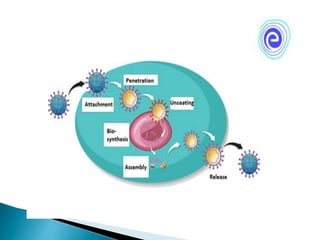
Viruses have two life cycles: lytic and lysogenic. The lytic cycle involves the replication of viruses within a host cell, forcing it to rapidly produce thousands of identical virus copies. This cycle has five steps: 1) attachment of the virus to the host cell receptor, 2) penetration of viral DNA/RNA inside, 3) protein synthesis using the host cell's machinery, 4) assembly of new viral particles using replicated DNA and proteins, and 5) lysis of the host cell to release new viruses.