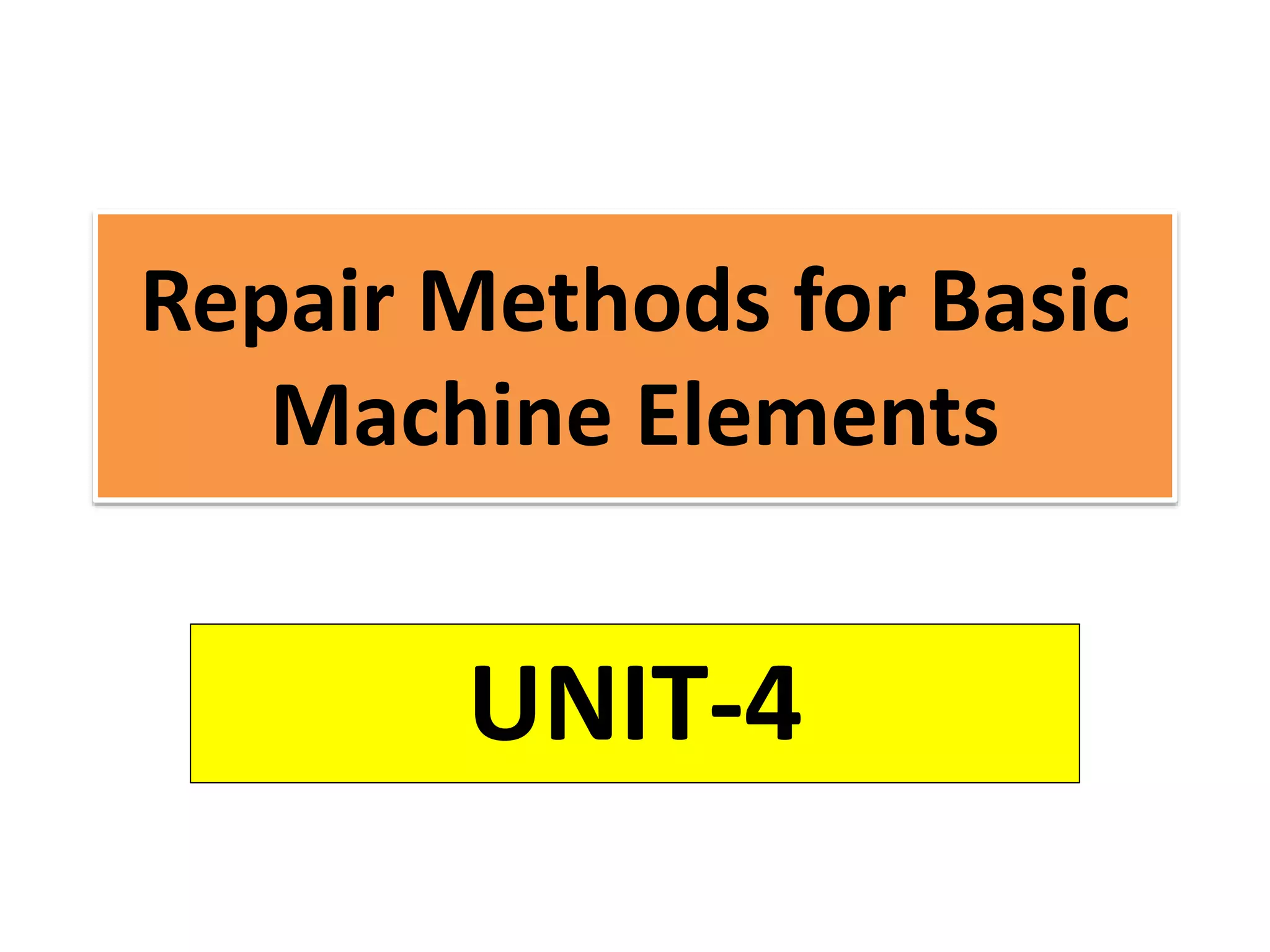
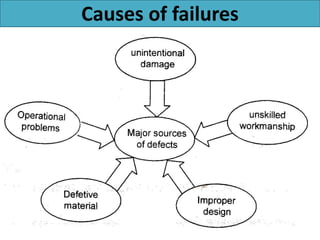
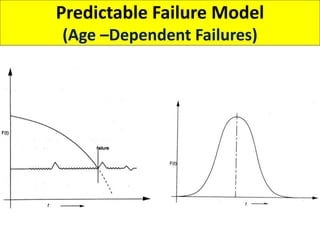
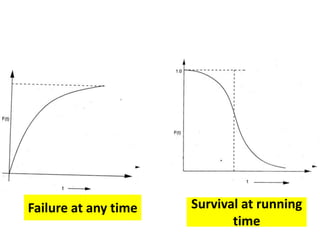
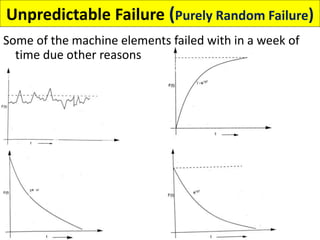
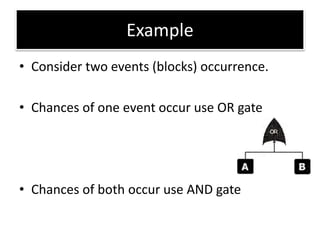
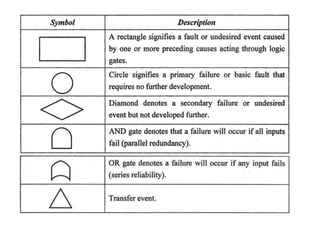
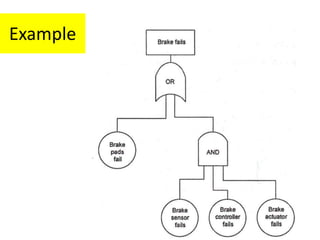
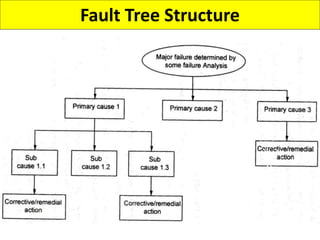
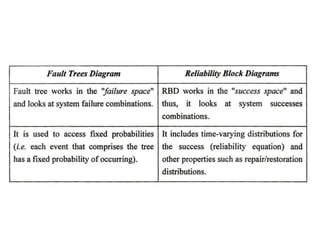
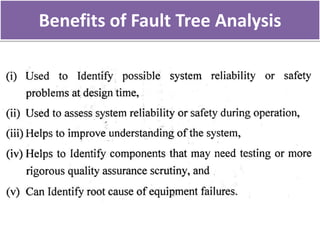
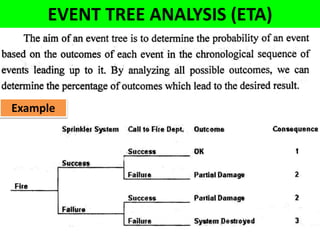
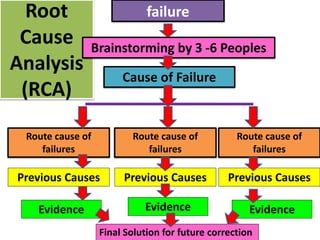
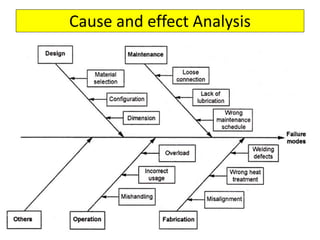
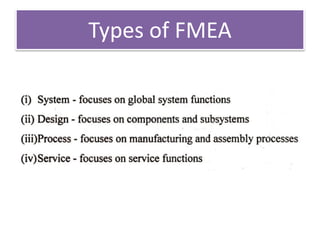
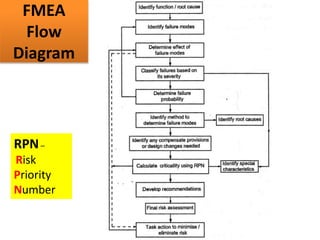
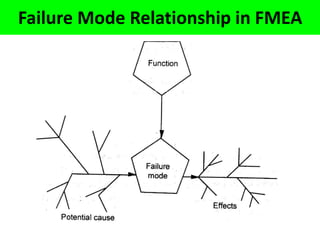
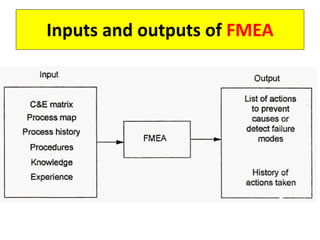
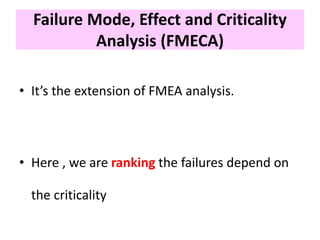
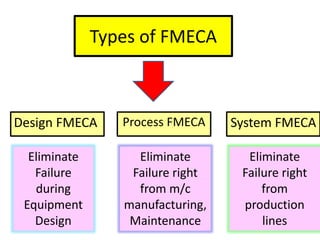
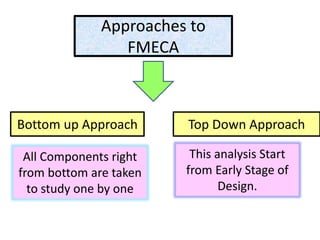
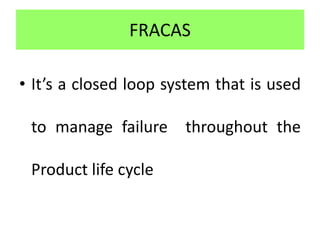
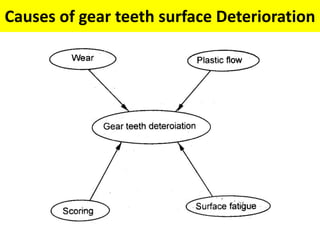
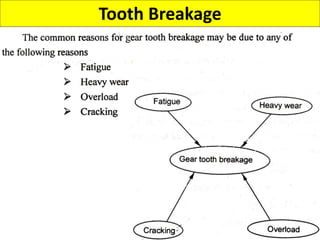
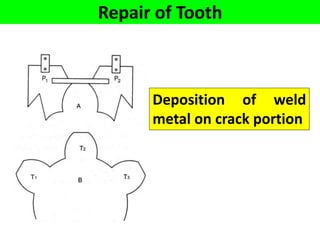
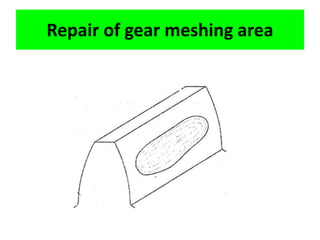
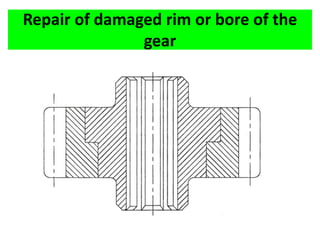
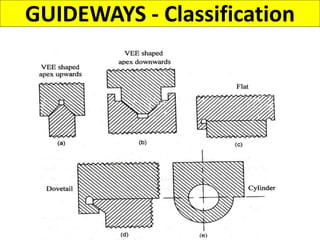
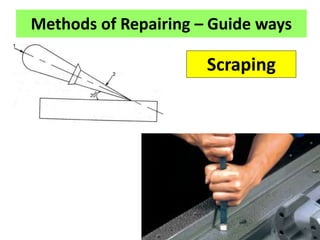
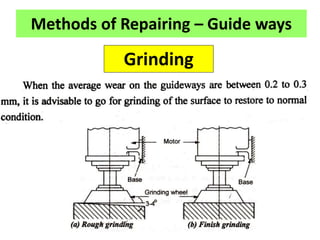
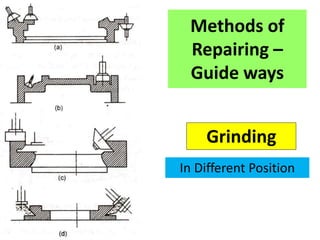
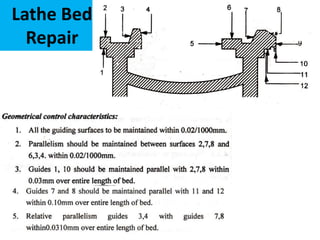
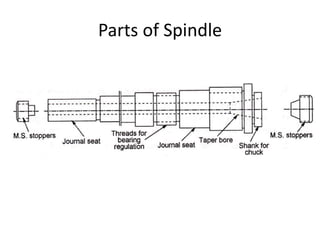
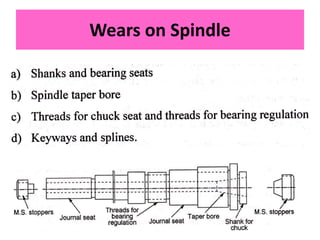
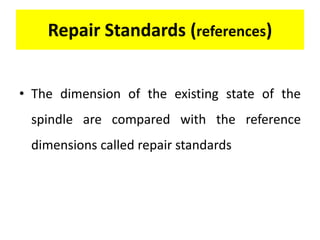
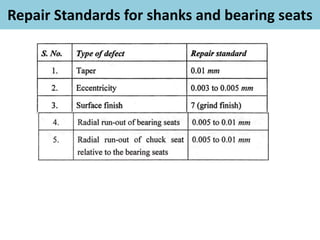
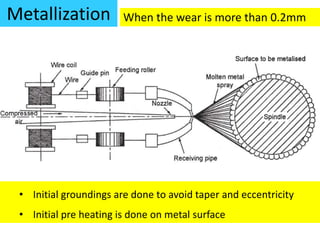
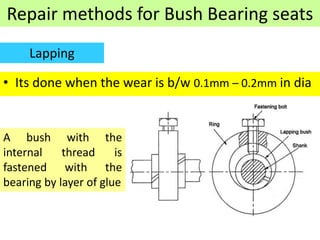
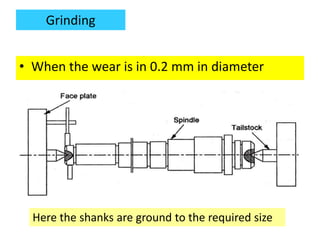
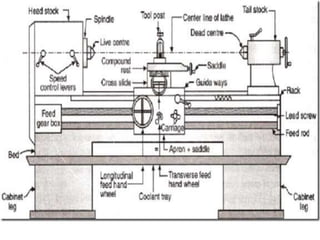
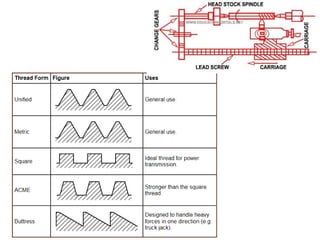
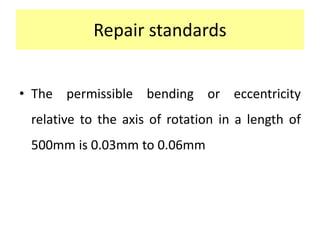
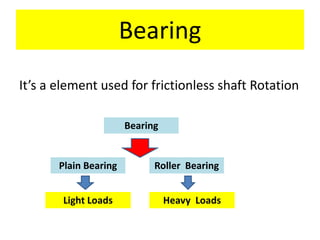
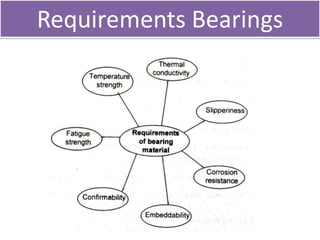
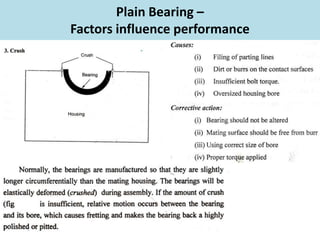
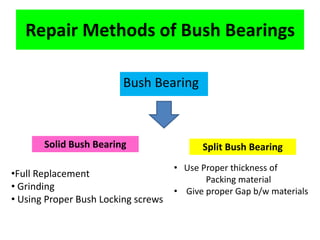
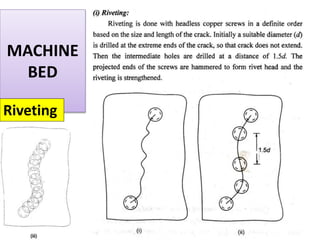
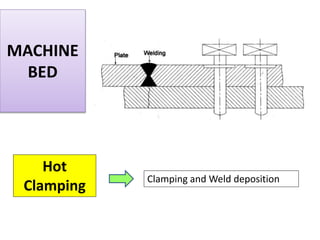
This document discusses various failure modes and repair methods for machine elements. It covers failures in gears, guideways, spindles, lead screws, bearings, and machine beds. The main causes of failure include wear, fatigue, overload, and corrosion. Repair methods depend on the type and extent of damage, and may include grinding, welding, bush fitting, replacement of parts, and preventing future failures through improved maintenance and design. Failure analysis techniques help identify root causes and prevent recurrence.