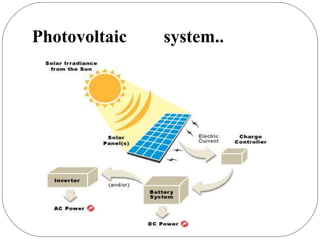
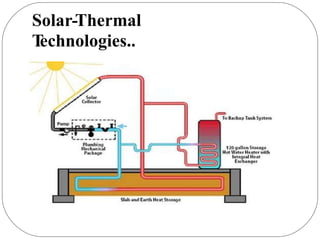
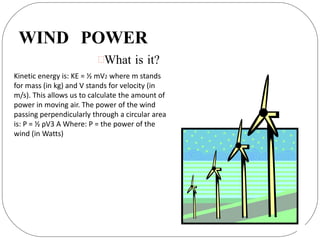
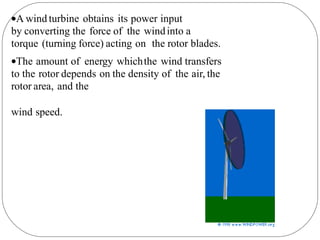
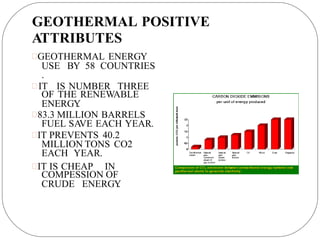
This document discusses various types of renewable energy sources including sunlight, wind, rain, geothermal heat, hydroelectricity, biomass, and others. It provides statistics on current global usage of renewables such as 13% of energy coming from traditional biomass. The document also focuses in more detail on certain renewable technologies for energy generation including wind power, hydroelectric power, solar energy, biofuels, wave power, and geothermal power. It provides examples of each technology and their advantages for sustainable energy production.