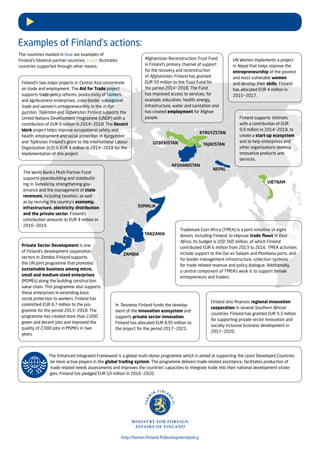
Finland supports developing countries' economies through partnerships with organizations like the UN, World Bank, and bilateral initiatives. This support promotes private sector growth, job creation, and economic opportunities by strengthening business environments, infrastructure, access to finance, and trade capacity. Finland contributes over 500 million euros from 2016-2019 to mobilize sustainable investments and support programs in countries like Zambia, Tanzania, Nepal, and Somalia.