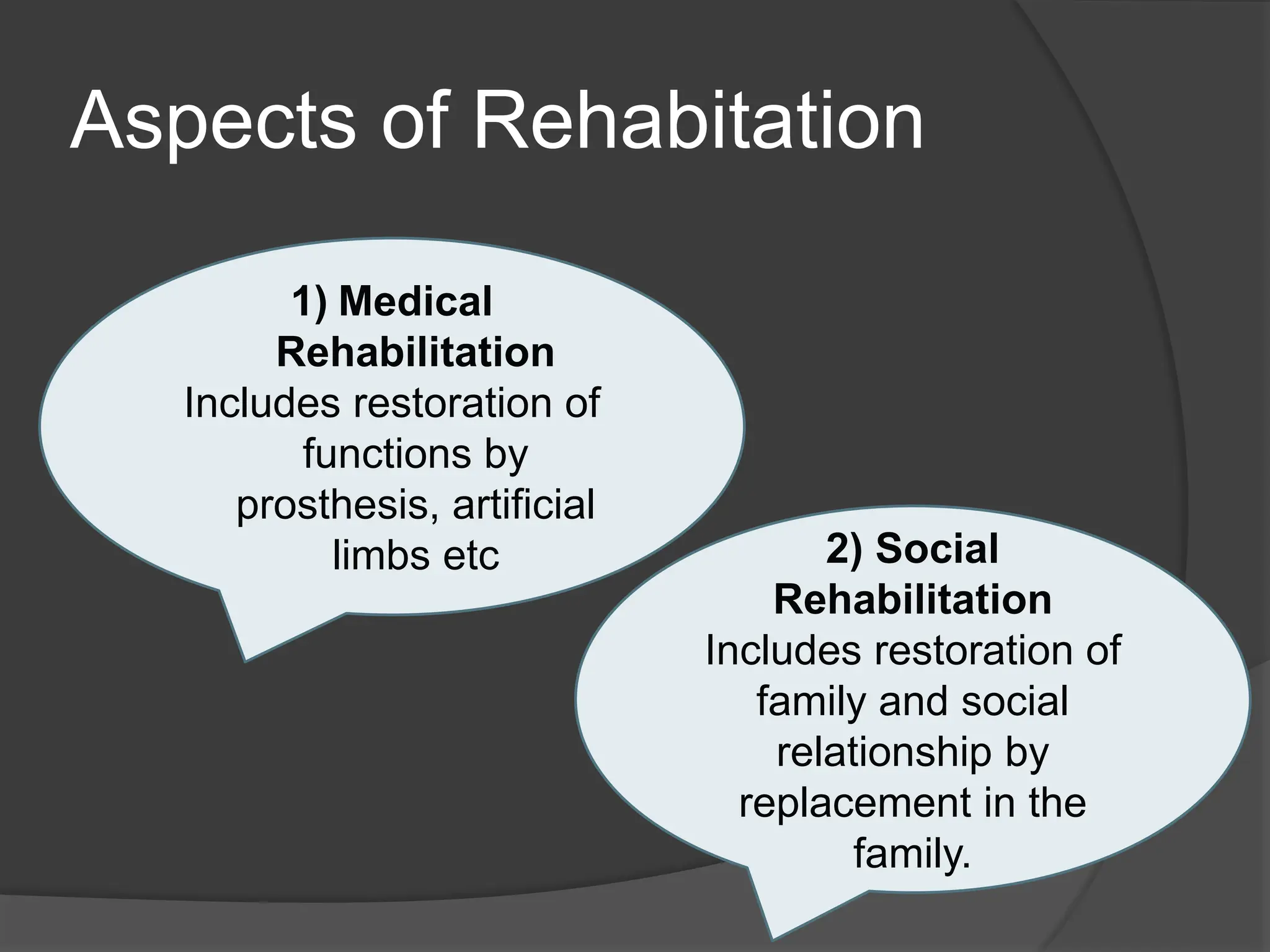
The document discusses rehabilitation according to the WHO definition and principles. It describes the four main aspects of rehabilitation as medical, social, educational, and psychological. The types of rehabilitation therapy discussed include physical, occupational, cognitive, speech/swallow, and vocational rehabilitation. Physical rehabilitation aims to restore functions through exercise programs. Occupational therapy focuses on daily living skills. Cognitive rehabilitation helps restore thinking and memory abilities. Vocational rehabilitation services help disabled individuals secure and retain employment.