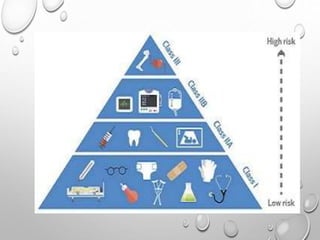
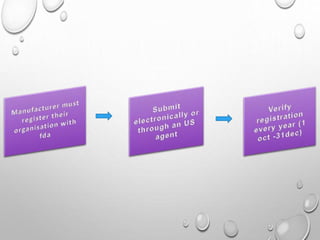
This document discusses regulations for medical devices in various countries and regions. It provides an overview of the regulatory bodies that oversee medical devices in Australia, Europe, the US, Canada, China, Japan, Brazil, and India. For the US, it describes the Food and Drug Administration's role and classifications of medical devices. It also summarizes key concepts around establishing registration and listing of devices, premarket notification (510(k)), de novo classification, premarket approval, and quality system regulations.