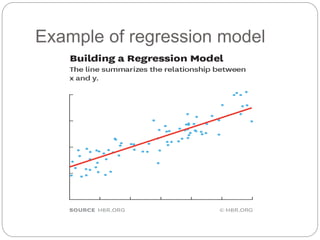
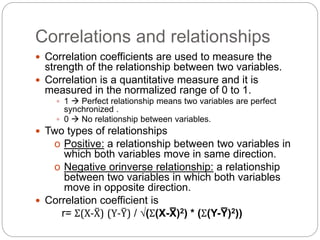
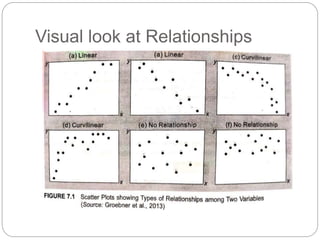
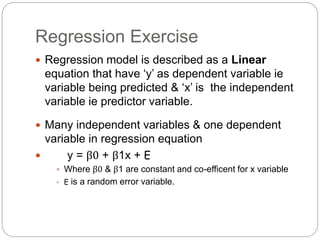
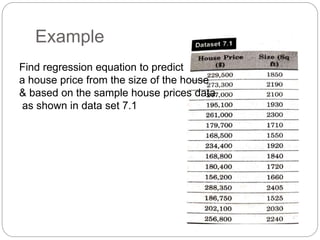
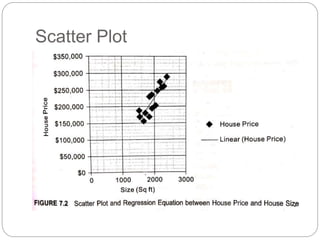
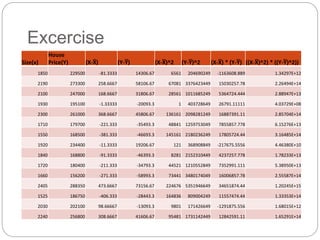
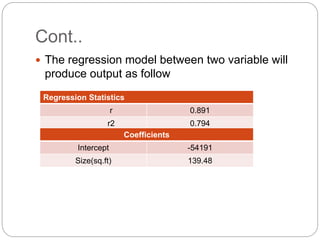
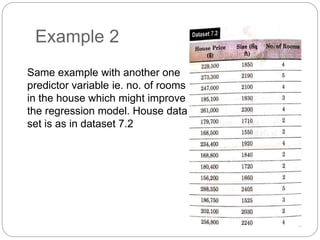
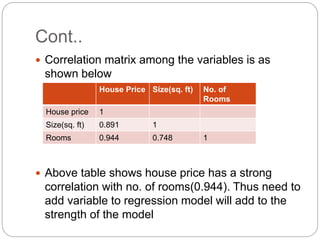
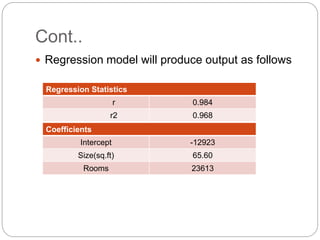
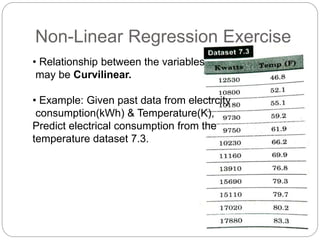
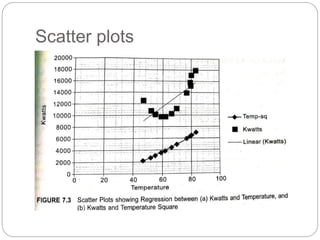
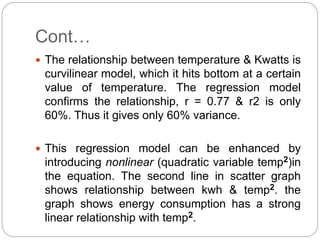
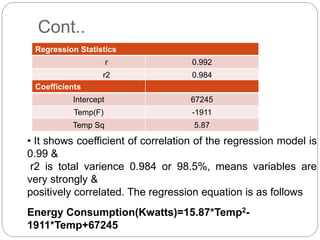
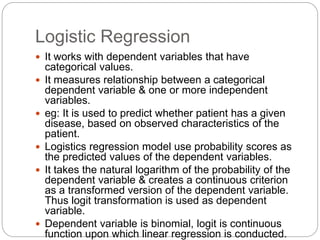
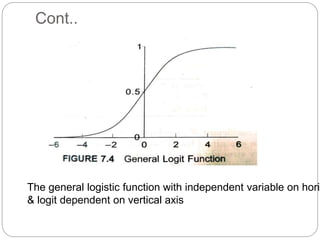
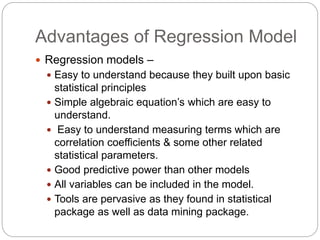
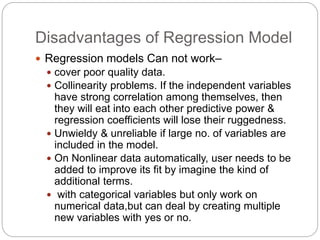
Regression is a statistical technique used to model relationships between variables. The key steps are to identify variables, select a dependent variable to predict, examine relationships visually, and find a way to predict the dependent variable using other variables. Correlation coefficients measure the strength of relationships between 0-1. Positive relationships have variables moving in the same direction, while negative relationships have them moving in opposite directions. Non-linear regression can model curvilinear relationships using quadratic terms. Logistic regression is used for categorical dependent variables.