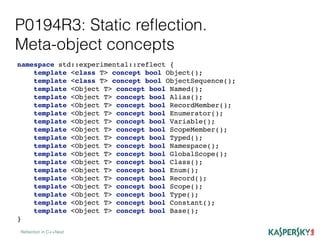
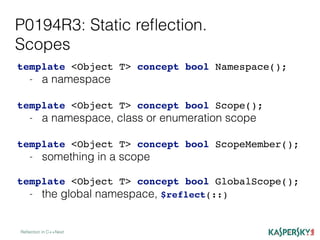
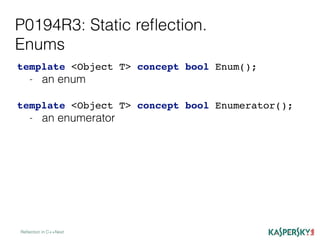
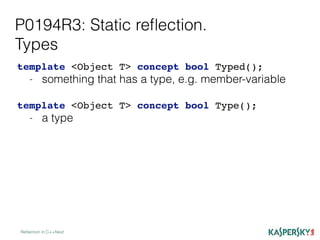
The document discusses the development of static reflection in C++, highlighting key proposals and concepts such as type introspection and metaprogramming. It describes the core language and library changes necessary for static reflection, with examples of its implementation and use cases. Additionally, the document contrasts two proposals (p0194r3 and p0590r0) and outlines the pros and cons of static reflection in the context of C++ programming.

















![Reflection in C++Next
class Person
{
[[getter, setter]] std::string name;
[[getter, setter]] std::string email;
};
What we actually need…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-18-320.jpg)
![Reflection in C++Next
class Person
{
[[getter, setter, serialized]] std::string name;
[[getter, setter, serialized]] std::string email;
};
What we actually need…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-19-320.jpg)
![Reflection in C++Next
class [[polymorphically_serialized]] Person: IPerson
{
Person() { /* initializing code here */ }
[[getter, setter, serialized]] std::string name;
[[getter, setter, serialized]] std::string email;
};
What we actually need…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-20-320.jpg)








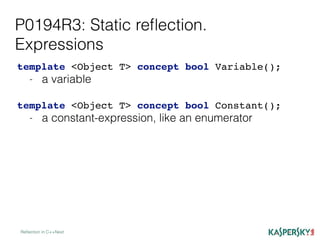


 {
using en_m = decltype(m);
if (get_constant_v<en_m> == e)
result = get_base_name_v<en_m>;
});
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-36-320.jpg)
 {
using m_t = decltype(m);
result &= a.*get_pointer_v<m_t> ==
b.*get_pointer_v<m_t>;
});
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-37-320.jpg)
 {
result &= a.$unreflect(m) ==
b.$unreflect(m);
});
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-38-320.jpg)

![P0194R3: Static reflection.
Templates parametrized by namespace
Reflection in C++Next
template <class MN>
void algorithm(const string& str, int i) {
// [foo|bar]::func1(str)
$unreflect(MN)::func1(str);
// [foo|bar]::func2([foo|bar]::func3(i))
$unreflect(MN)::func2($unreflect(MN)::func3(i));
}
void func(const string& str, int i, bool want_foo) {
if (want_foo)
algorithm<$reflect(foo)>(str, i);
else
algorithm<$reflect(bar)>(str, i);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-40-320.jpg)


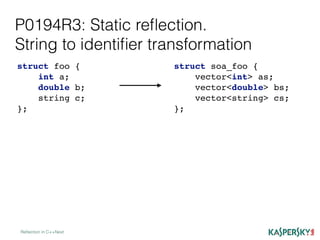









 {
using en_m = decltype(m);
if (get_constant_v<en_m> == e)
result = get_base_name_v<en_m>;
});
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-53-320.jpg)
 {
if (m.value() == e)
result = m.name();
});
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170223222752/85/Reflection-in-C-Next-54-320.jpg)




