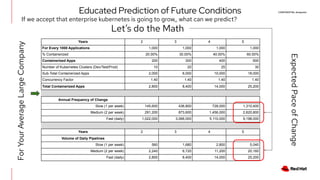
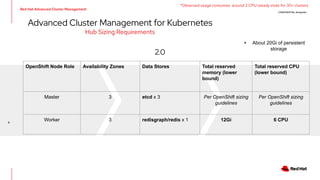
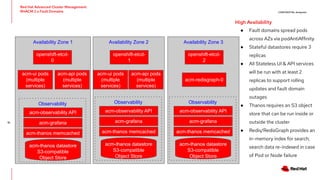
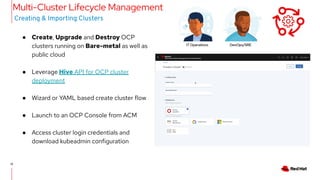
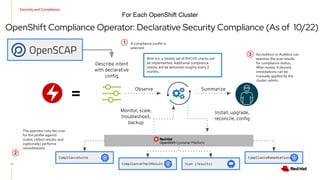
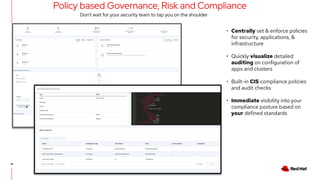
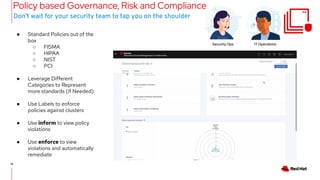
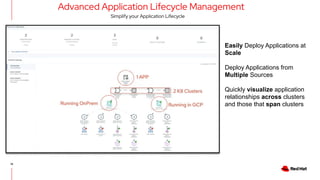
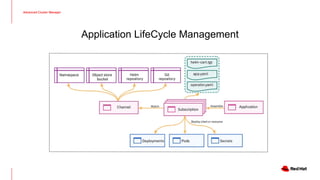
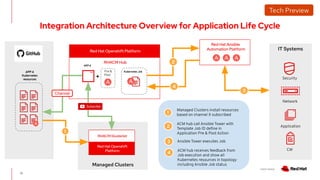
The document outlines an advanced cluster management presentation focusing on features and benefits, particularly for enterprise Kubernetes environments. It covers aspects such as policy enforcement, application deployment, operational cost reduction, and compliance requirements. Additionally, it addresses the architecture for managing application lifecycles and emphasizes the importance of centralized control over multiple clouds.