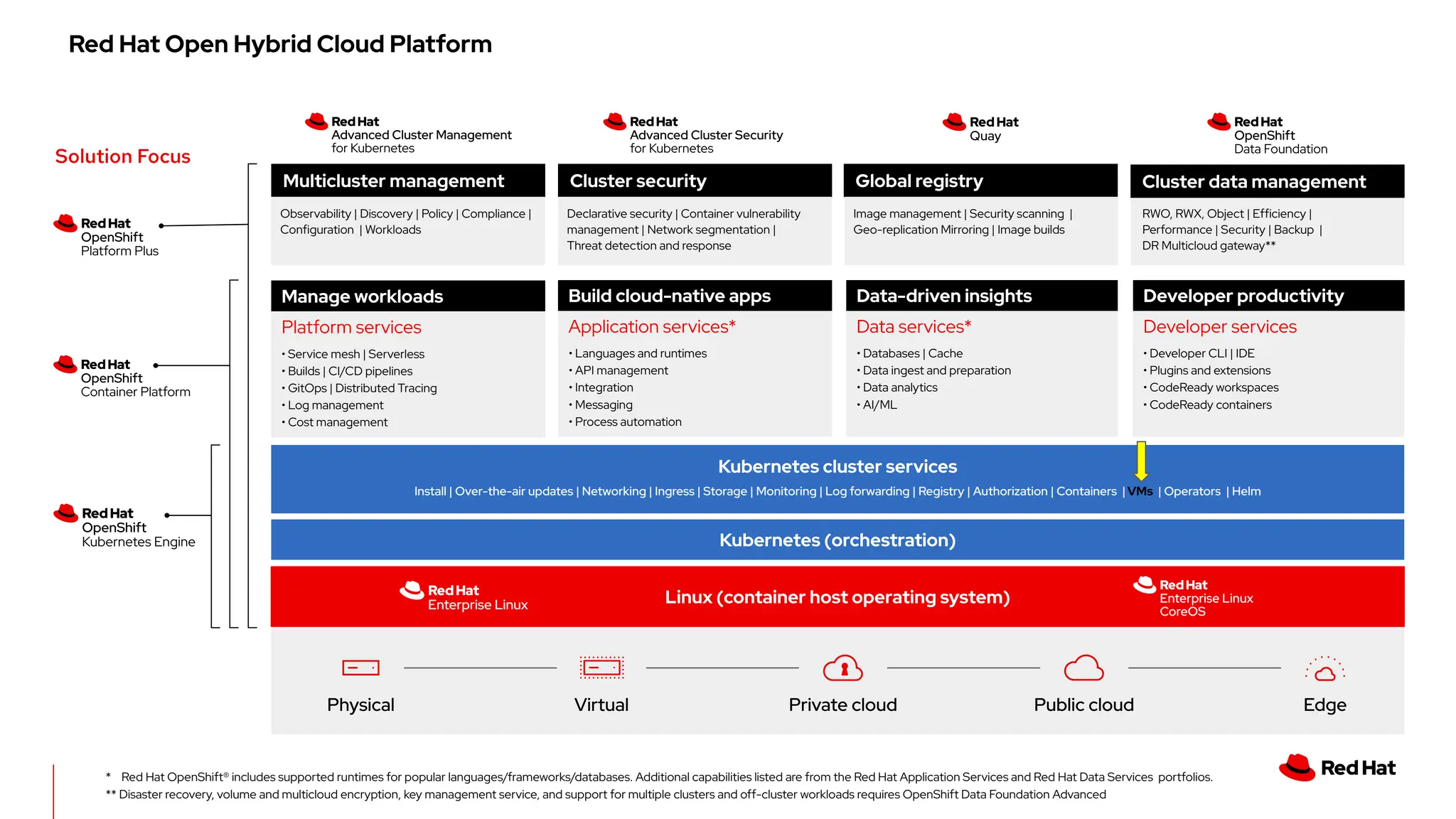
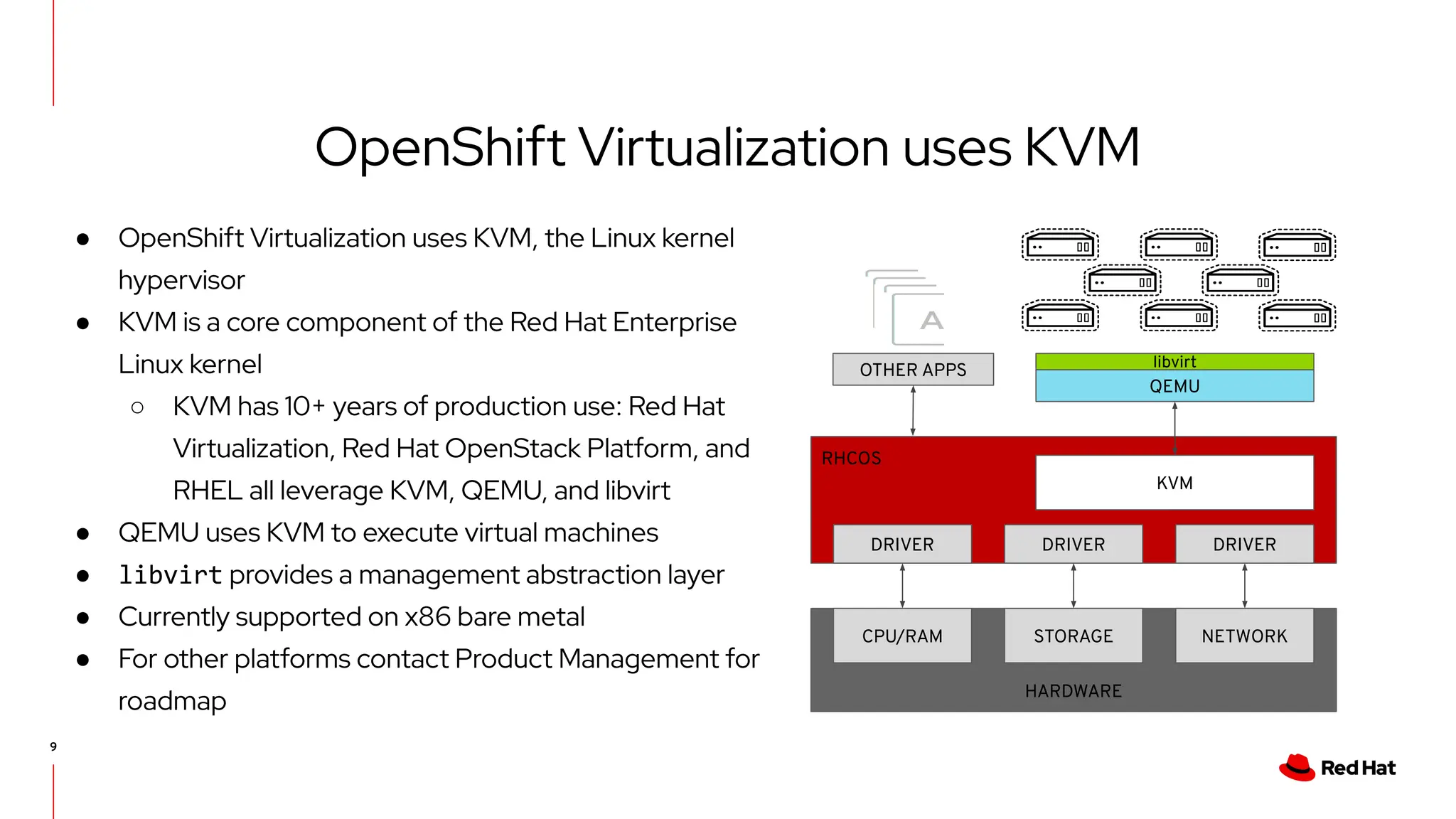
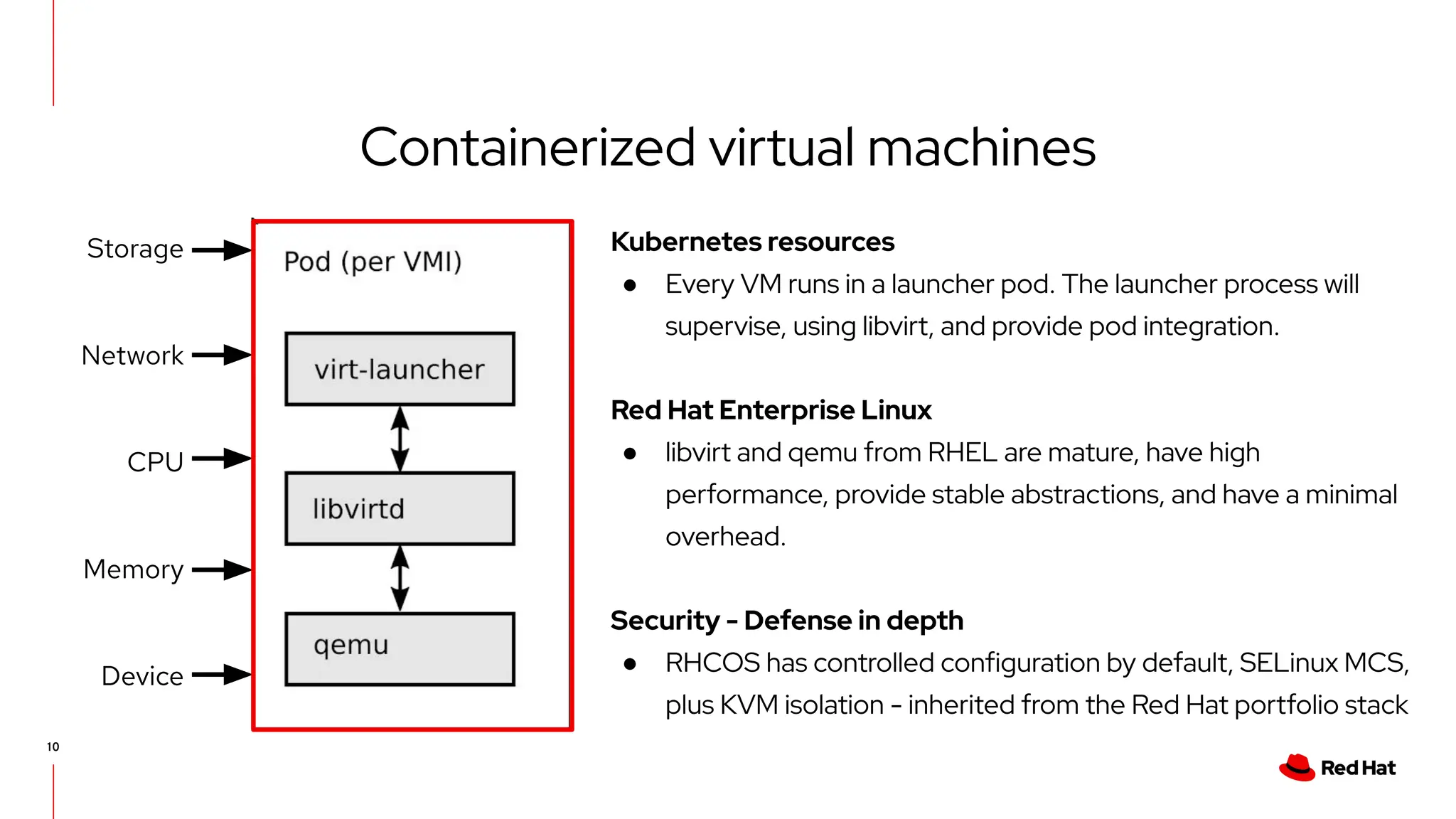
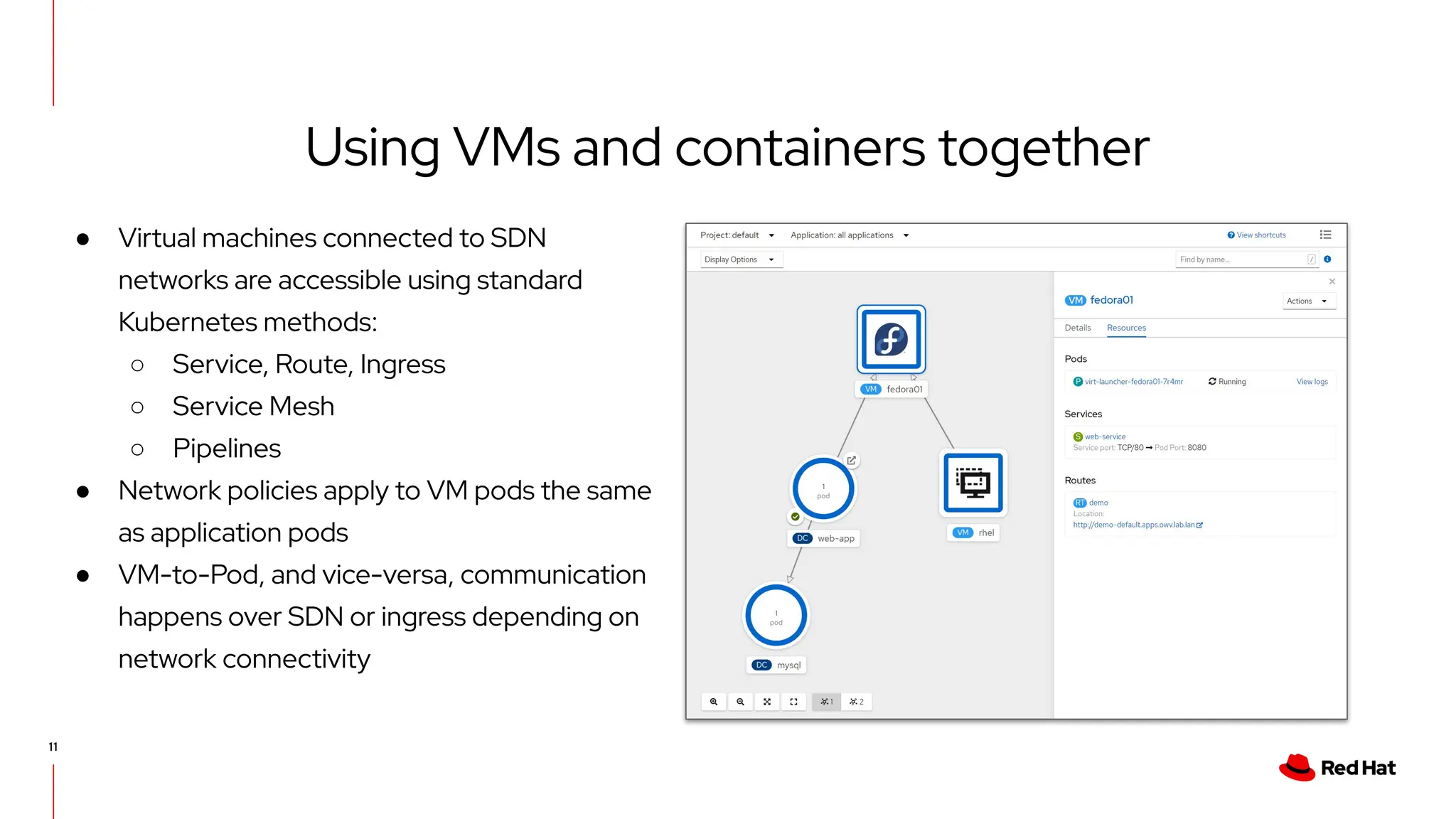
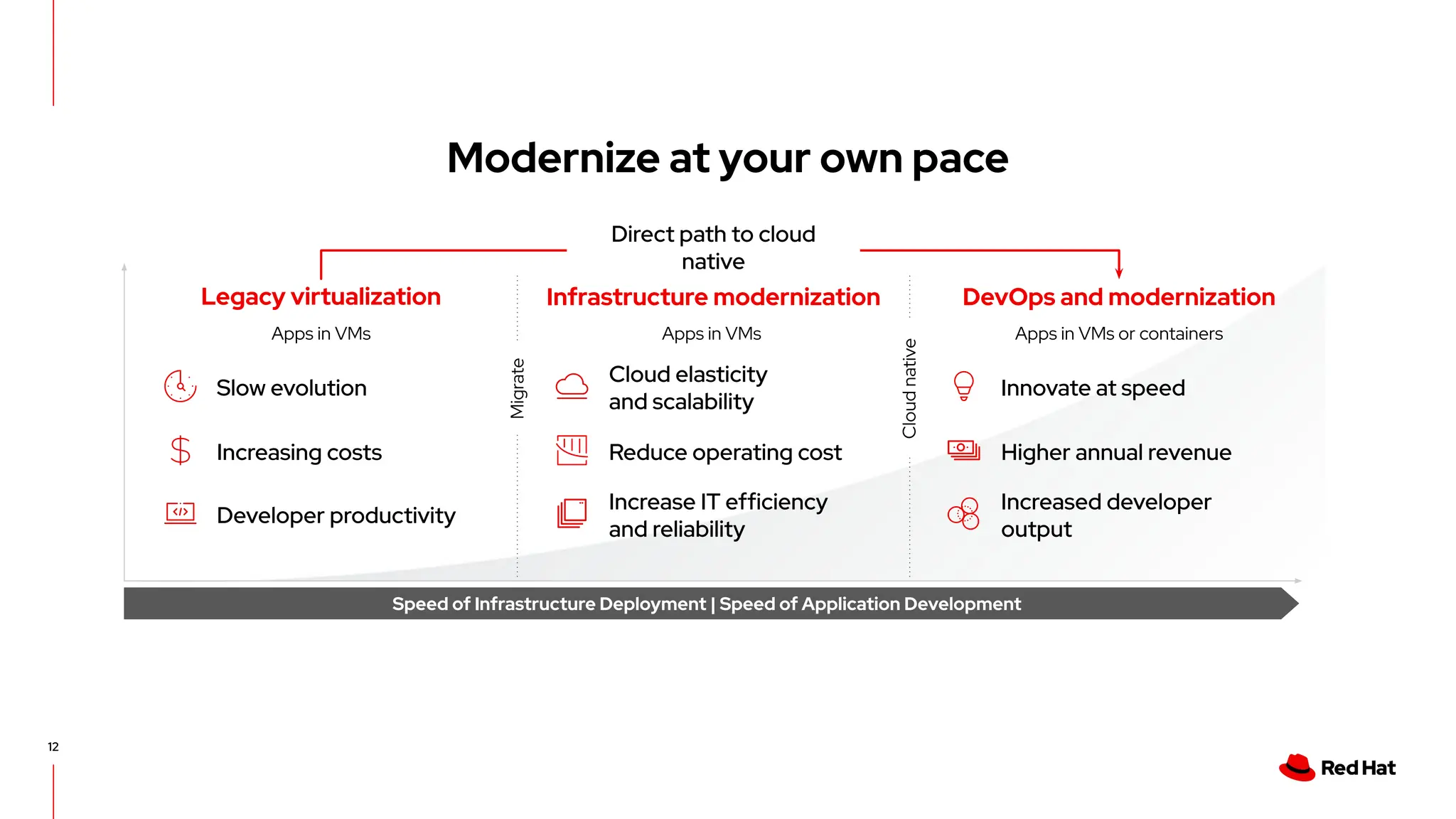
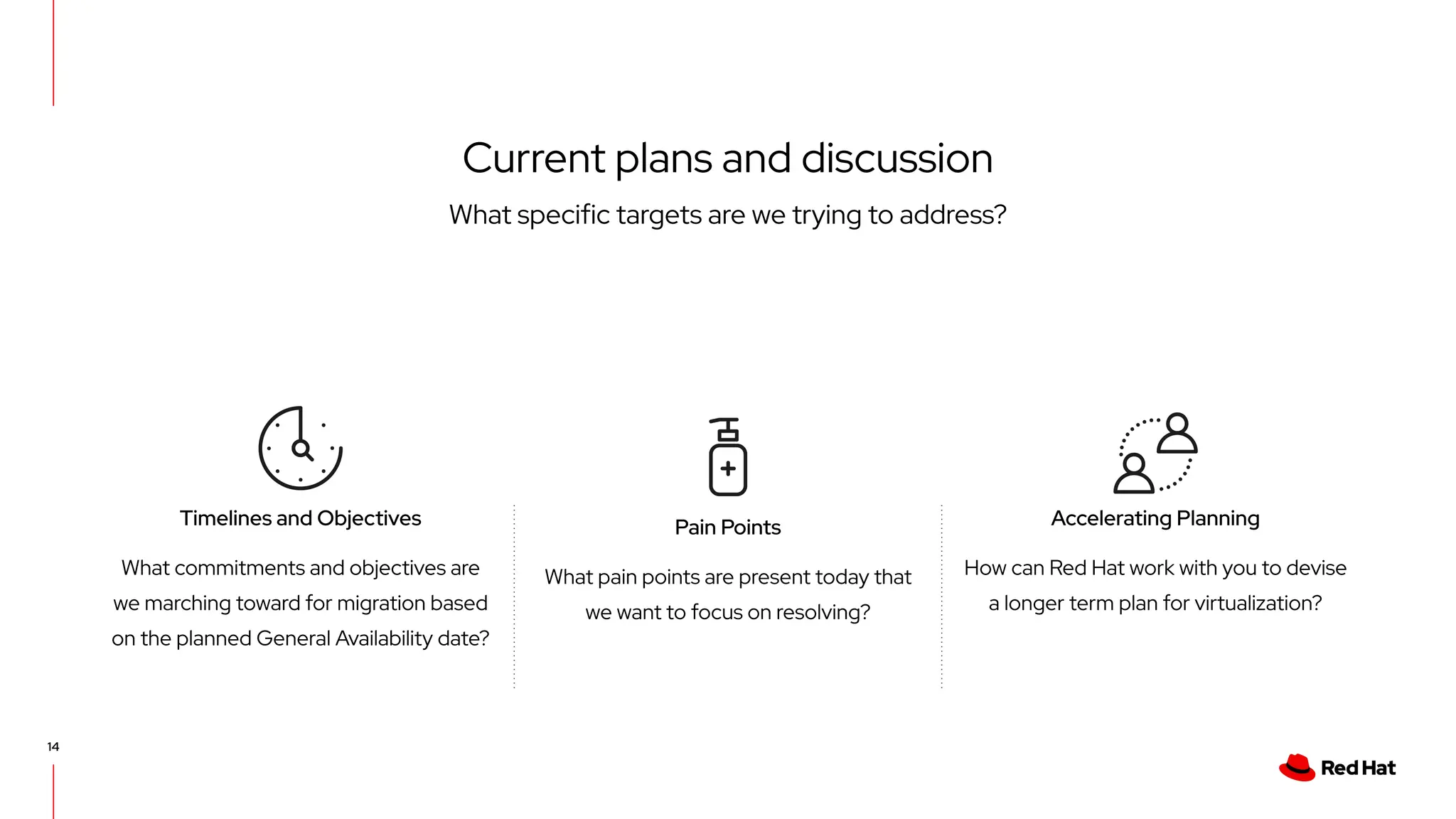
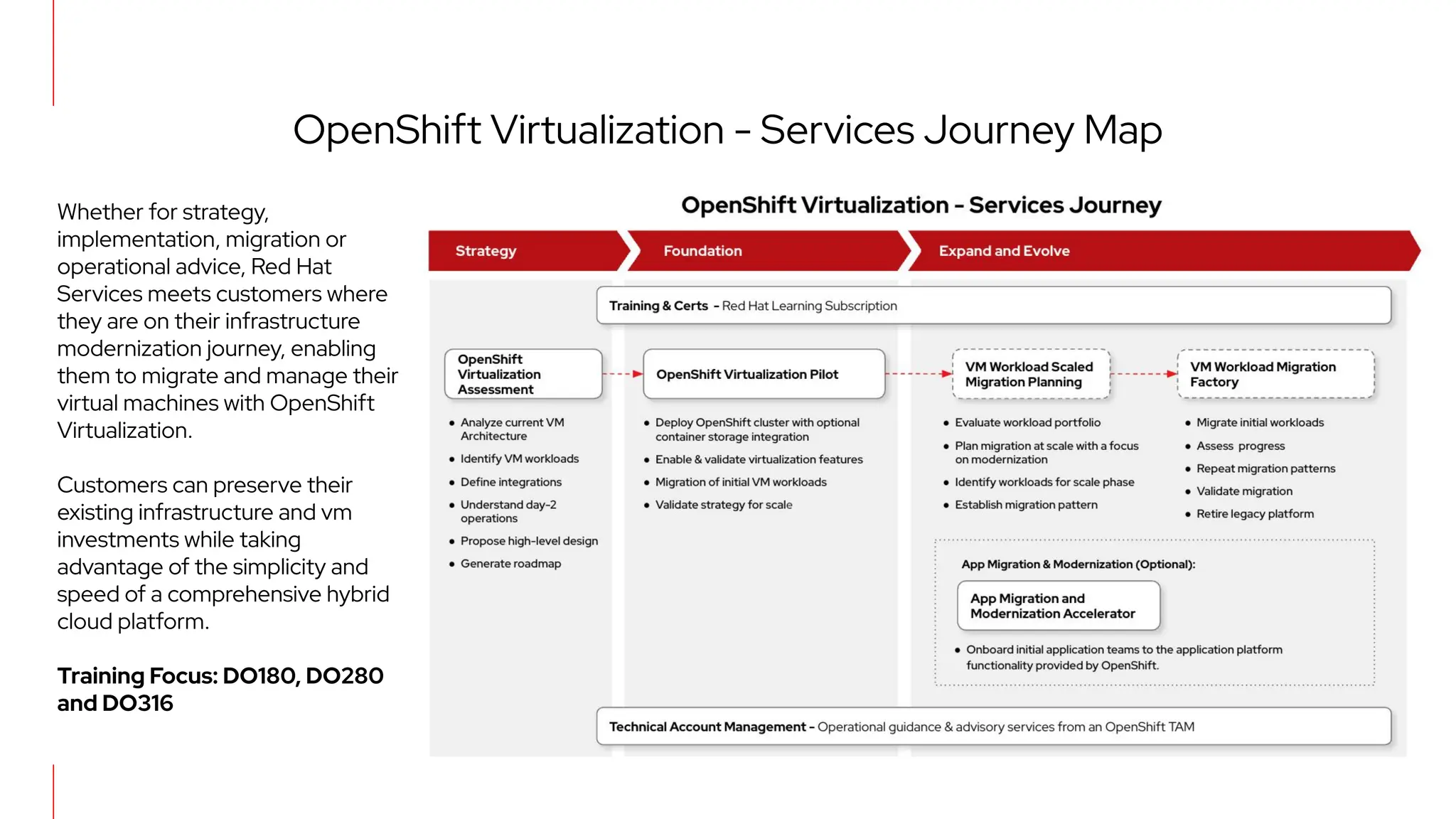
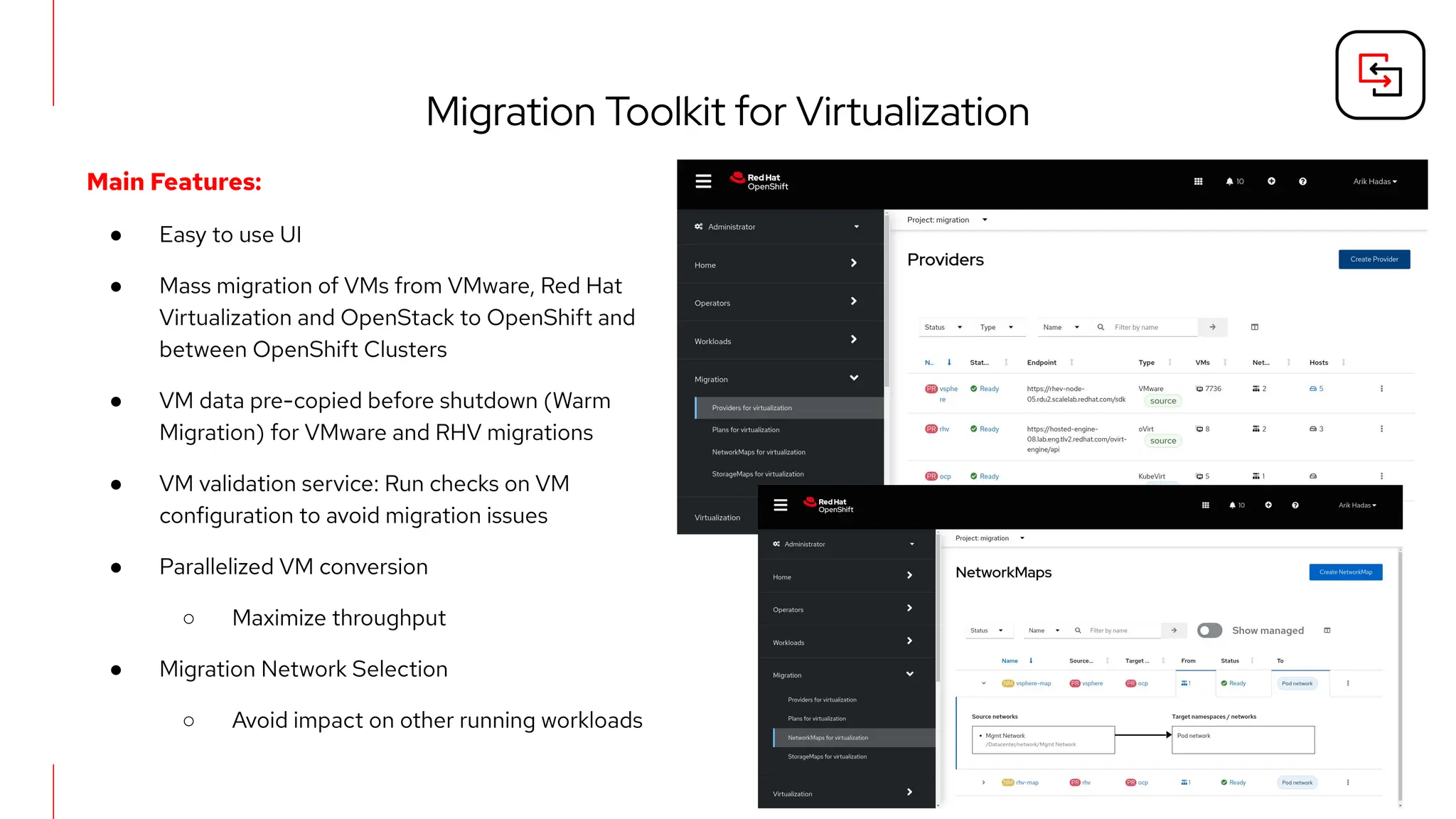
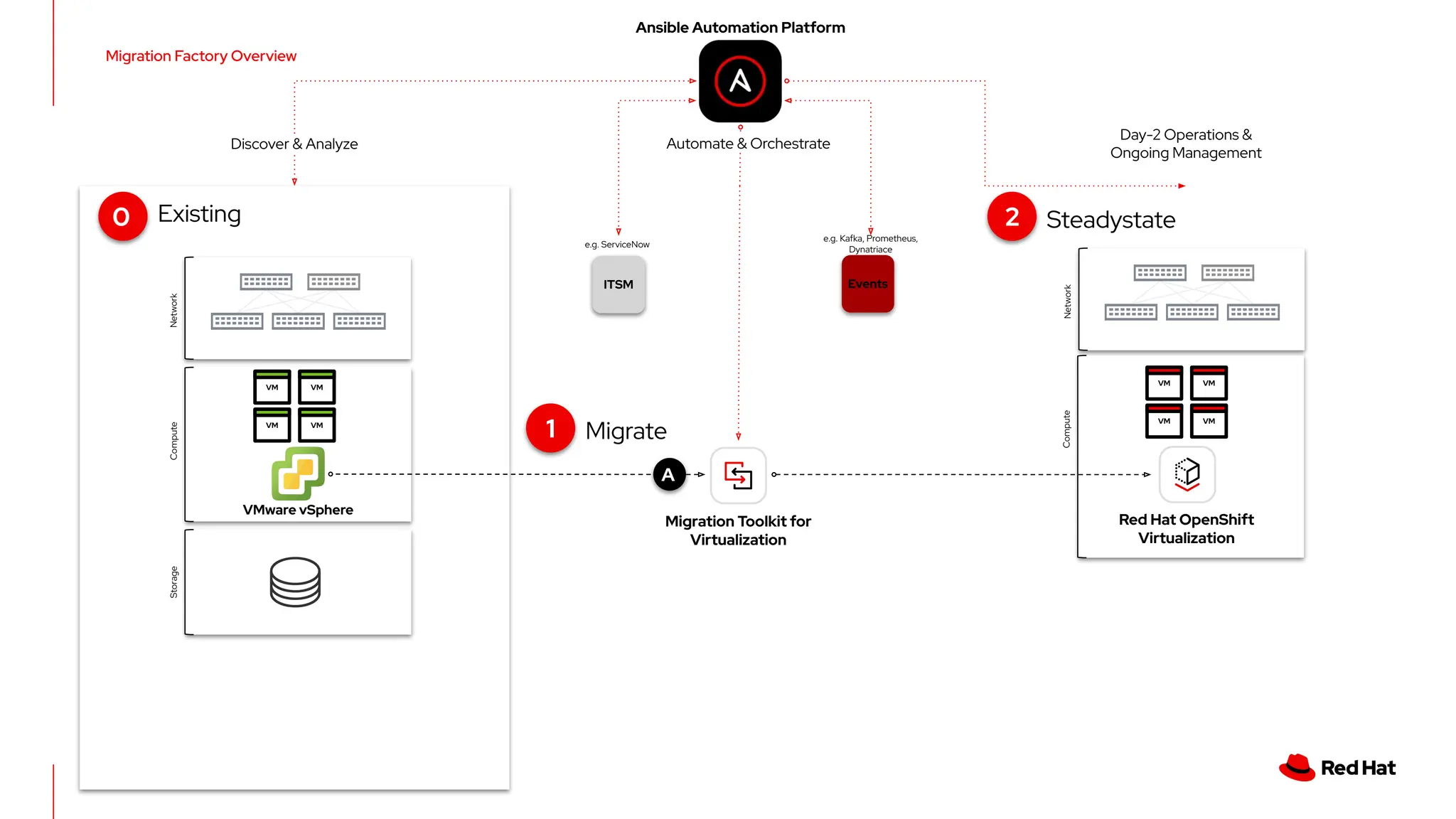
The document outlines Red Hat's OpenShift Virtualization, emphasizing its integration with Kubernetes and the capabilities for managing virtual machines and containers. It describes a migration methodology designed to assist organizations in transitioning to OpenShift Virtualization, focusing on features like easy UI, mass migration tools, and validation services. Additionally, it details the process of modernization and collaboration offerings from Red Hat to ensure seamless migration and management of virtual environments.