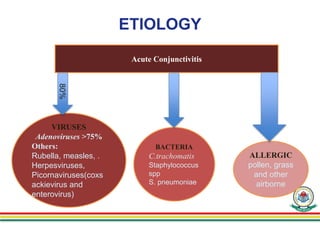
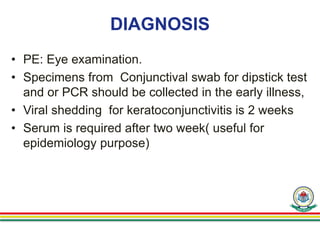
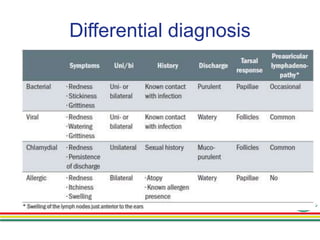
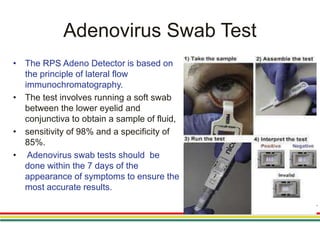
1. Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis (EKC), also known as adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis, is a highly contagious eye infection caused by adenoviruses, most commonly serotypes 8, 19, and 37.
2. It spreads through hand-to-eye contact or respiratory droplets and tends to occur in clusters in places like schools and workplaces.
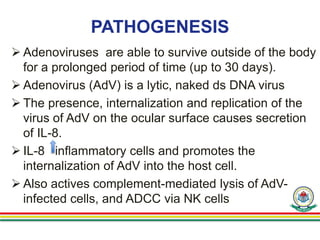
3. The virus can survive outside the body for up to 30 days and enters host cells, causing inflammation and viral shedding for 10-14 days after symptoms appear. Diagnosis involves eye exams and viral testing of conjunctival swabs. While there is no vaccine or approved treatment, prevention focuses