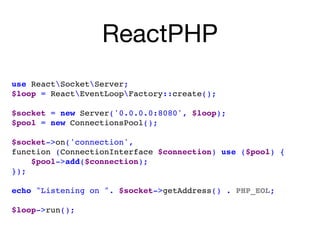
This document discusses ReactPHP, an event-driven non-blocking I/O framework for PHP. It begins by explaining how ReactPHP applications are event-driven and non-blocking. It then covers key ReactPHP concepts like streams, closures, and loops. Examples are provided of building an HTTP server and chat application with ReactPHP. Resources for learning more about ReactPHP and related libraries are listed at the end.