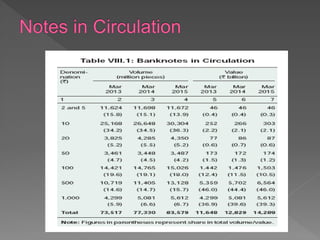
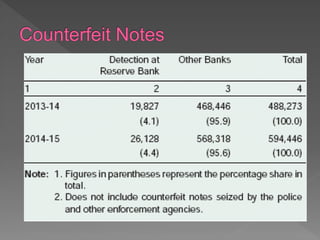
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as the central bank and currency authority of India. It issues currency notes in various denominations and regulates the country's money supply through its monetary policy tools. RBI maintains a network of currency chests across India to facilitate distribution and storage of currency. It also takes various measures to manage currency logistics, assess demand, and ensure quality and security of currency in circulation.