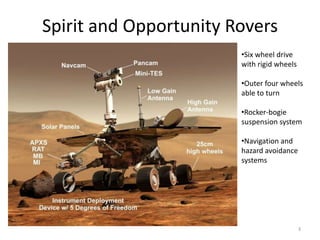
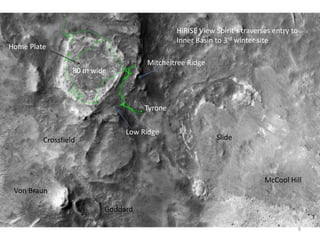
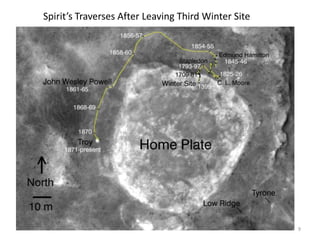
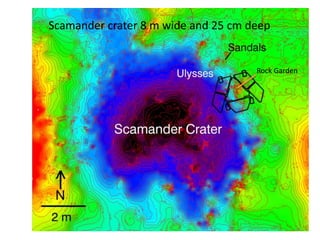
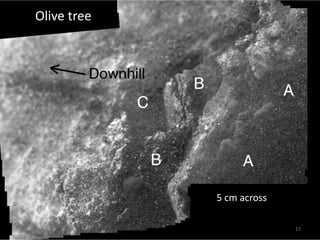
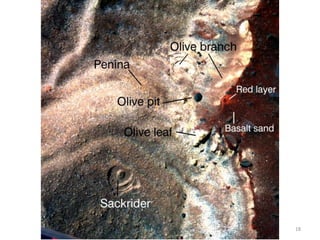
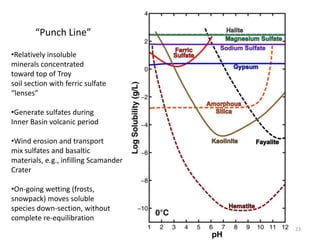
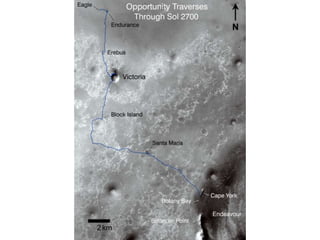
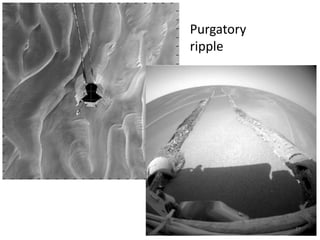
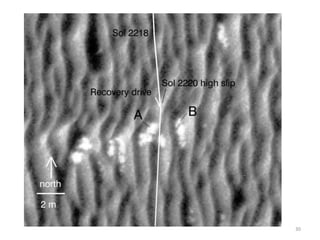
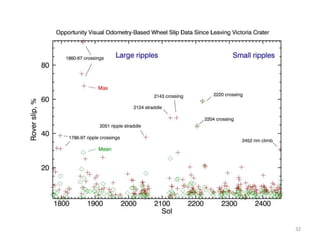
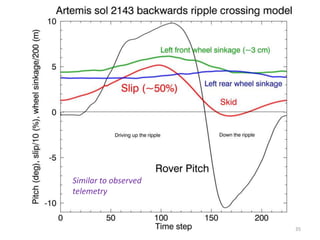
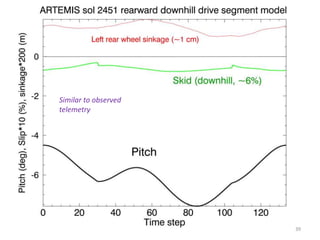
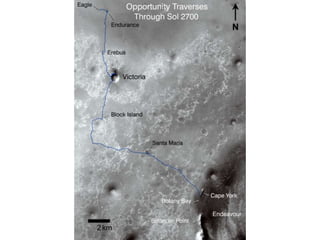
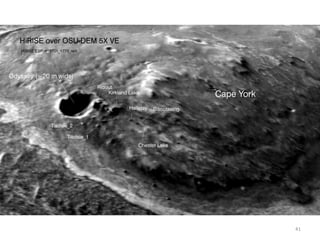
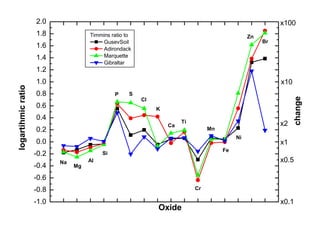
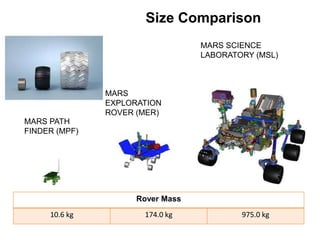
The document discusses the Mars Exploration Rover missions, specifically the Spirit and Opportunity rovers, detailing their design, operational challenges, and geological findings during their missions. Key aspects include the rovers' navigation systems, machine-terrain interactions, and the effects of soil composition on their performance. The presentation features graphs, images, and data related to the rovers' traverses and soil analysis on Mars.