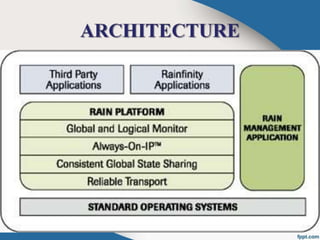
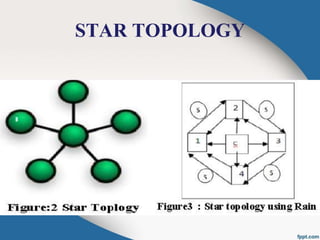
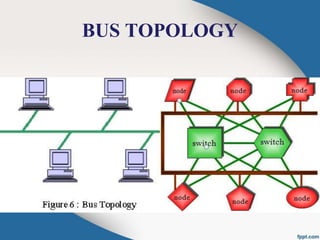
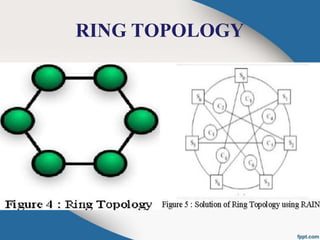
The document introduces RAIN (Reliable Array of Independent Nodes) technology, which provides fault-tolerant distributed computing and data storage. RAIN originated from research at Caltech and was commercialized by the startup Rainfinity. RAIN uses redundant network connections and automatic application restart to tolerate processor failures. It stores data across distributed processors to retrieve it even if some fail. Key features include communication protocols, group membership tracking to handle faults, and error-correcting data storage codes. RAIN technology allows for high availability applications and scalable solutions with advantages like unlimited cluster size and multiple node failure tolerance.


















![REFERENCES
[1]. www.wikipedia.com
[2]. www.searchdatacenter.techtarget.com
[3]. www.campusfever.com
[4]. www.seminartime.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raintechnology-ppt-180722075347/85/Rain-technology-ppt-23-320.jpg)
