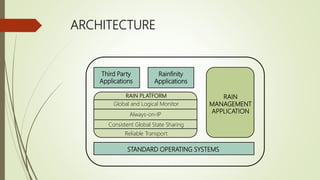
This document summarizes a seminar on RAIN technology. RAIN (Reliable Array of Independent Nodes) originated at Caltech to create a redundant network of processors that could automatically recover from failures. It aims to minimize connections between clients and servers and make nodes robust and independent. The architecture includes reliable transport, consistent global state sharing, and local/global fault monitors. Key features are scalability, high availability, fault tolerance for nodes, networks and data storage. Applications include high availability video and web servers. Future work involves further developing APIs and a distributed file system.








![High Availability
The availability of a system or any component in that system is defined
by the percentage of time that it works normally. The formula for
determining the availability for a system is: Availability average time to
failure (ATTF) / [average time to failure (ATTF) + average time to recover
(ATTR)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/raintechnologyseminarreport-211011174839/85/Rain-technology-seminar-10-320.jpg)








