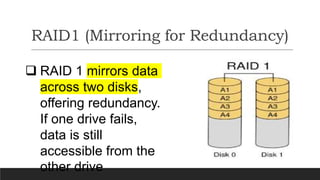
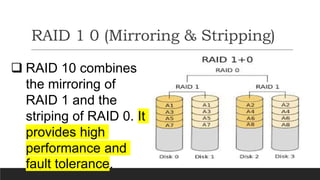
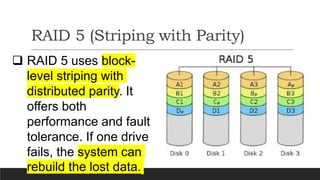
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that combines multiple disk drives into a single logical unit to improve data reliability, increase input/output performance, or achieve both. There are different RAID levels serving different purposes - RAID 0 stripes data across disks for performance; RAID 1 mirrors data across disks for redundancy; RAID 5 uses block-level striping with distributed parity for both performance and fault tolerance. The document then provides commands to implement a RAID 5 array using 3 disks on a RHEL system and test failure recovery functionality.