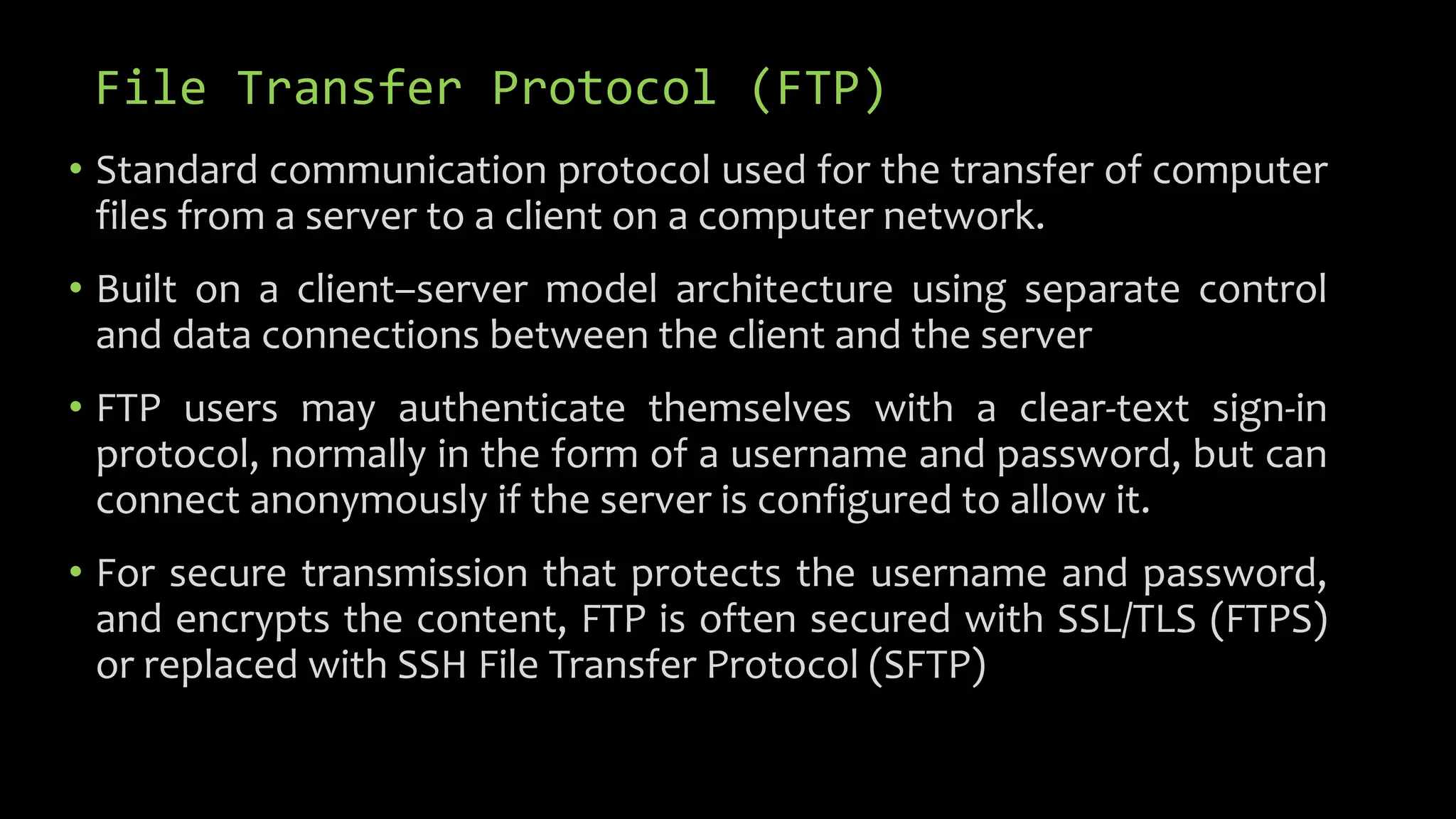
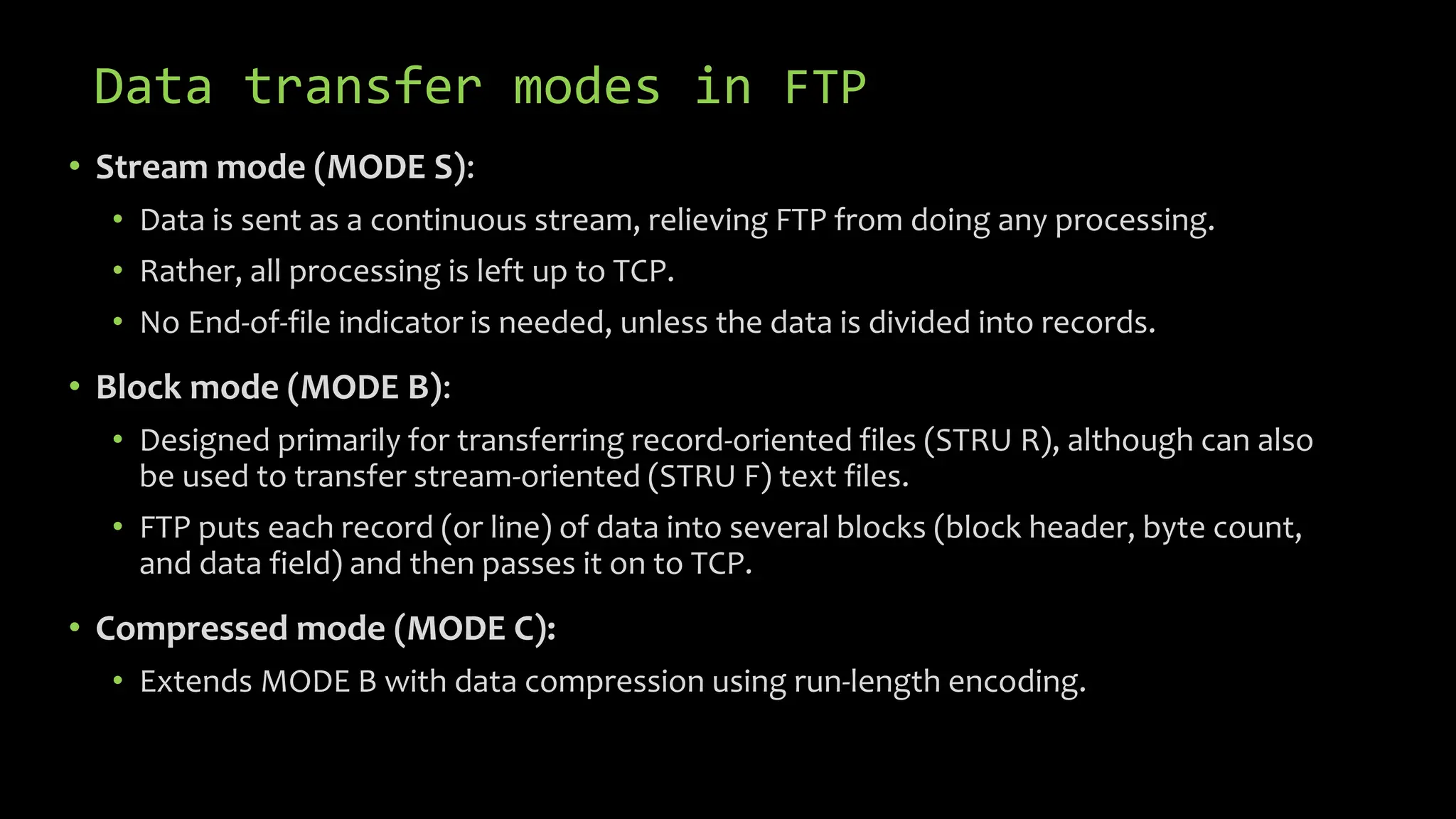
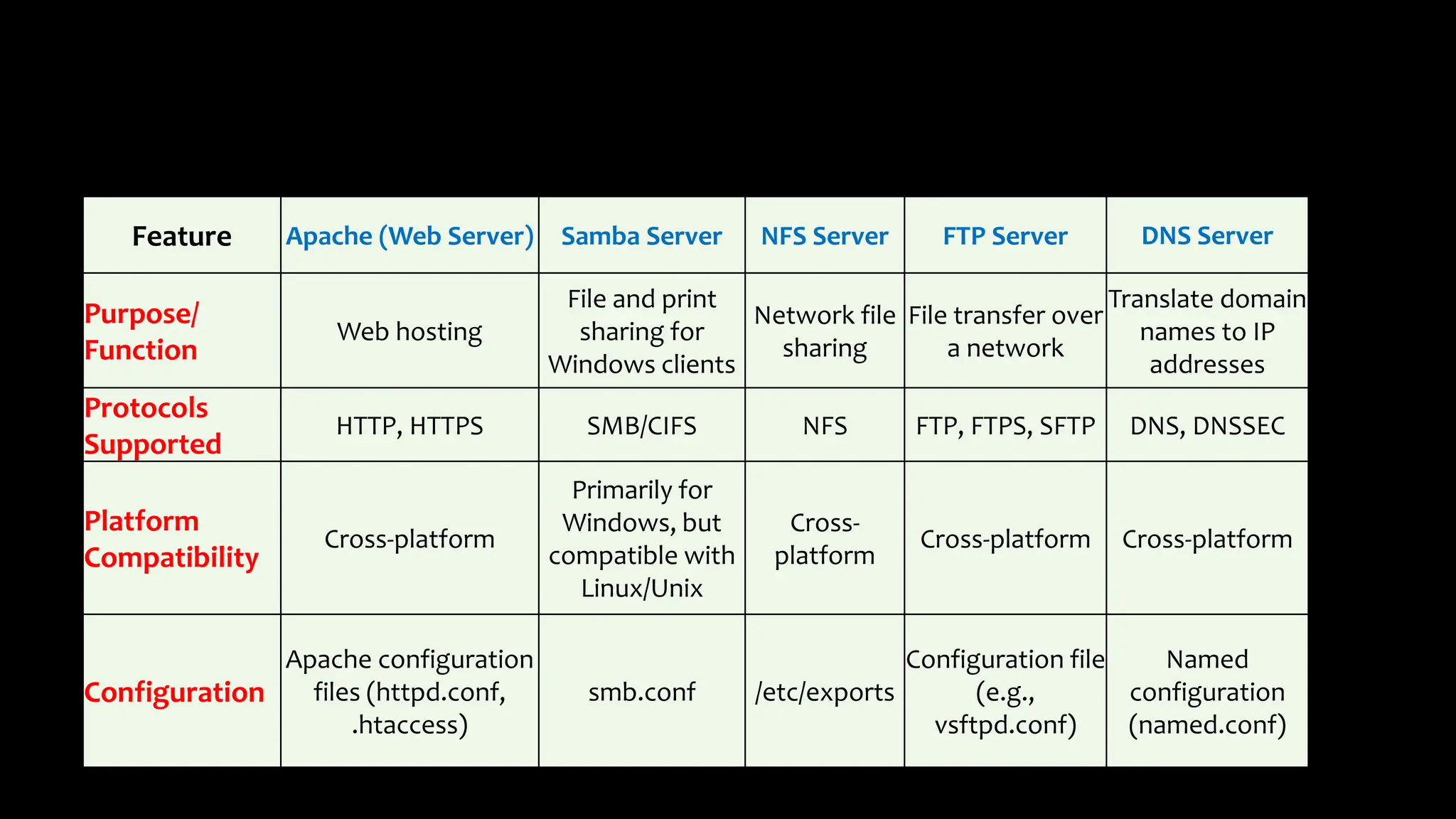
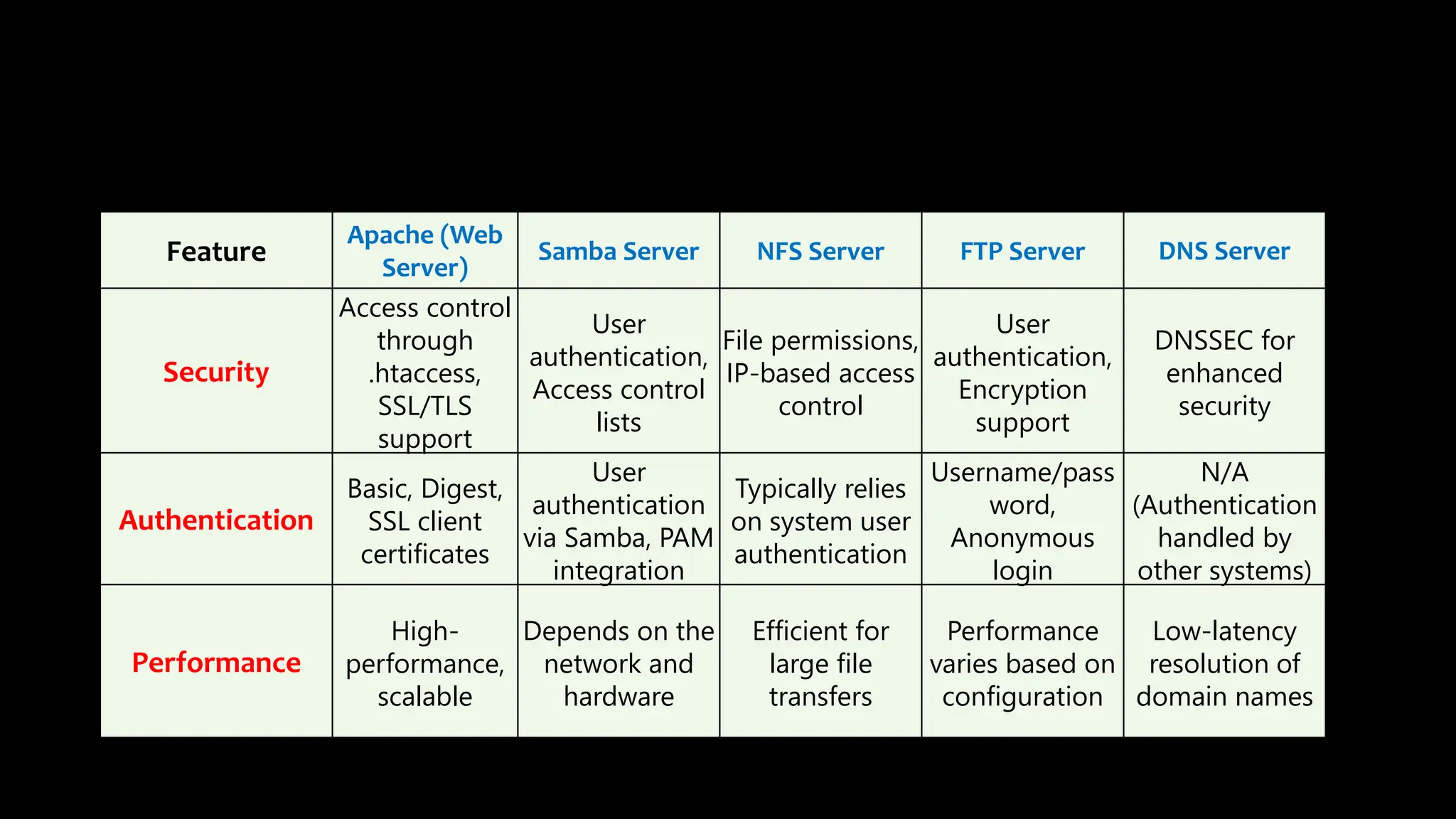
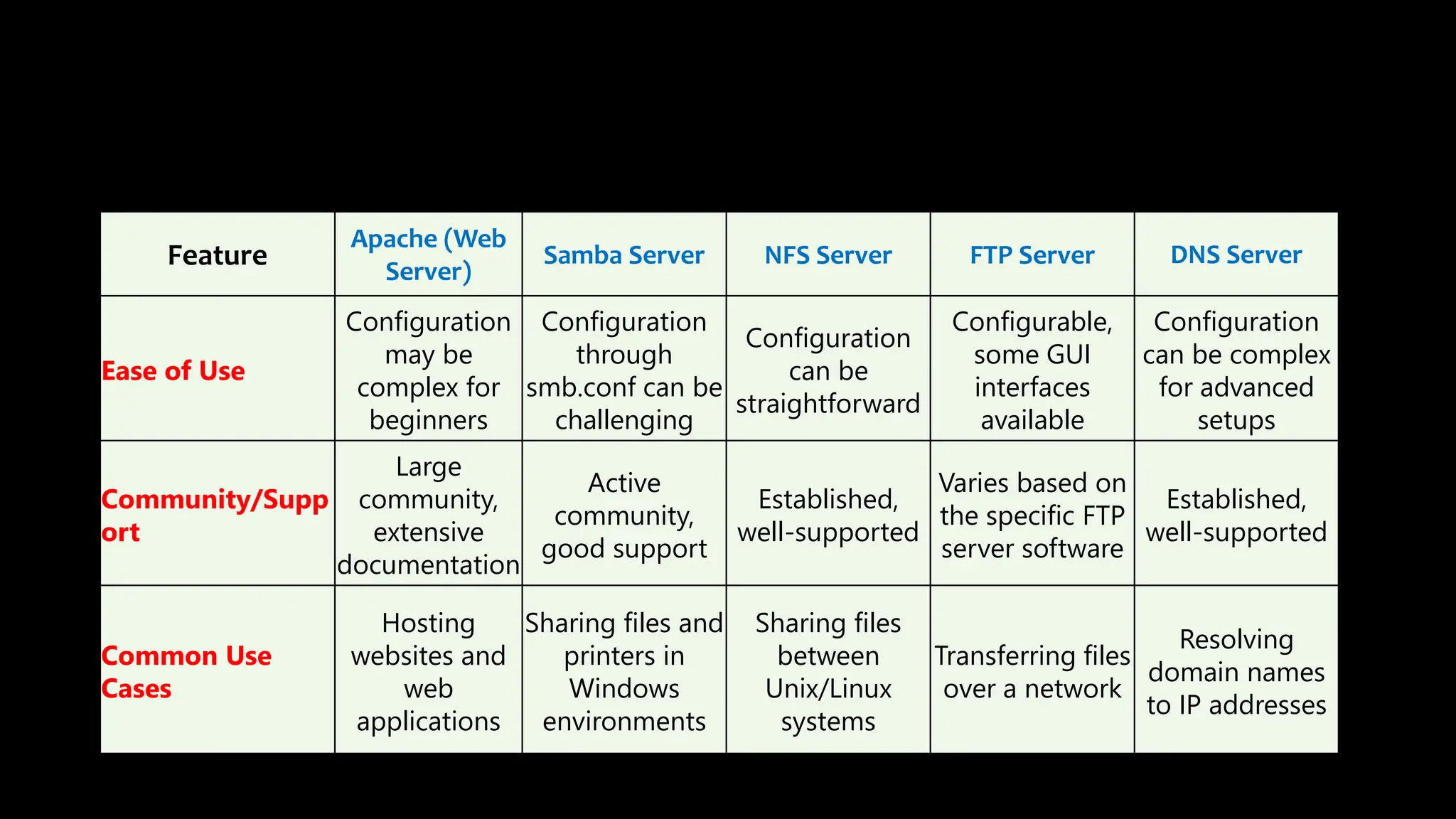
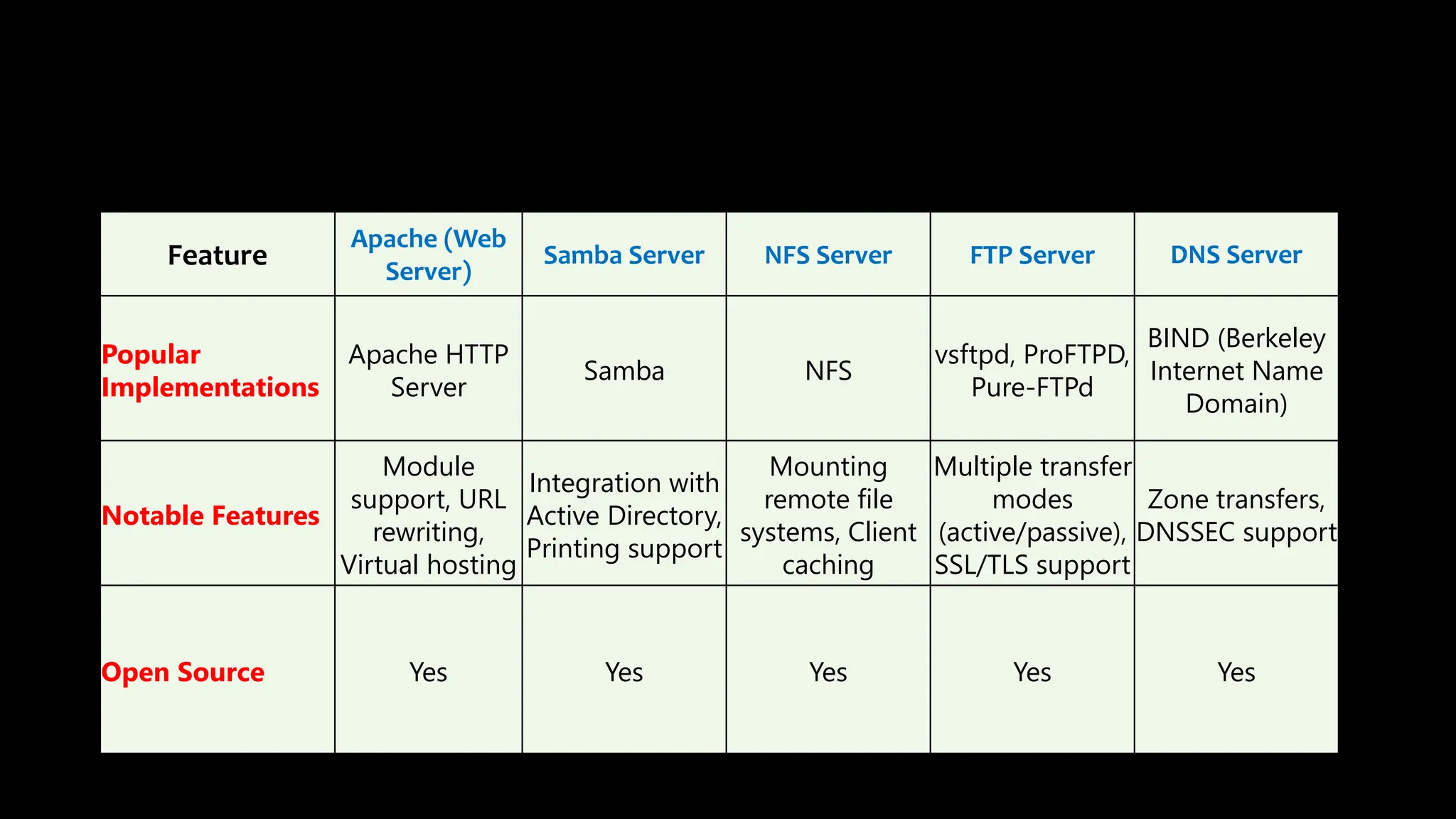
This document provides an overview of common Linux server software including Samba, FTP, NFS, Apache, and Docker. It describes the purpose and key features of each type of server such as Samba for file sharing with Windows clients, FTP for file transfers, NFS for network file sharing, Apache as a popular web server, and Docker for containerization. Security considerations and configurations are also summarized for each server software.