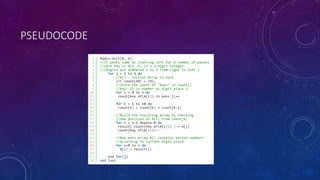
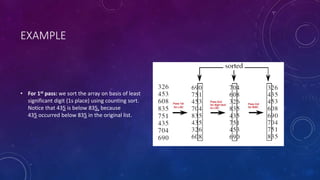
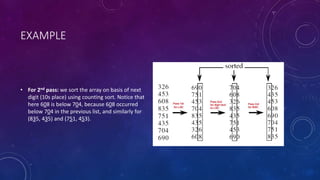
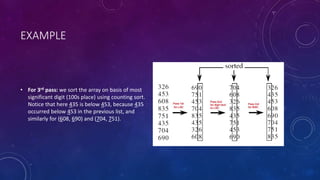
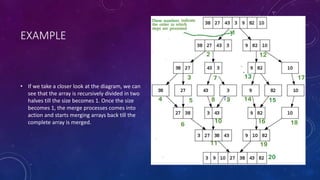
Radix sort and merge sort are sorting algorithms. Radix sort sorts data with integer keys by grouping keys by the individual digits. It has linear time complexity and is very fast, but only works for integers. Merge sort divides an array in half recursively until the subarrays contain one element, then merges the subarrays back together in sorted order. It has time complexity of O(n log n) in all cases and is easy to implement, but requires additional space.