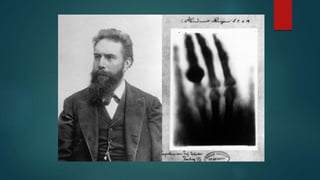
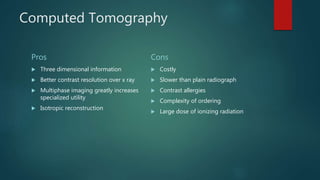
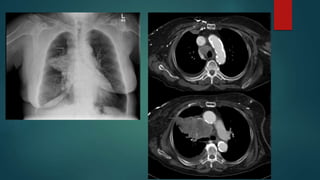
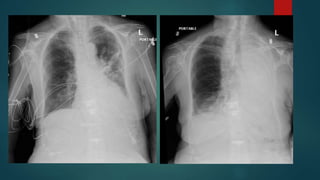
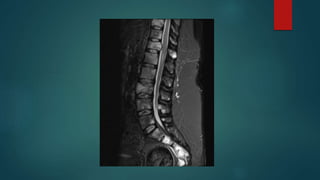
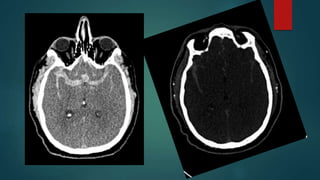
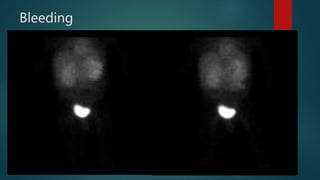
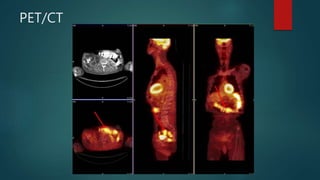
This document provides a rapid introduction to the field of radiology. It defines radiology as the use of various types of radiation to diagnose and treat diseases. It outlines the main modalities in radiology including x-ray, CT, ultrasound, MRI, and nuclear medicine. For each modality, it discusses the pros and cons in terms of features like speed, cost, radiation dose, and clinical utility. The document aims to give readers a broad overview of the speciality of radiology and the physical concepts and modalities used.