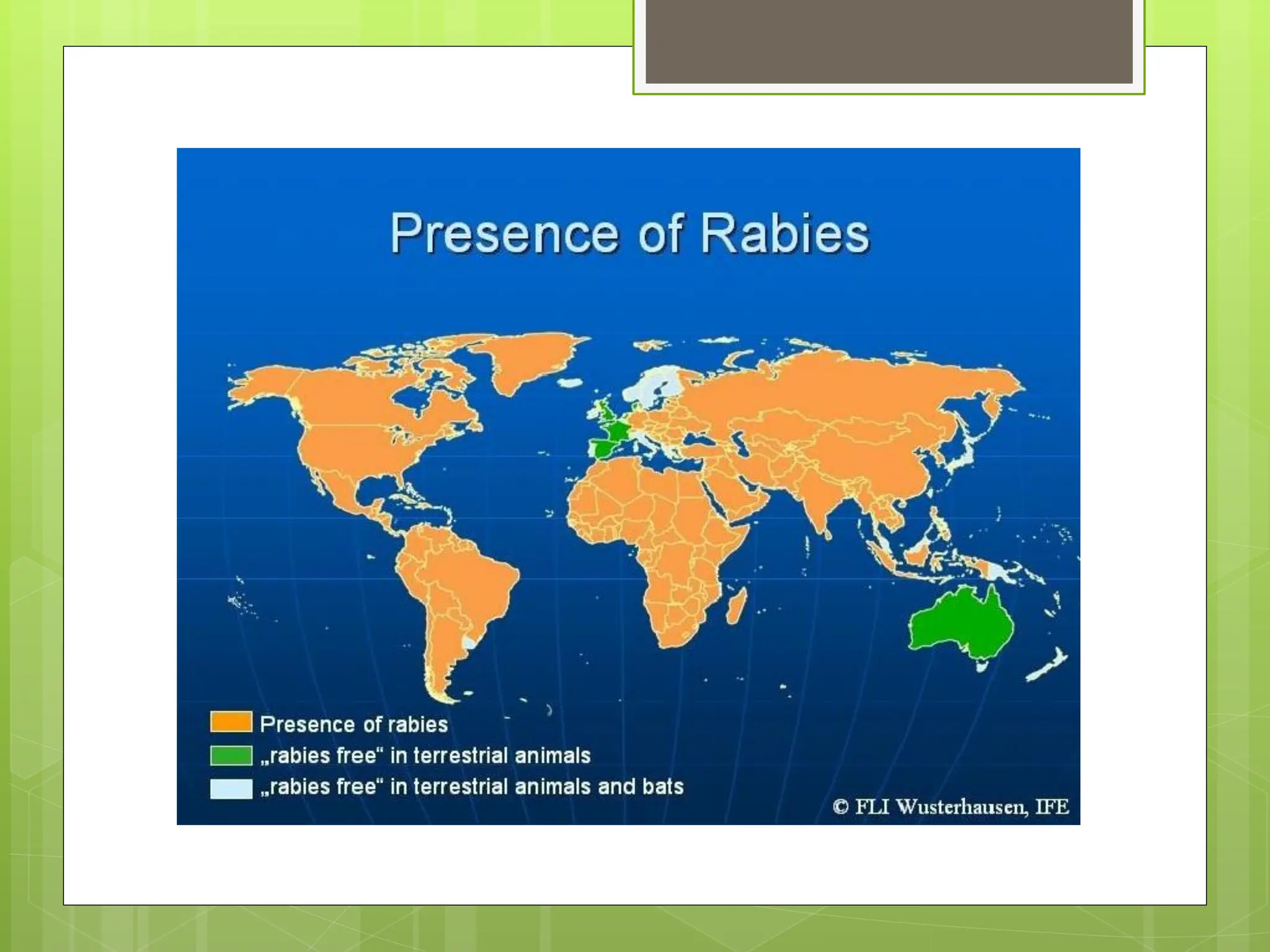
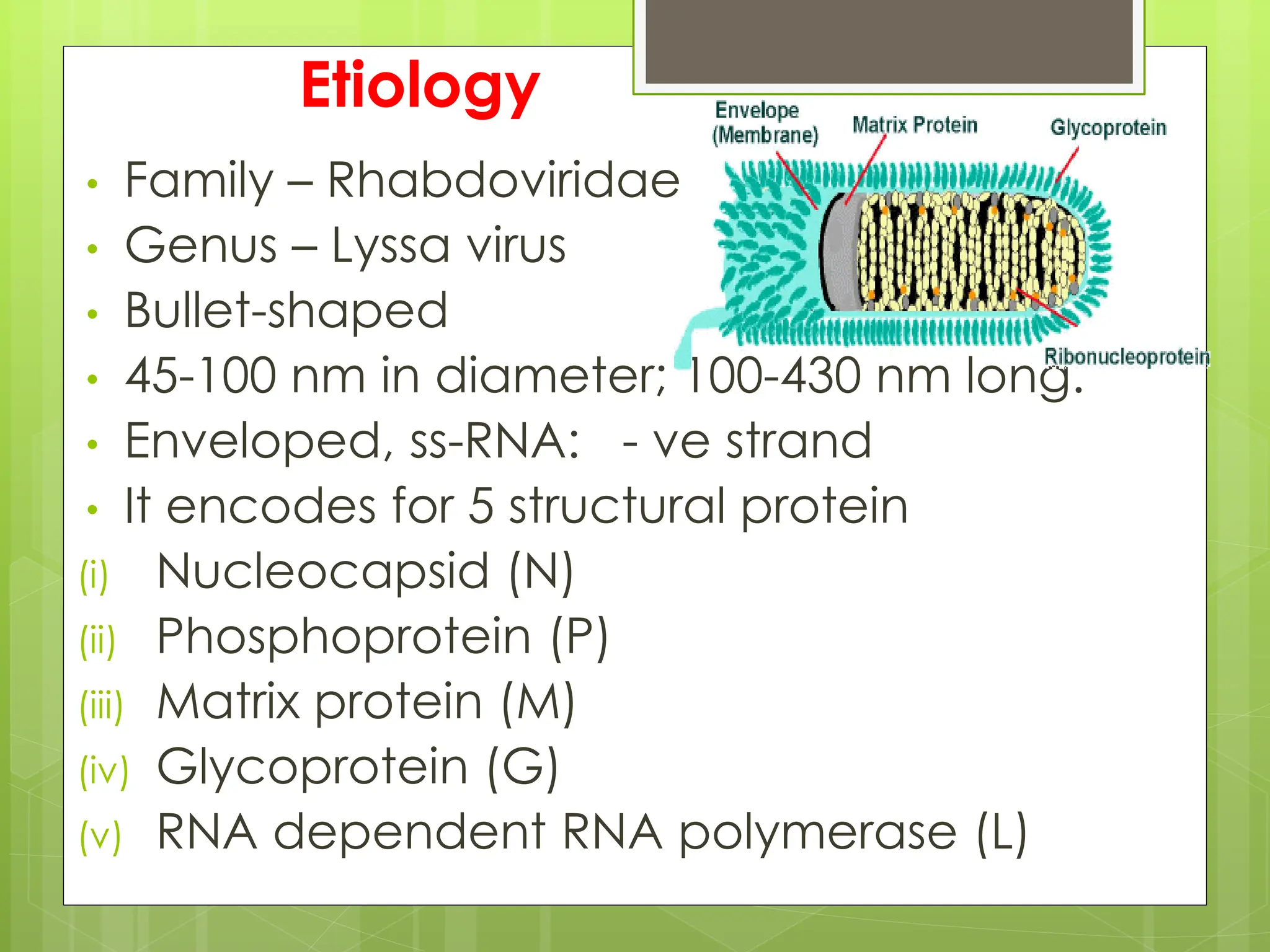
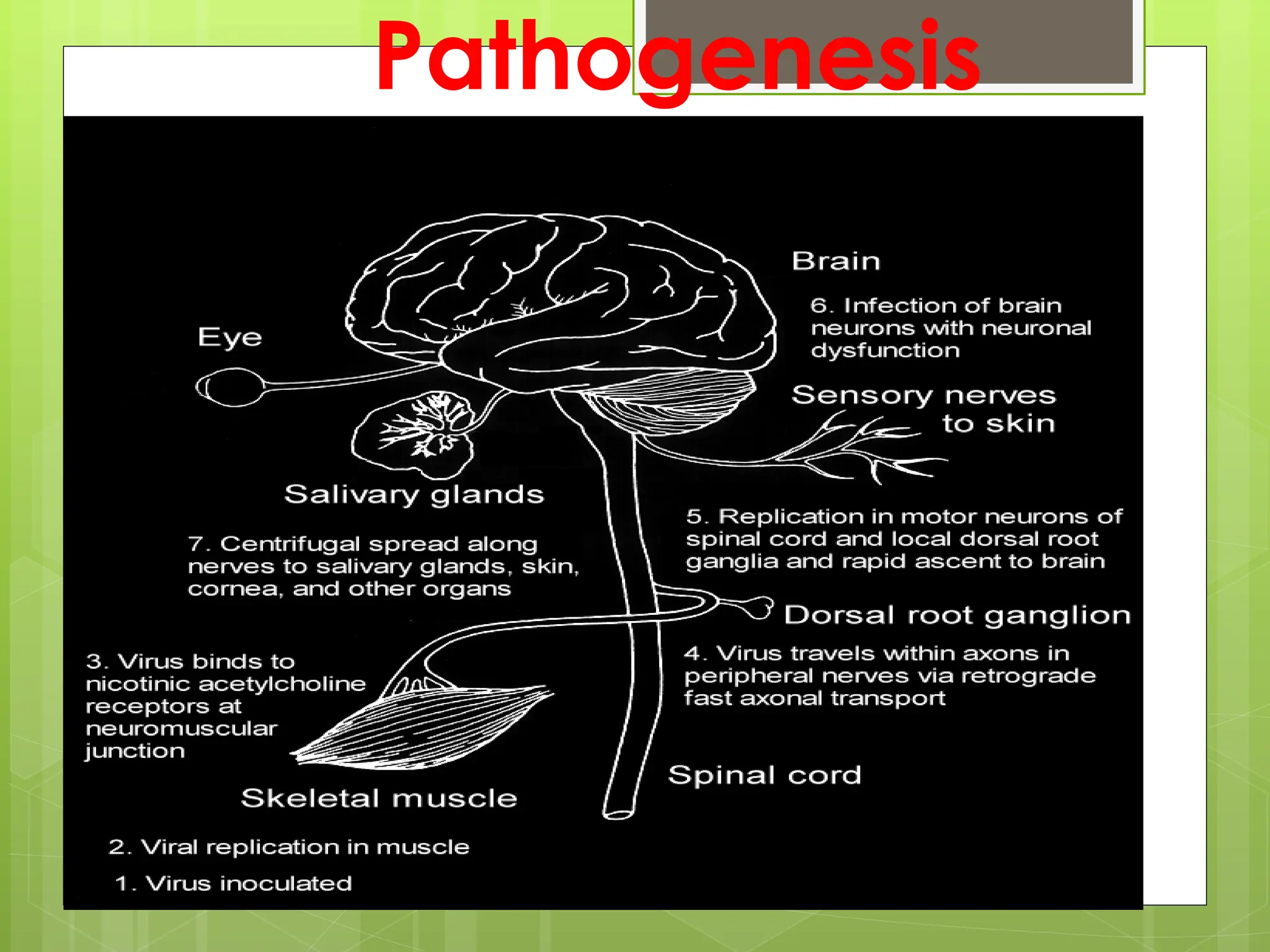
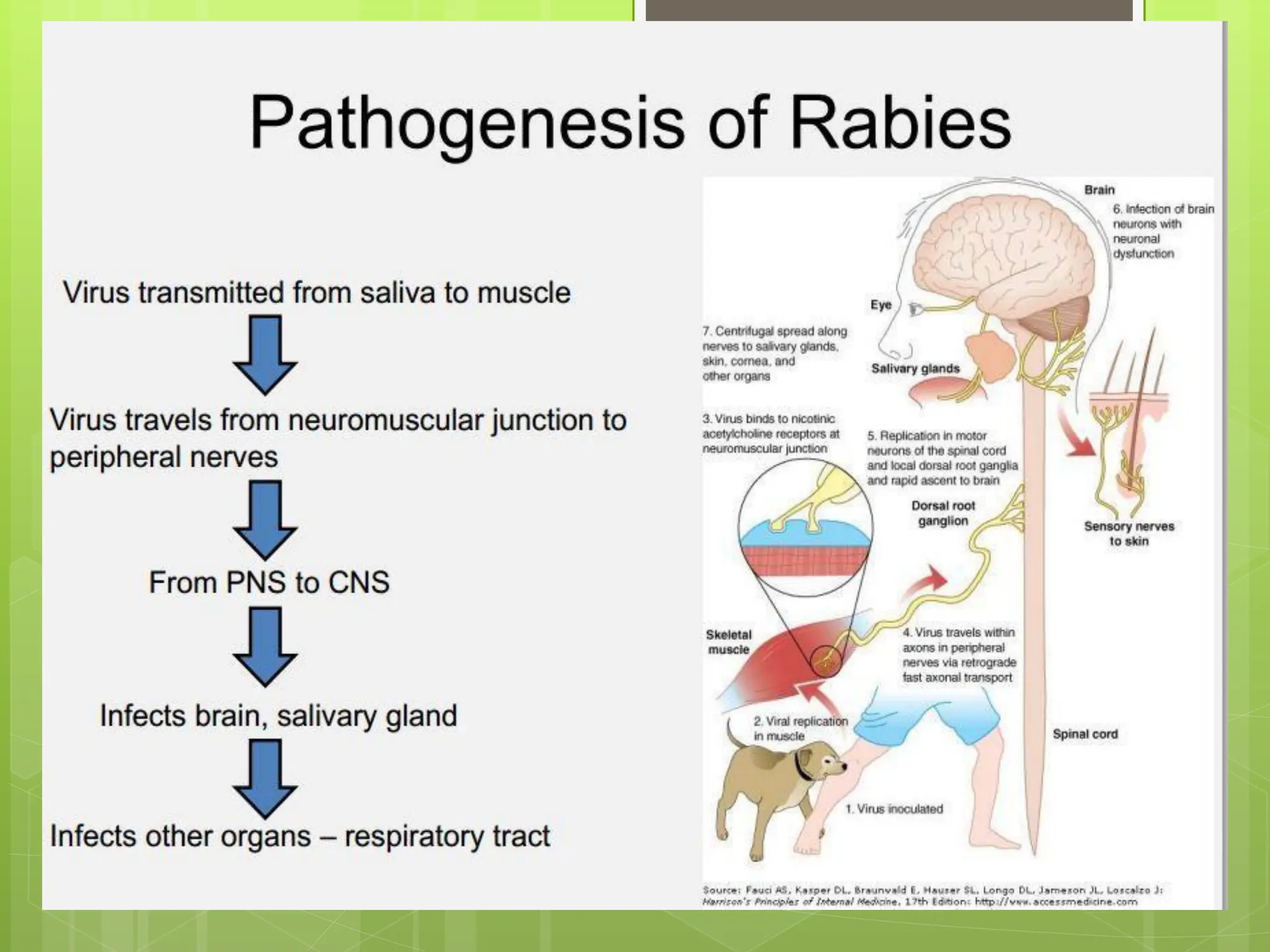
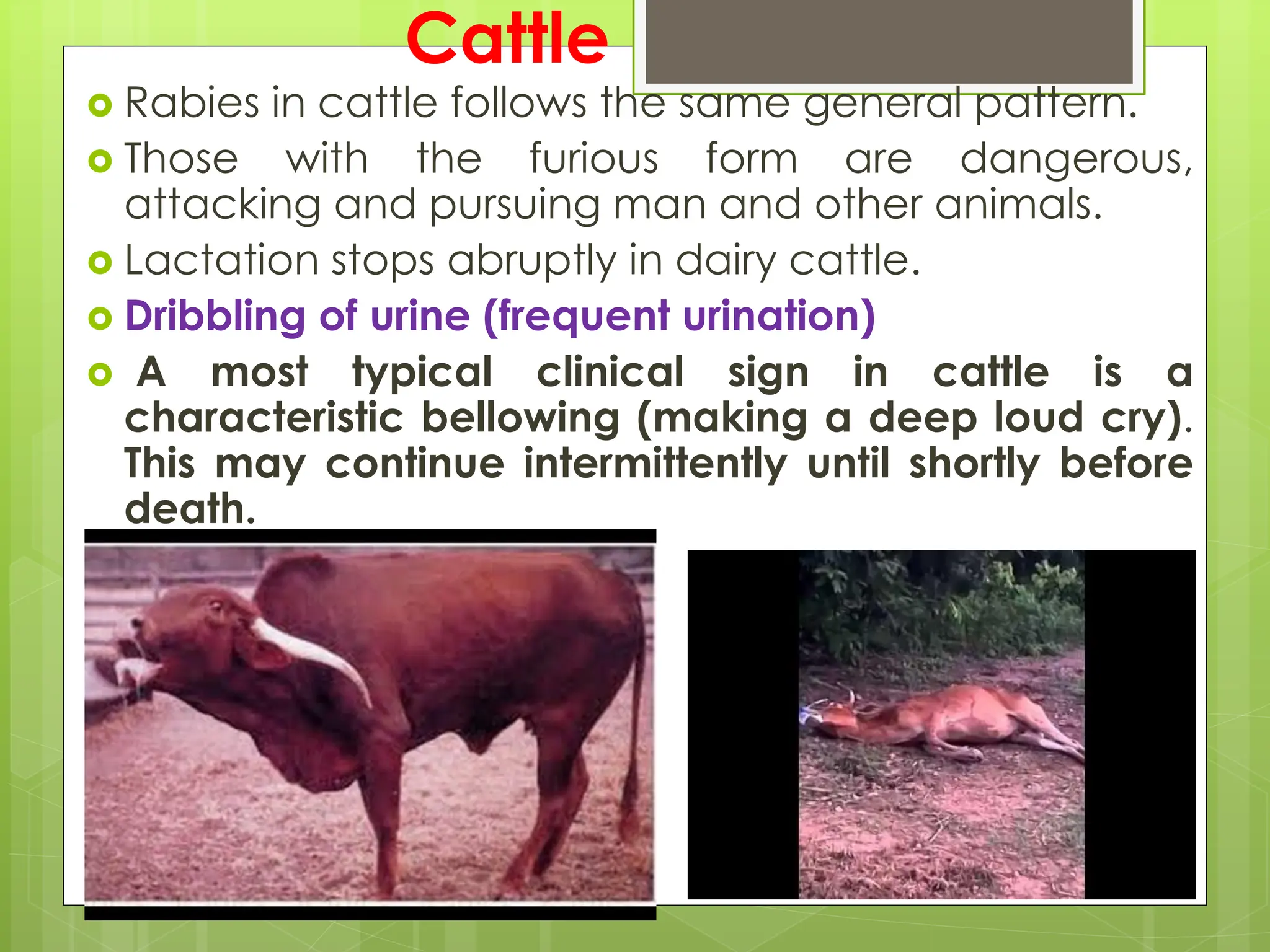
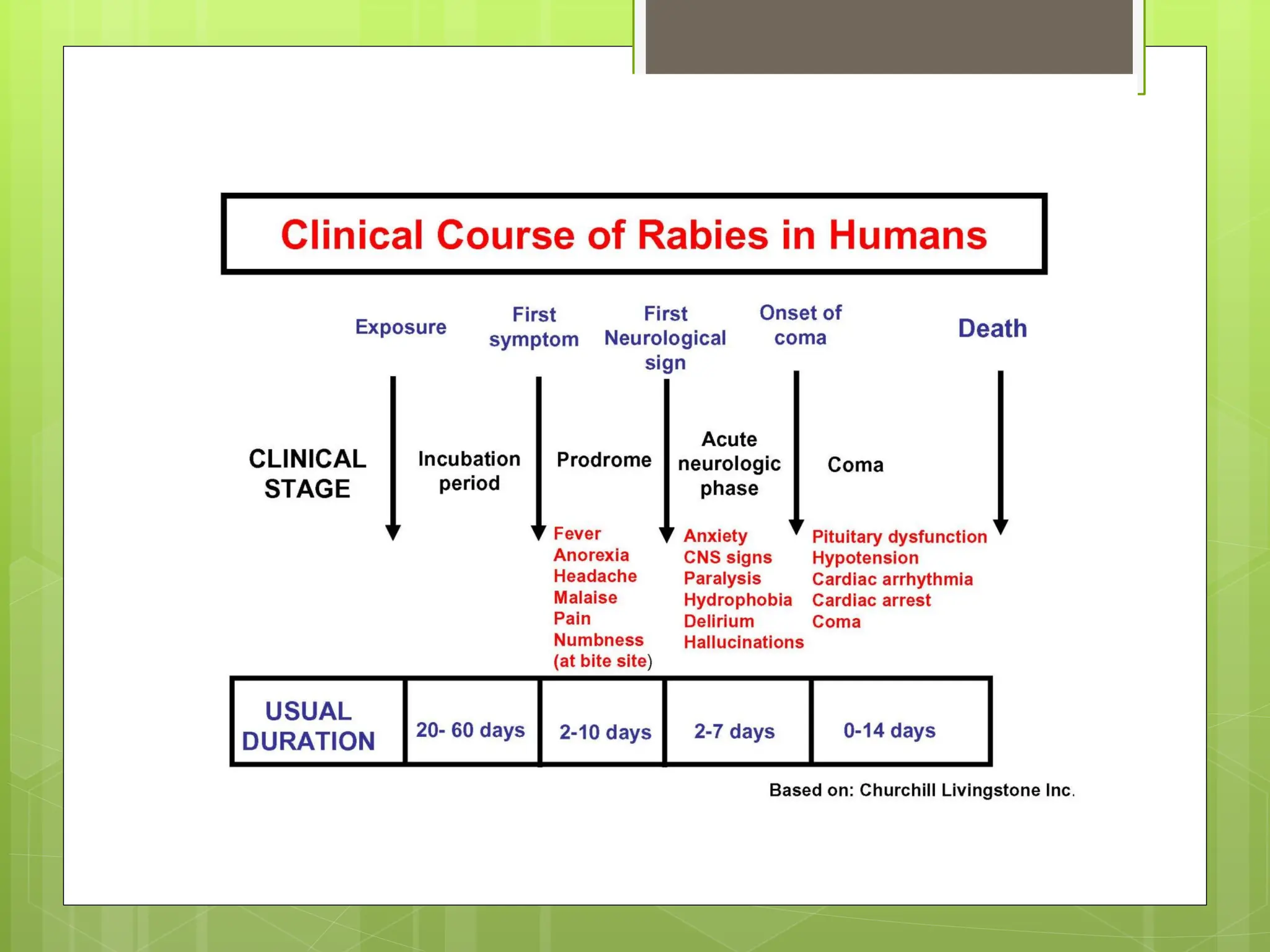
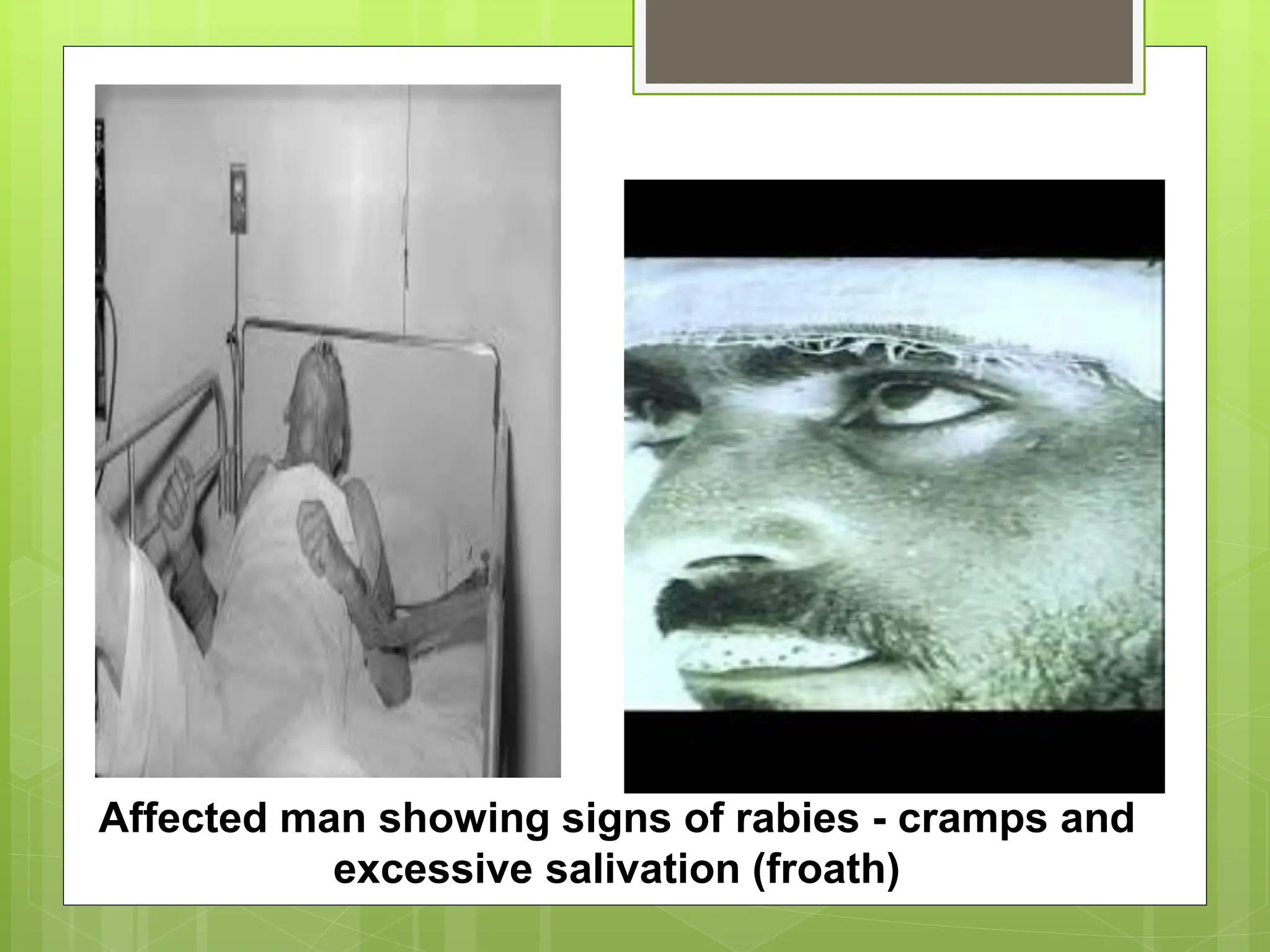
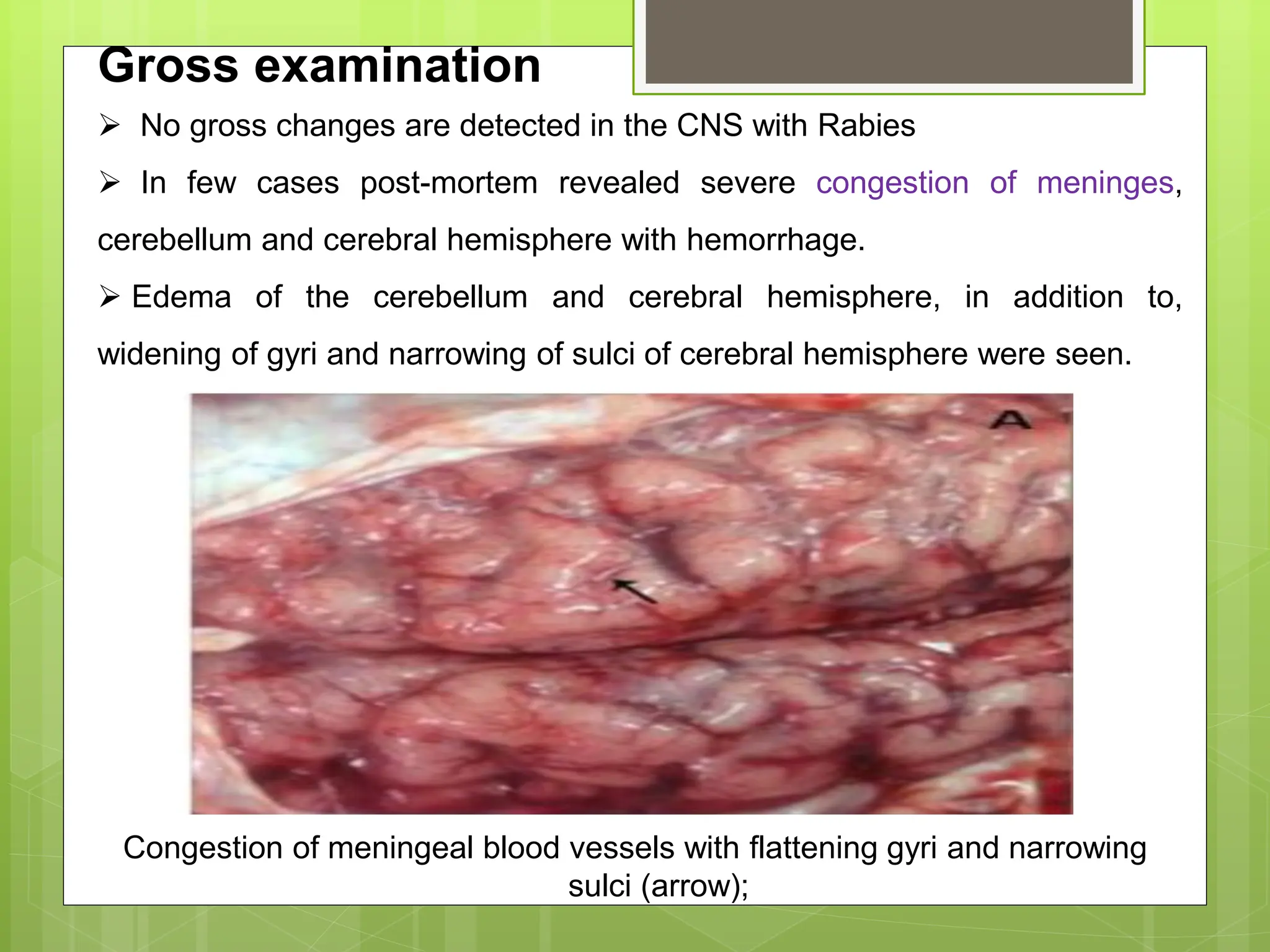
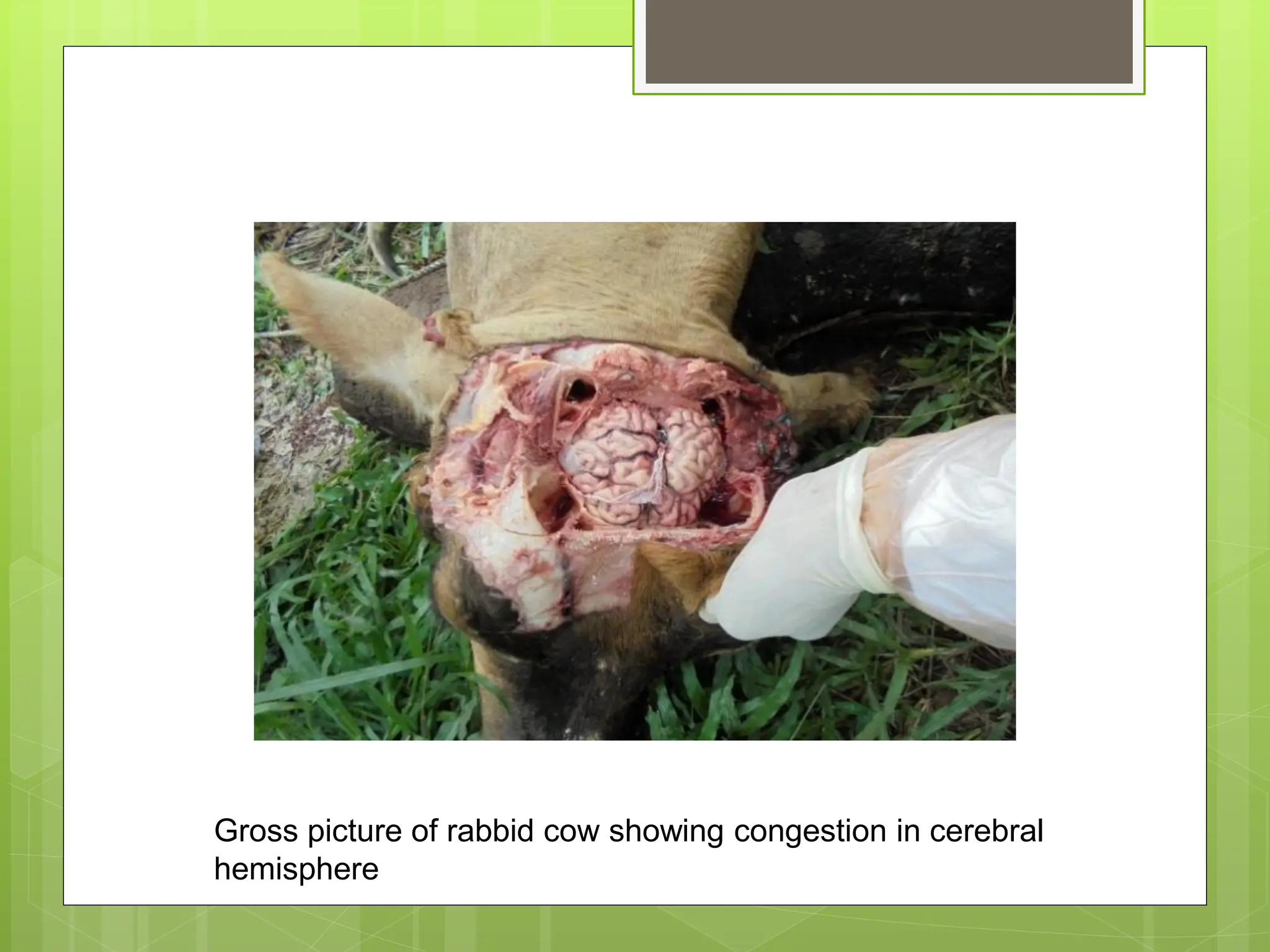
Rabies is a fatal viral disease that affects the nervous system of humans and other mammals. It is caused by the rabies virus, which is bullet-shaped and can be transmitted via bites or scratches from infected animals. Dogs are the primary carrier of the virus and transmission from dogs accounts for over 95% of all human rabies cases. There is no cure once symptoms develop, making vaccination an important preventative measure.