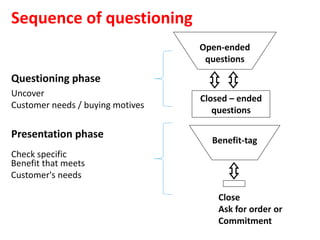
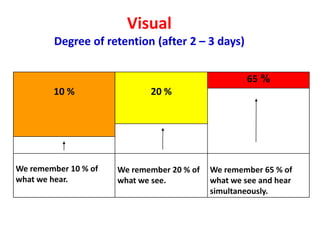
The document discusses different types of questions that can be used in sales questioning, including open-ended questions, closed-ended questions, choice questions, and benefit-tag questions. It provides examples for each type and explains when each should be used. The document also discusses positive and negative customer responses, typical closes used in sales, and the importance of post-call reviews. Overall, the document provides guidance on effective questioning techniques and handling customer responses during the different phases of a sales call.