The document discusses various methods for pharmaceutical sales, including:
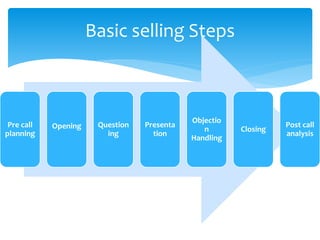
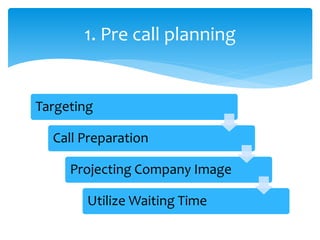
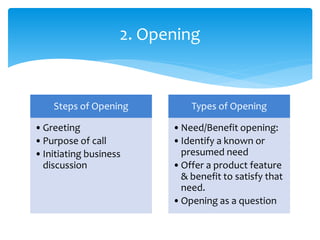
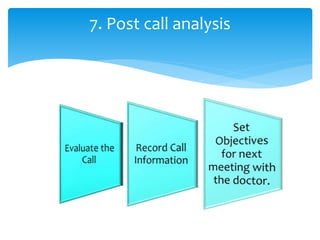
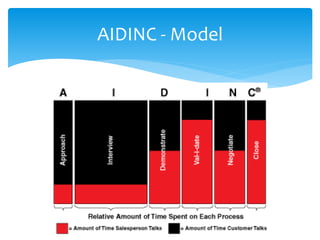
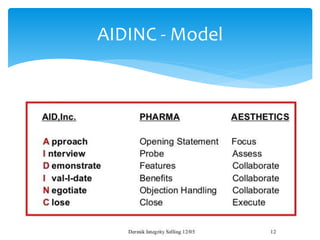
1. It outlines the basic steps of selling such as pre-call planning, opening, questioning, presentation, objection handling, closing, and post-call analysis.
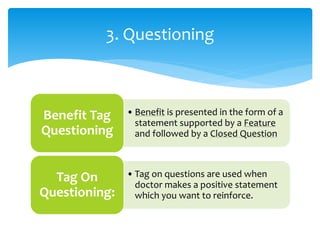
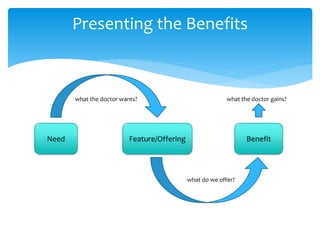
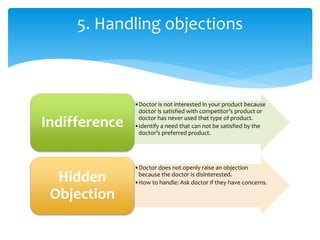
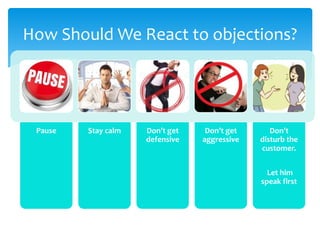
2. It describes techniques for each step, like using open-ended questions to probe for information during questioning, addressing different types of objections, and emphasizing benefits before presenting price.
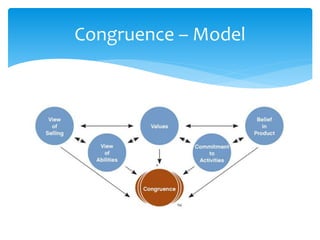
3. Integrity selling and maintaining congruence between words and actions are emphasized as important for establishing trust with doctors.