Embed presentation
Download to read offline





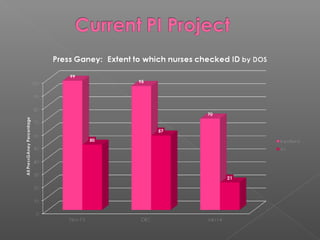

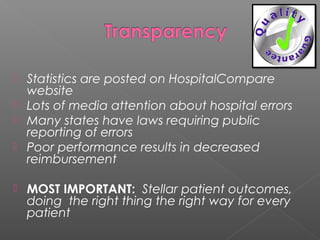


This document outlines a multidisciplinary framework for improving patient outcomes and safety. The goal is to embrace the hospital's mission while reducing risks. It describes identifying problems as process failures, exploring why processes failed, implementing improvements, and monitoring results. Examples of quality metrics that could be assessed are listed, such as antibiotic selection and falls prevention. Data on patient falls from 2010 to 2013 is provided, showing improvements were made but not sustained. Statistics are publicly reported and tied to reimbursement, so the most important thing is stellar patient outcomes.









