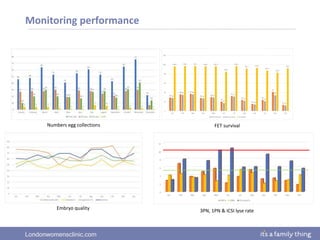
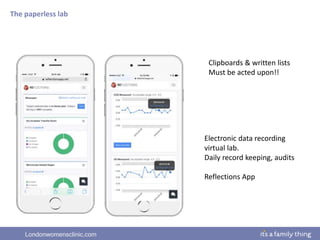
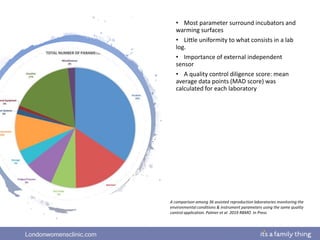
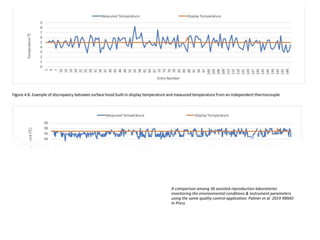
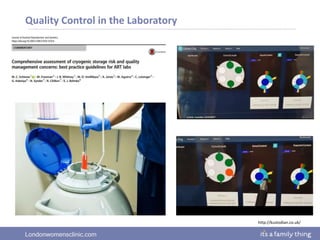
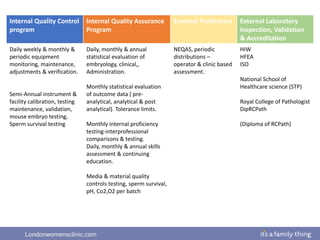
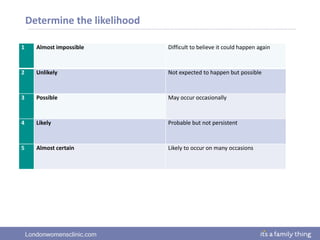
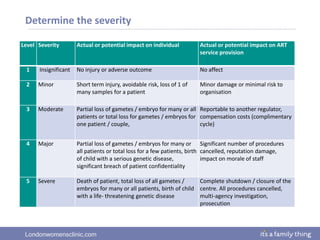
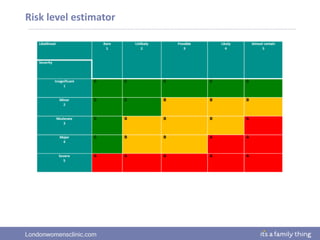
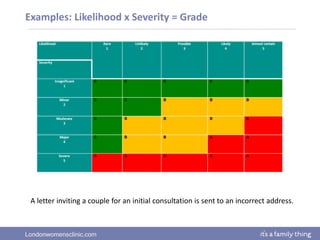
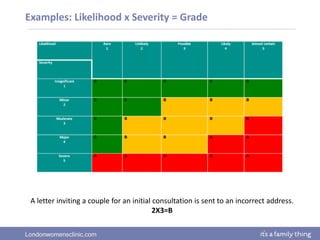
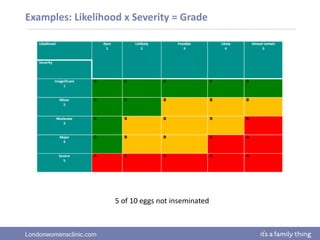
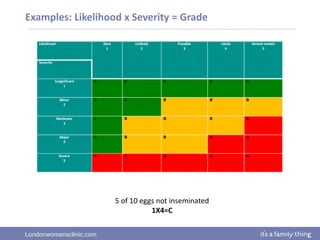
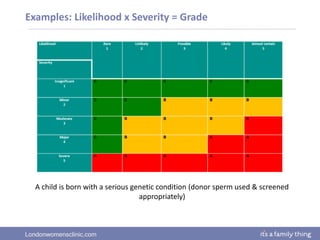
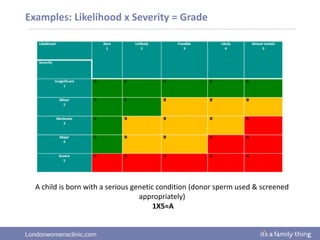
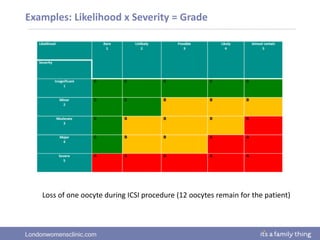
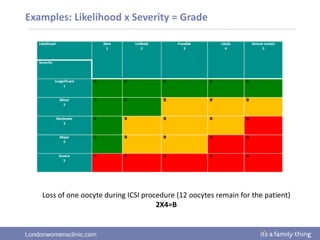
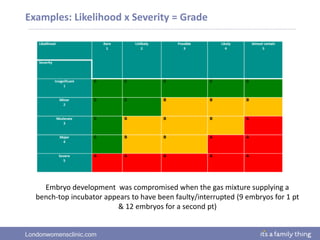
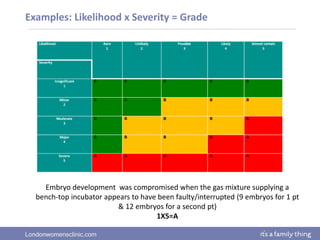
This document provides information about quality management in embryology laboratories. It discusses how quality standards have evolved from an apprentice-based system with little monitoring to today's highly regulated environment. Key aspects of quality management systems are described, including quality control, document control, audits, risk assessment, and meeting regulatory requirements from bodies like the HFEA. The role of the quality manager is to ensure the quality management system is functional and that quality standards are continuously improved.