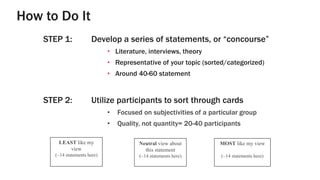
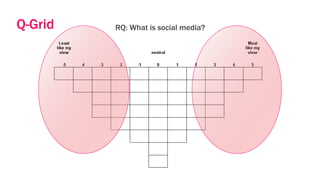
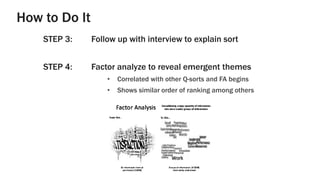
This document provides an overview of Q-methodology, which analyzes subjective viewpoints in a group. It involves having participants sort statements about a topic from least to most like their view. Factor analysis of the sorted statements reveals common perspectives. The document outlines the steps, including developing statements, having participants sort them, interviewing about their sorts, and analyzing the results. Q-methodology originated in the 1930s and has grown with over 335 peer-reviewed articles in the last 20 years. Questions are welcomed.









![References
Herrington, N., & Coogan, J. (2011). Q methodology: An overview. Research in Secondary
Teacher Education, 1(2), 24-28.
McKeown, B., & Thomas, D. B. (2013). Q methodology (Vol. 66). Sage Publications.
Stephen, T. D. (1985). Q‐methodology in communication science: An introduction.
Communication Quarterly, 33(3), 193-208.
Contact
Ignacio Cruz
USC Annnenberg
ignacioc [at] usc [dot] edu
www.ignaciocruz.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qmethodology-ignaciocruz-151018034846-lva1-app6891/85/Q-Methodology-13-320.jpg)