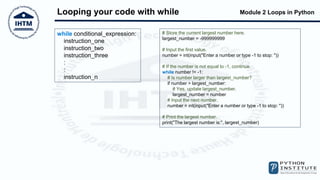
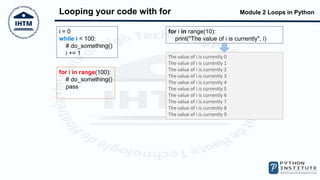
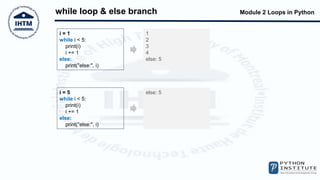
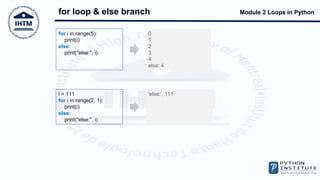
The document discusses loops in Python, including while and for loops. It provides examples of using while loops to find the largest number input by a user and count even and odd numbers. It also demonstrates using for loops with the range() function, and using break and continue statements to change loop flow. The else block that can be used with while and for loops is also covered.