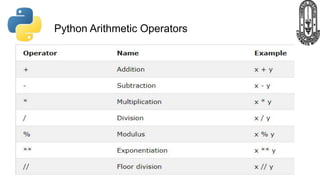
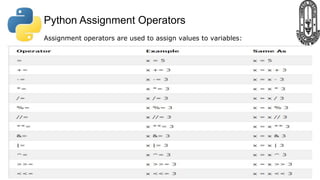
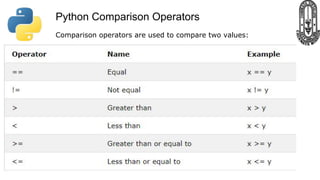
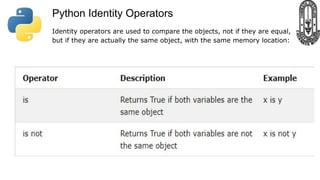
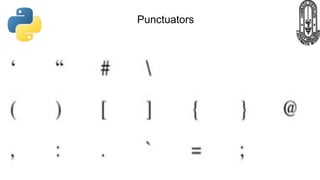
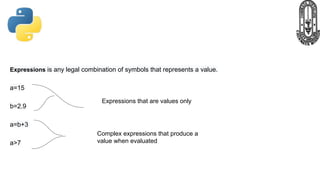
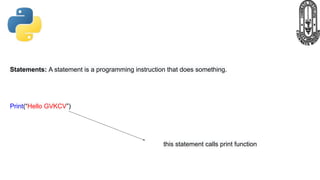
The document provides an overview of Python fundamentals for a class at GVK Chinmaya Vidyalaya, covering various types of operators, expressions, statements, functions, and the structure of Python programs. It explains arithmetic, assignment, comparison, logical, identity, membership, and bitwise operators along with concepts like variables, comments, and dynamic typing. Additionally, the document discusses input/output operations and how to use the print function effectively.