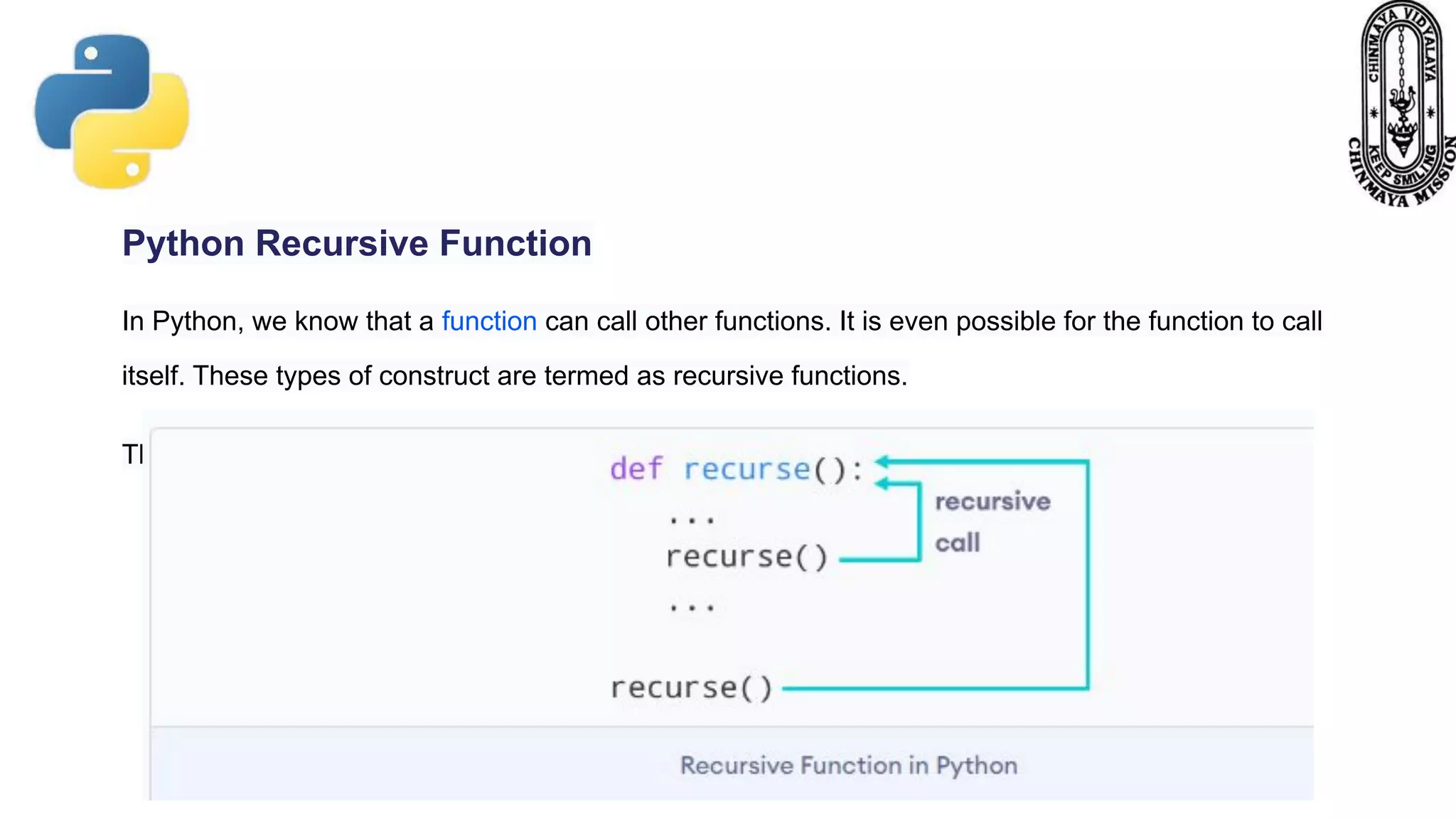
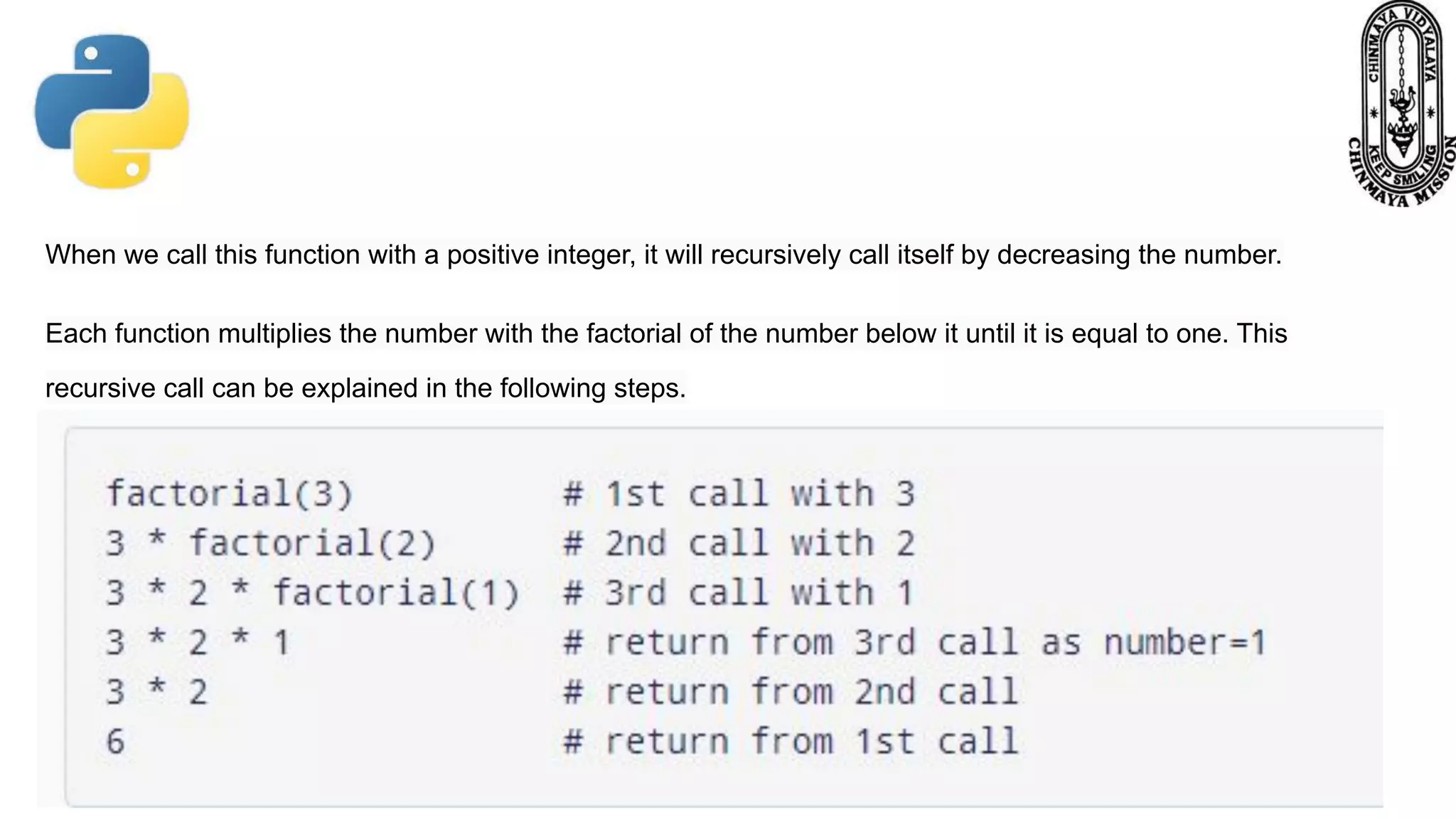
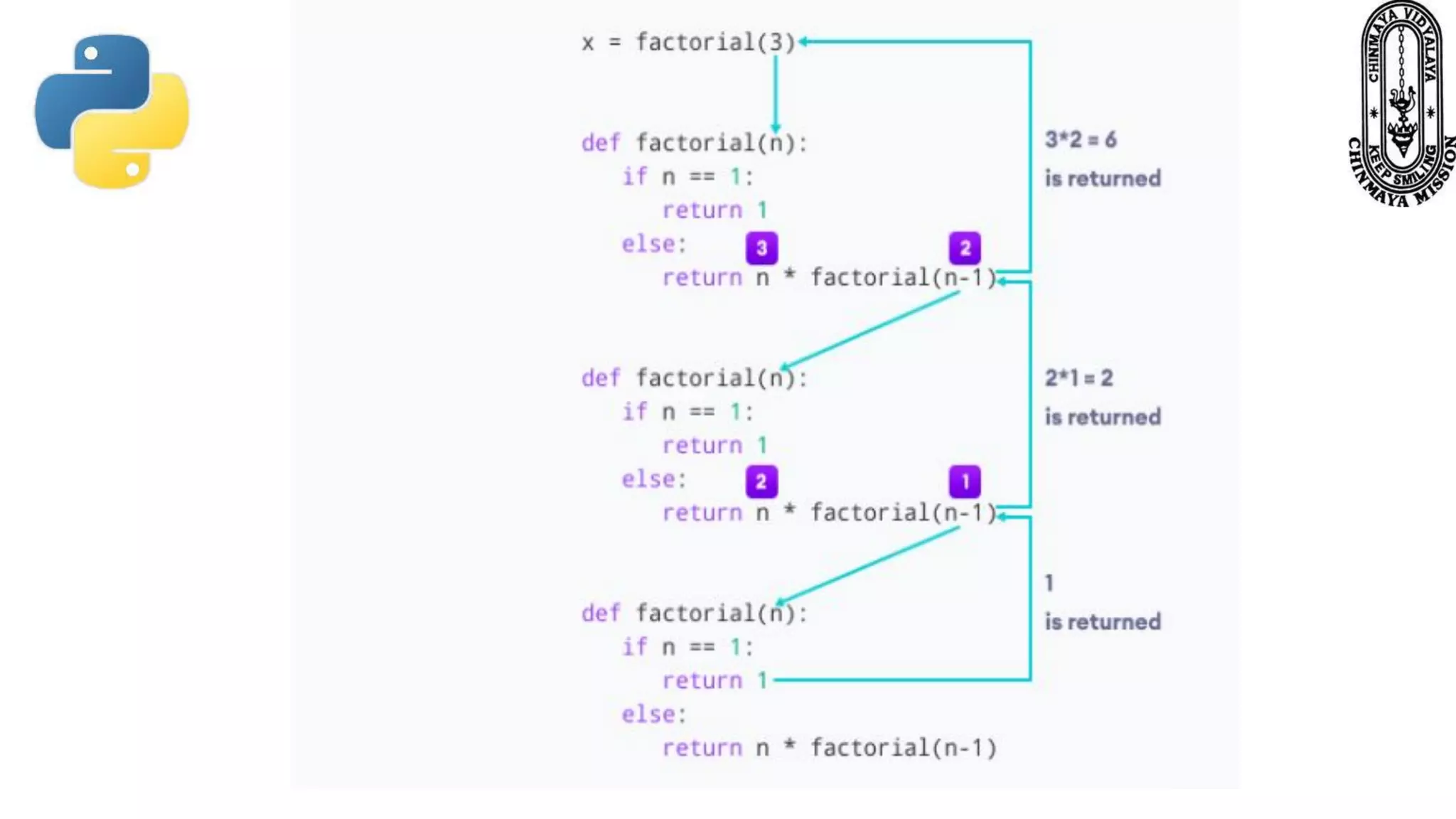
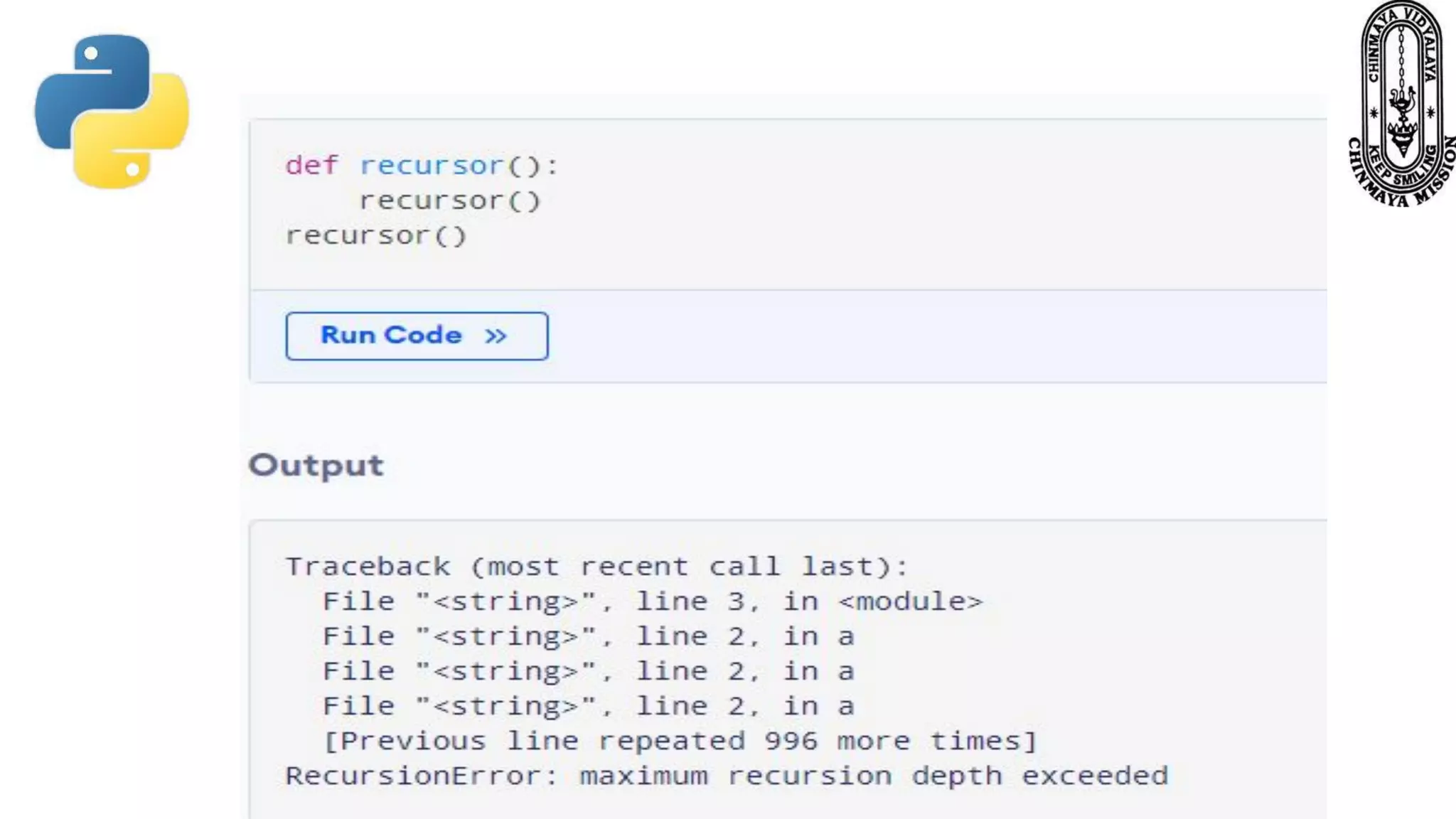
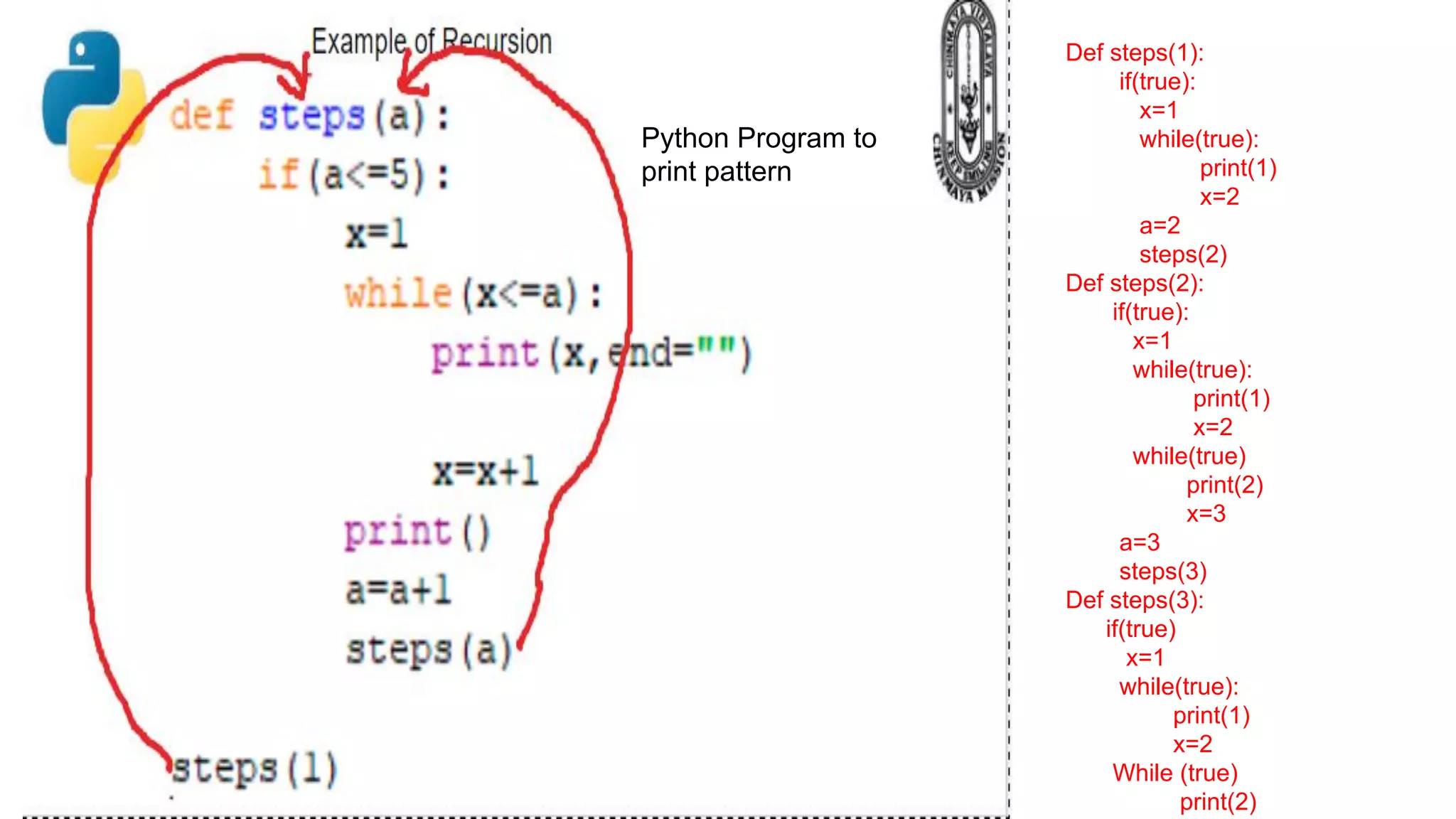
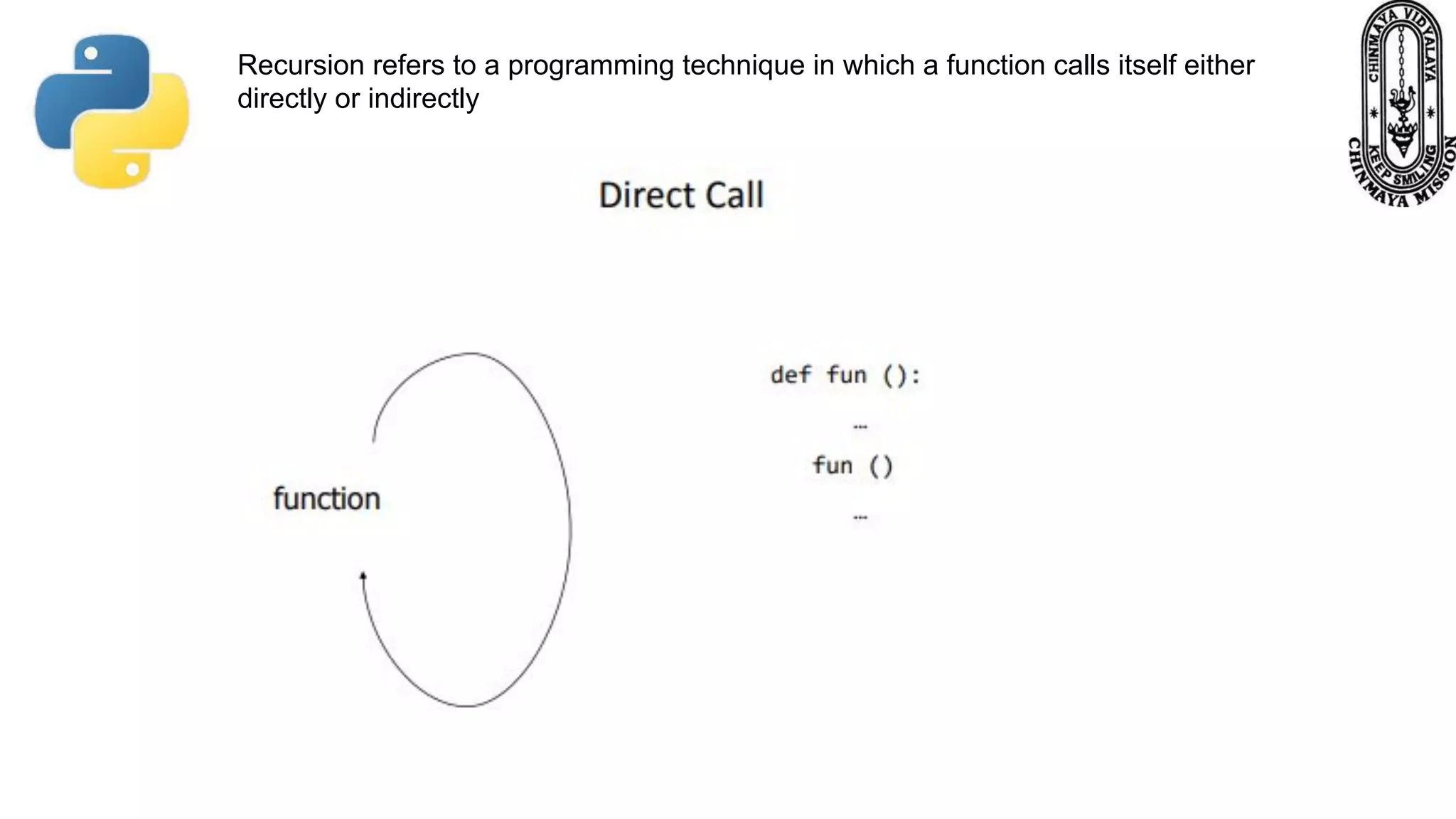
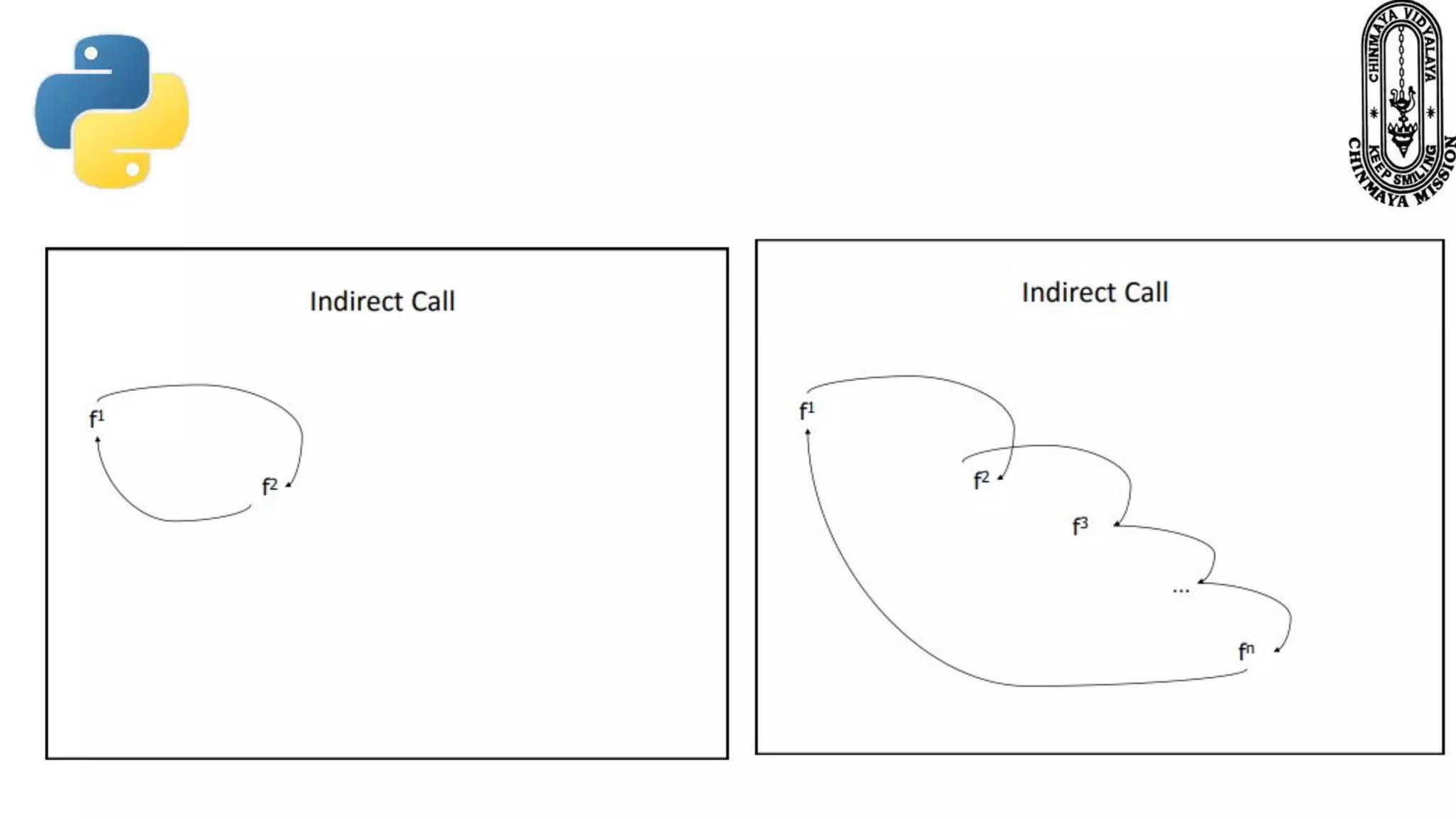
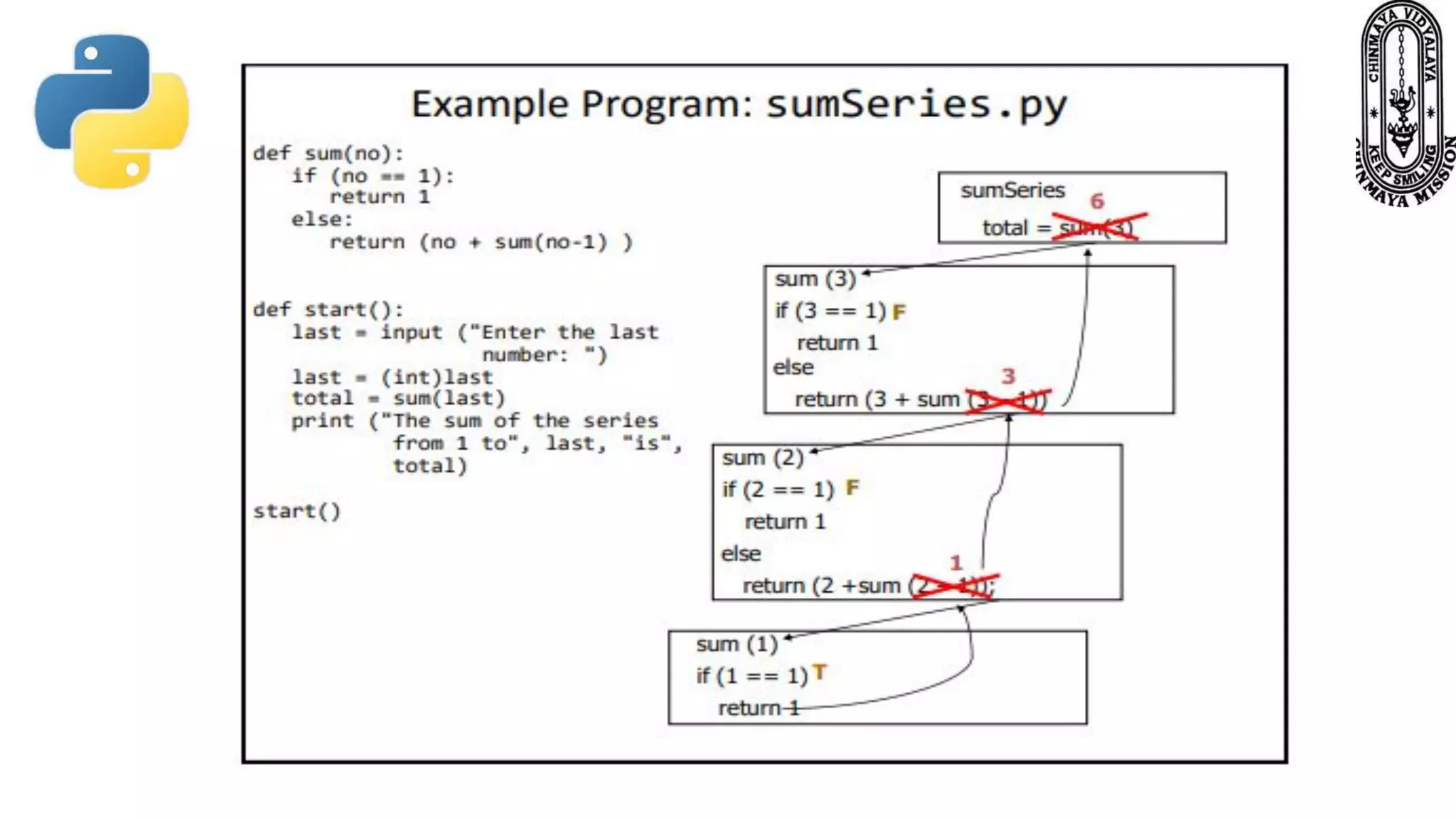
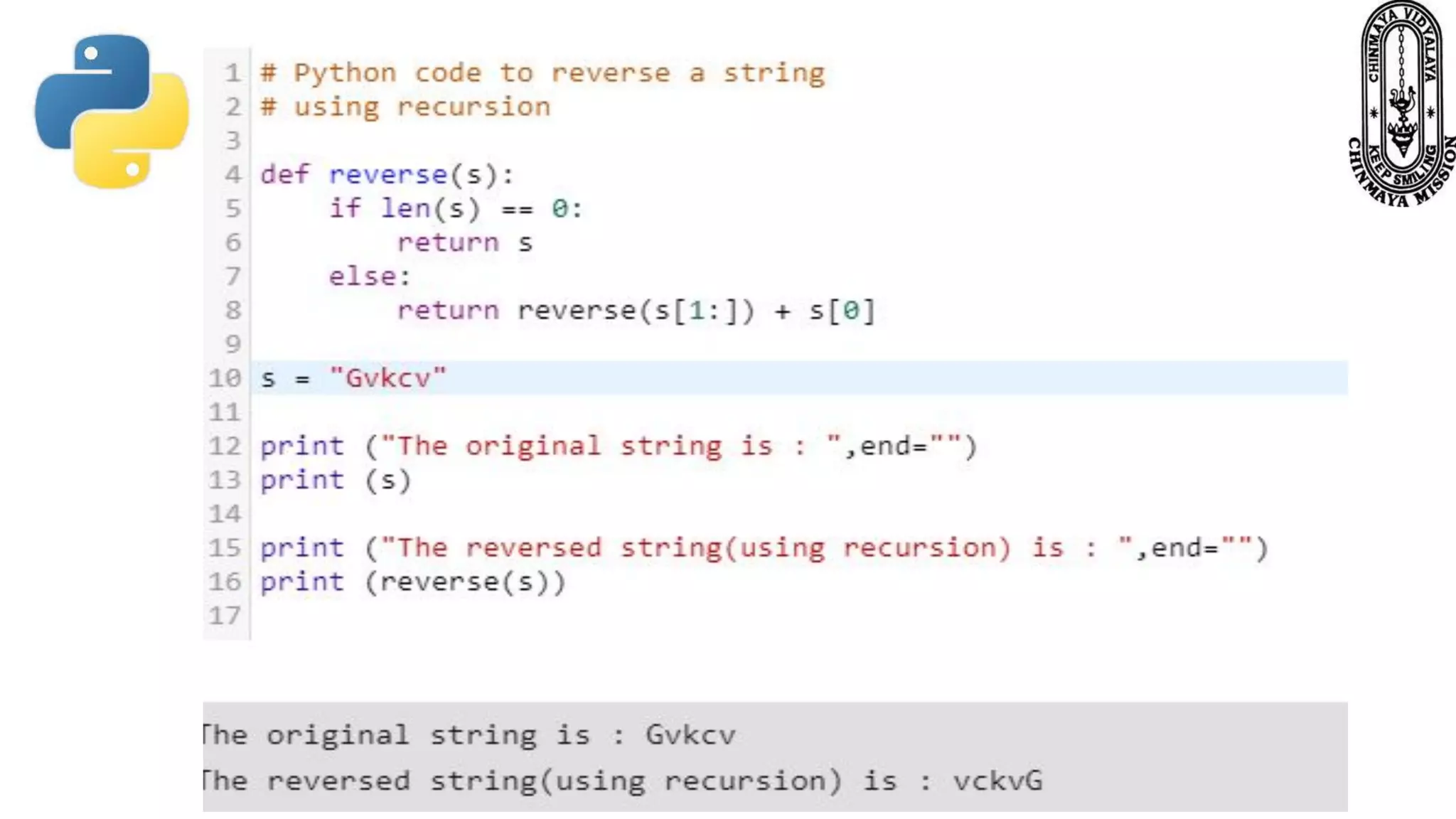
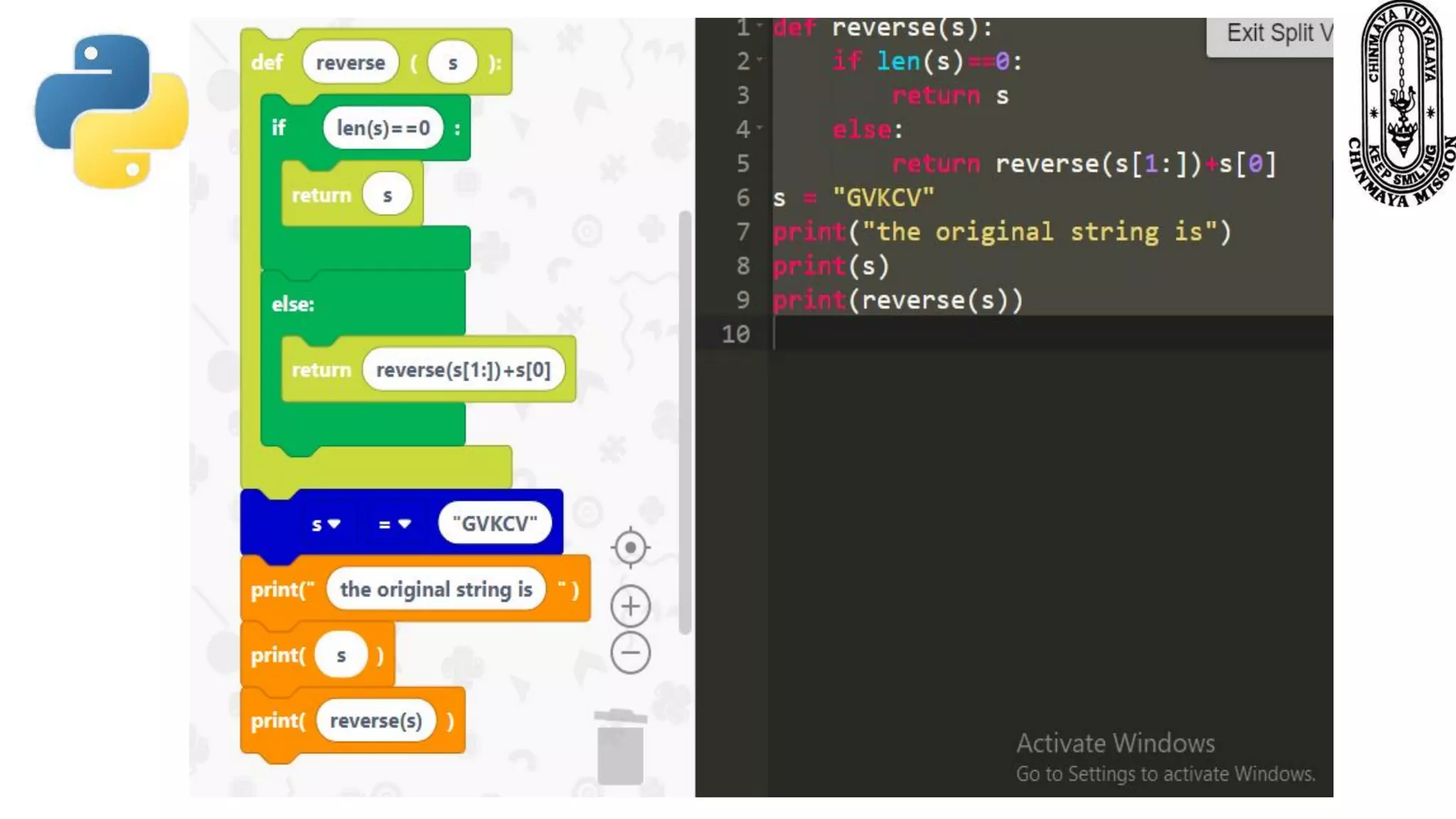
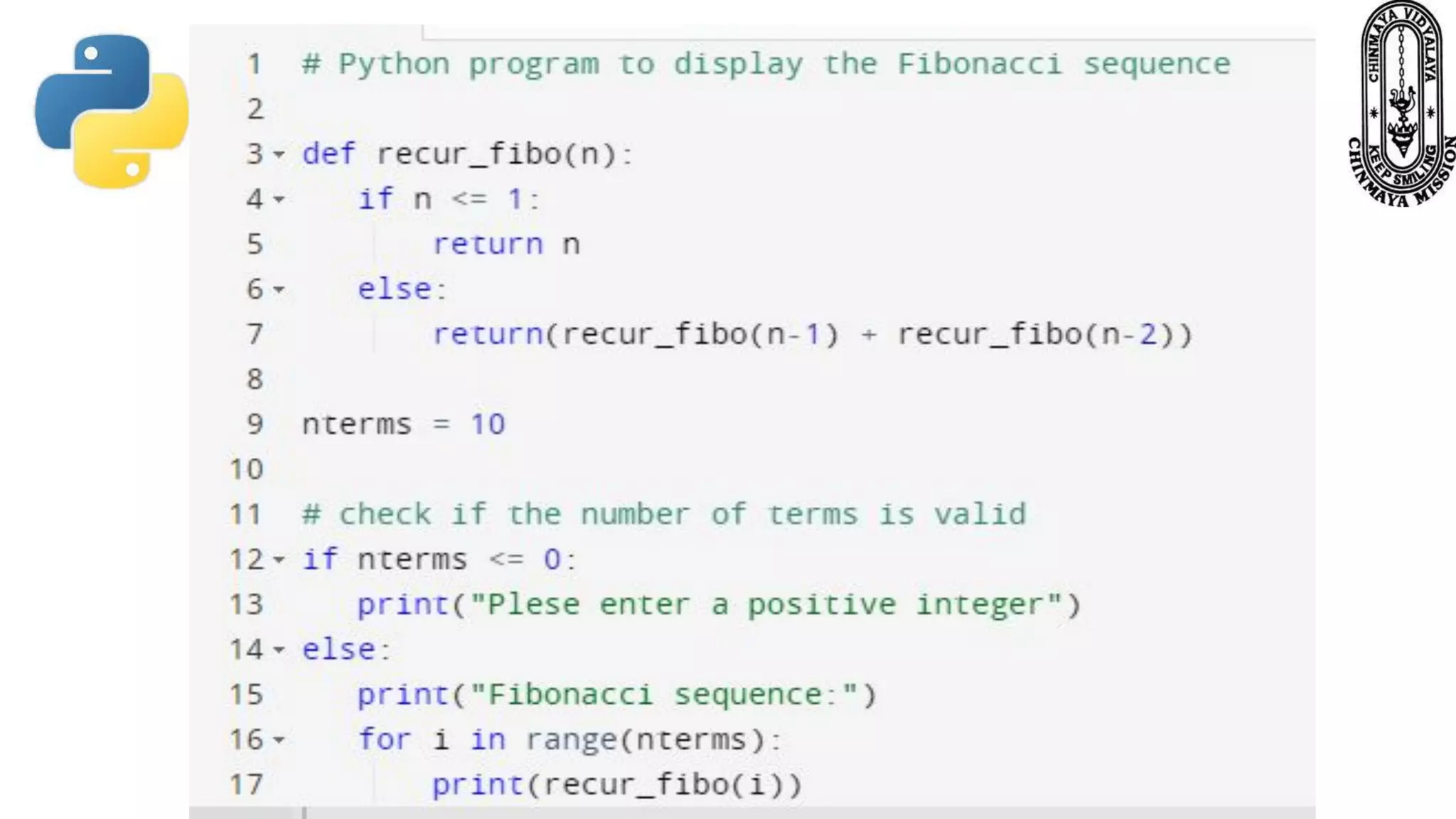
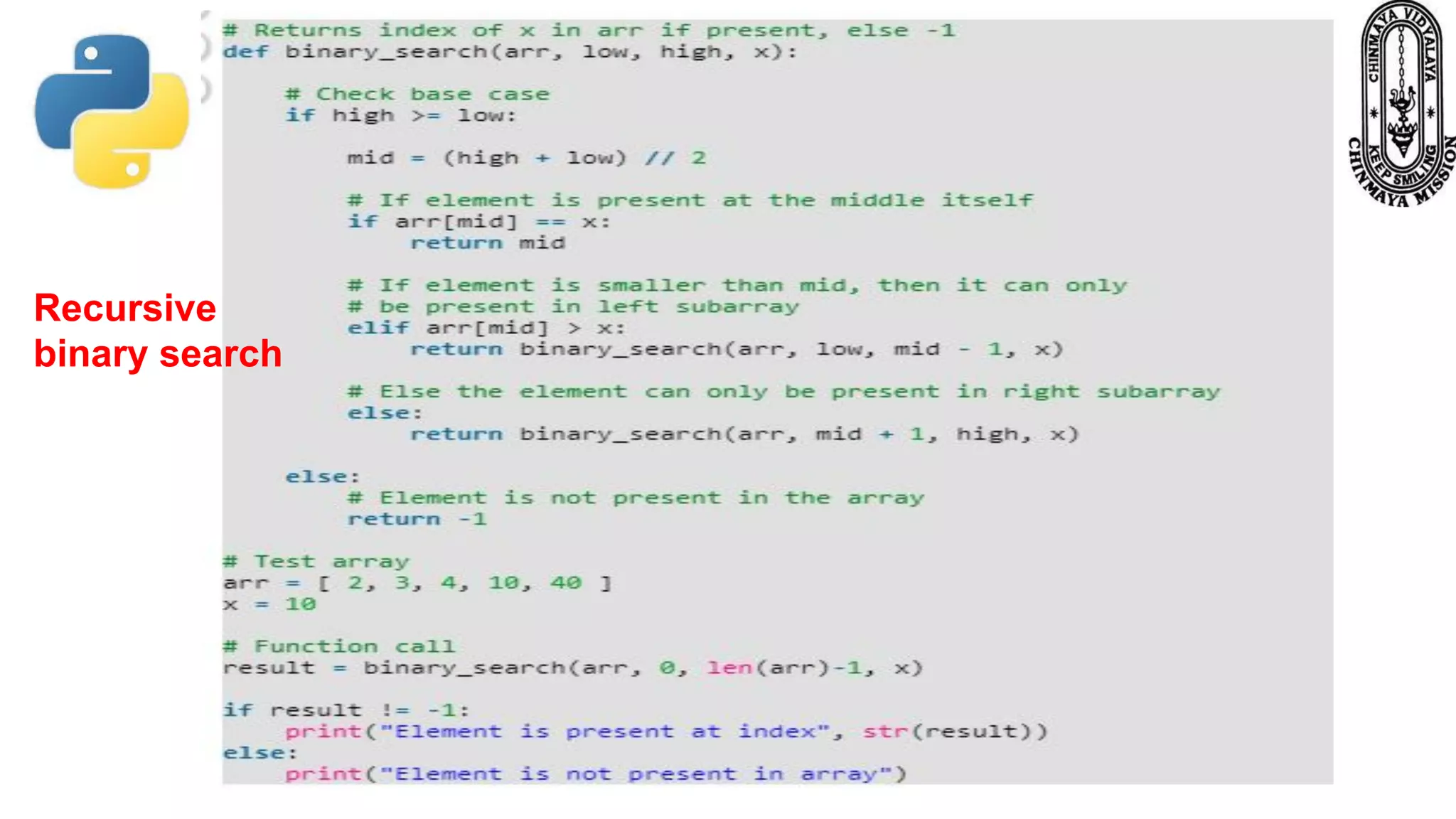
Recursion is a process where a function calls itself directly or indirectly. It is implemented in Python through recursive functions, where a function calls itself. As an example, a recursive function is provided to calculate the factorial of a number by recursively calling itself and multiplying the number by the factorial of the number below it until reaching the base case of 1. For recursion to terminate, there must be a base case condition specified. The Python interpreter limits recursion depth to 1000 by default to avoid stack overflows from infinite recursion.