The document explains the features and characteristics of dictionaries in Python, highlighting that they store data in key-value pairs with unique keys and do not allow duplicates. It discusses the structure of a dictionary, data types, and the rules around key immutability and the handling of duplicate keys. Additionally, it provides examples of how to define and manipulate dictionaries.




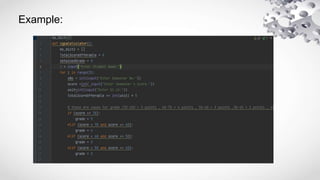
![Dictionary Length
• print(len(thisdict))
• String, int, boolean, and list data types:
• thisdict = {
"brand": "Ford",
"electric": False,
"year": 1964,
"colors": ["red", "white", "blue"]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dictionary-230125023033-a014a4f9/85/PYTHON-DICTIONARY-pptx-5-320.jpg)



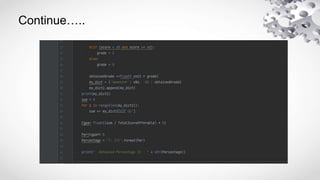
![• keys must be immutable
You can use string,numbers or tuples as dictionary
keys but something like [‘key’] is not allowed.
student={[‘Name’]: ZARA, ‘Age’:7}
print(“student[‘Name’]:”,student[‘Name’])//Type Error
Not Alllowed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dictionary-230125023033-a014a4f9/85/PYTHON-DICTIONARY-pptx-9-320.jpg)
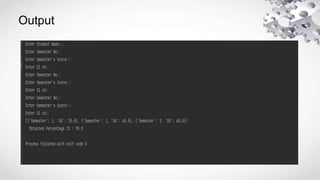
![• More than one entry per key not allowed
It means no duplicate key is allowed.When duplicate
keys encountered during assignment,the last
assignment wins.
student={‘Name’: ‘Zara’, ‘Age’:7, ‘Name’: ‘Manni’}
print(“student[‘Name’]:”,student[‘Name’])
//Output:
student[‘Name’]:Manni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dictionary-230125023033-a014a4f9/85/PYTHON-DICTIONARY-pptx-10-320.jpg)