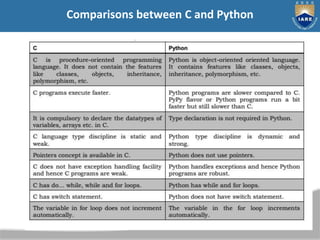
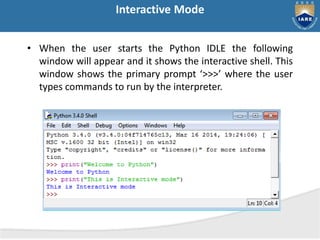
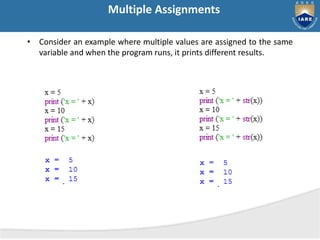
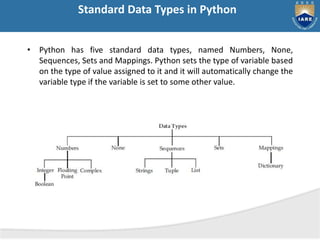
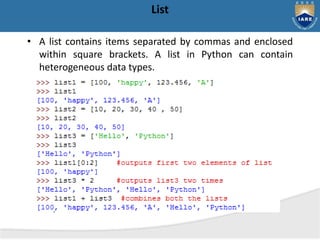
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Python, including its history, features, and various programming modes such as interactive and script mode. It also details the built-in data types, keywords, and the concept of variable assignment in Python. Additionally, it outlines different flavors of Python and discusses its capabilities as a general-purpose programming language.