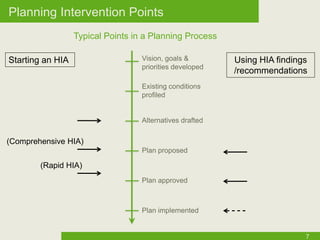
The document outlines the Health Impact Assessment (HIA) process, which evaluates the potential health effects of proposed policies and projects, emphasizing community engagement and health equity. It details the six steps of HIA, including screening, scoping, assessment, recommendations, reporting, and monitoring, and highlights the specific application of HIA to the Safe Routes to School initiative in Columbus. The report aims to address health disparities by focusing on schools and neighborhoods with significant health inequities, using various indicators to inform the assessment.