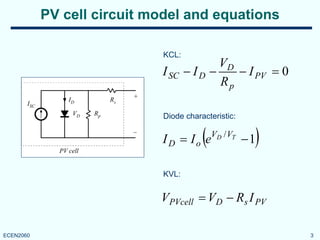
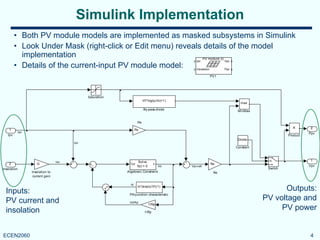
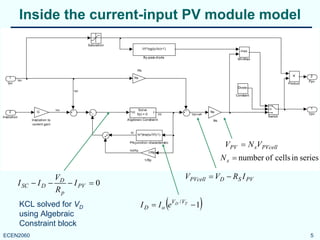
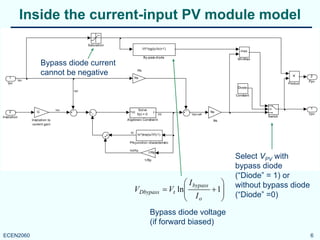
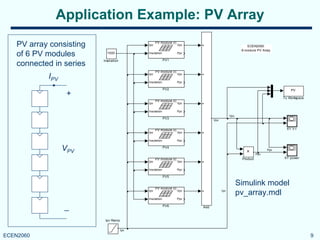
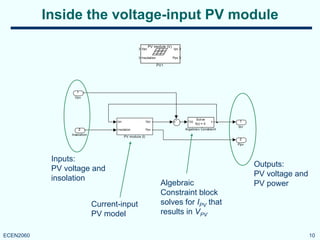
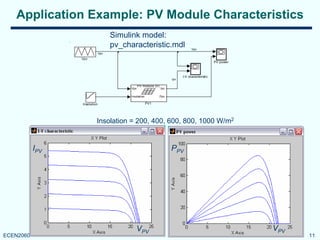
This document describes Simulink models for photovoltaic (PV) modules. It includes models for both current-input and voltage-input PV modules. The models are implemented as masked subsystems in Simulink using blocks like algebraic constraints to solve circuit equations. Example applications shown are a 6-module PV array and generating the I-V and P-V characteristics of a single PV module.

![2ECEN2060
Simulink models of PV modules
Vpv
Insolation
Ipv
Ppv
PV module (V)
PV1
Ipv
Insolation
Vpv
Ppv
PV module (I)
PV1
Current-input PV module Voltage input PV module
Inputs:
• PV current IPV [A]
• Insolation [W/m2
]
Outputs:
• PV voltage VPV [V]
• PV output power Ppv [W]
This model is well suited for the case
when modules are connected in
series and share the same current
Inputs:
• PV voltage VPV [V]
• Insolation [W/m2
]
Outputs:
• PV current IPV [A]
• PV output power Ppv [W]
This model is well suited for the case
when modules are connected in
parallel and share the same voltage
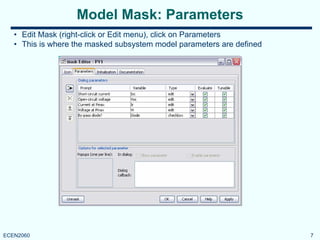
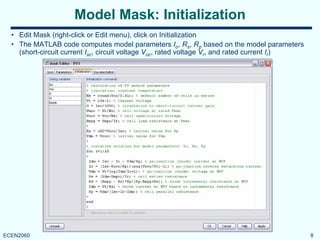
Model parameters, in both cases, are the standard
PV module data-sheet parameters:
• short-circuit current Isc
• open-circuit voltage Voc
• rated current IR at maximum power point (MPP)
• rated voltage VR at MPP
under standard test conditions (1kW/m2, 1.5 AM,
25oC). A bypass diode (a single diode across the
entire module) can be included. Temperature
effects are not modeled.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8843034f-3a1f-4293-bcb9-bb1d2c8dc980-150602044617-lva1-app6892/85/PV_module_model-2-320.jpg)