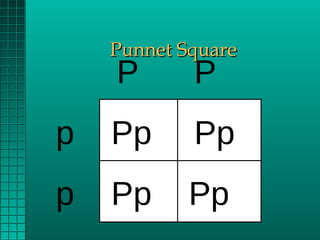
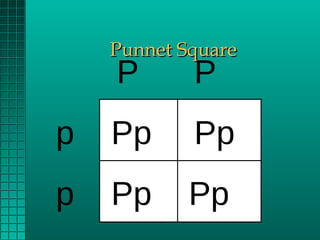
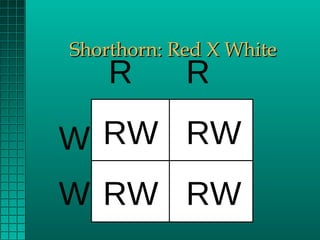
Genetics determines the physical traits of animals through genes. Genes are located on chromosomes and are received in pairs from each parent. Dominant genes fully express themselves when paired with a recessive gene. Recessive genes only express when paired with another recessive. Punnett squares can be used to determine the likelihood of offspring inheriting traits based on parents' genes. Some genes are sex-linked and mutations can also cause unexpected traits. Heritability determines the likelihood of traits being passed down from parents to offspring. Crossbreeding can result in hybrid vigor with offspring outperforming either parent breed.