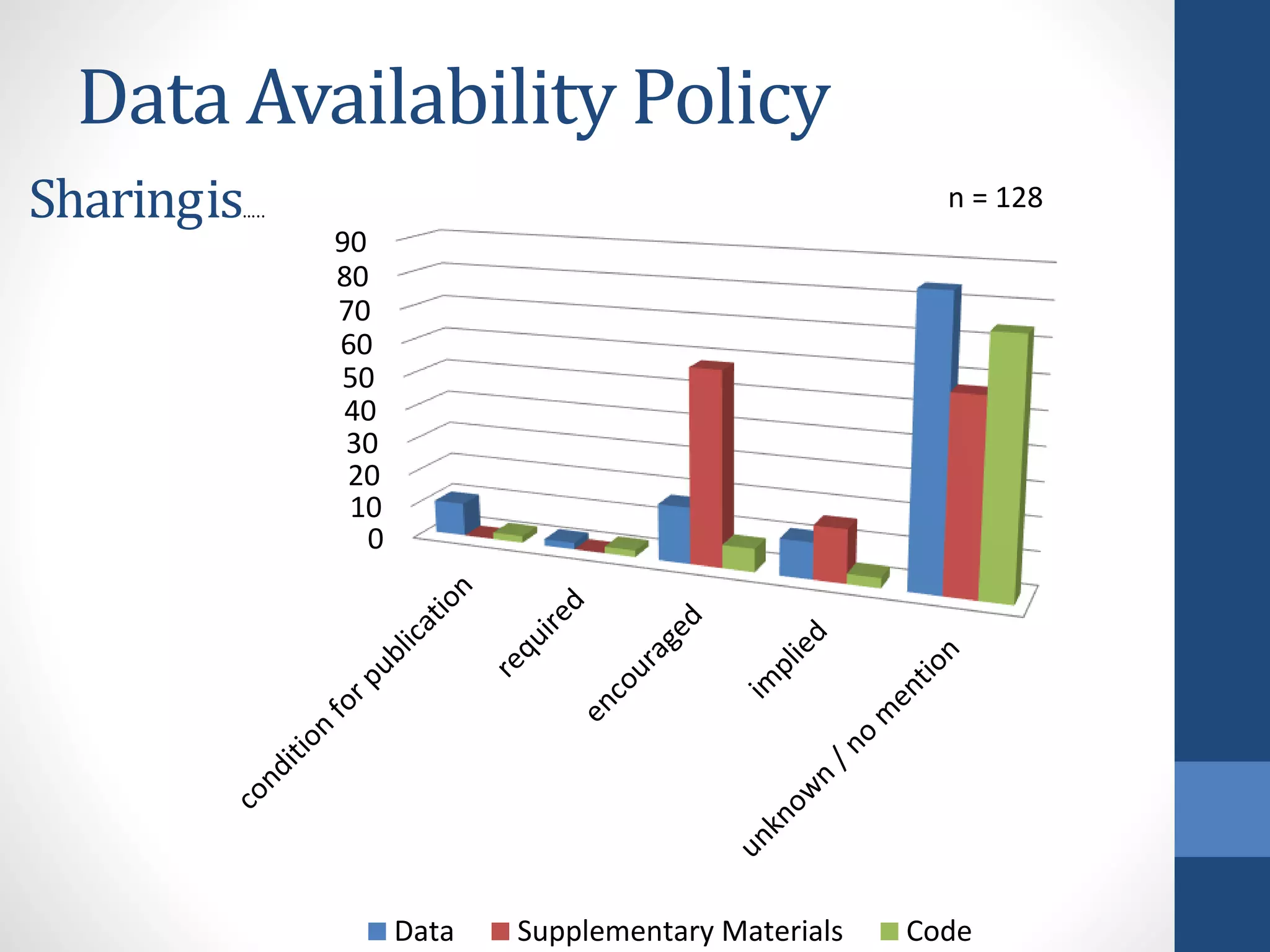
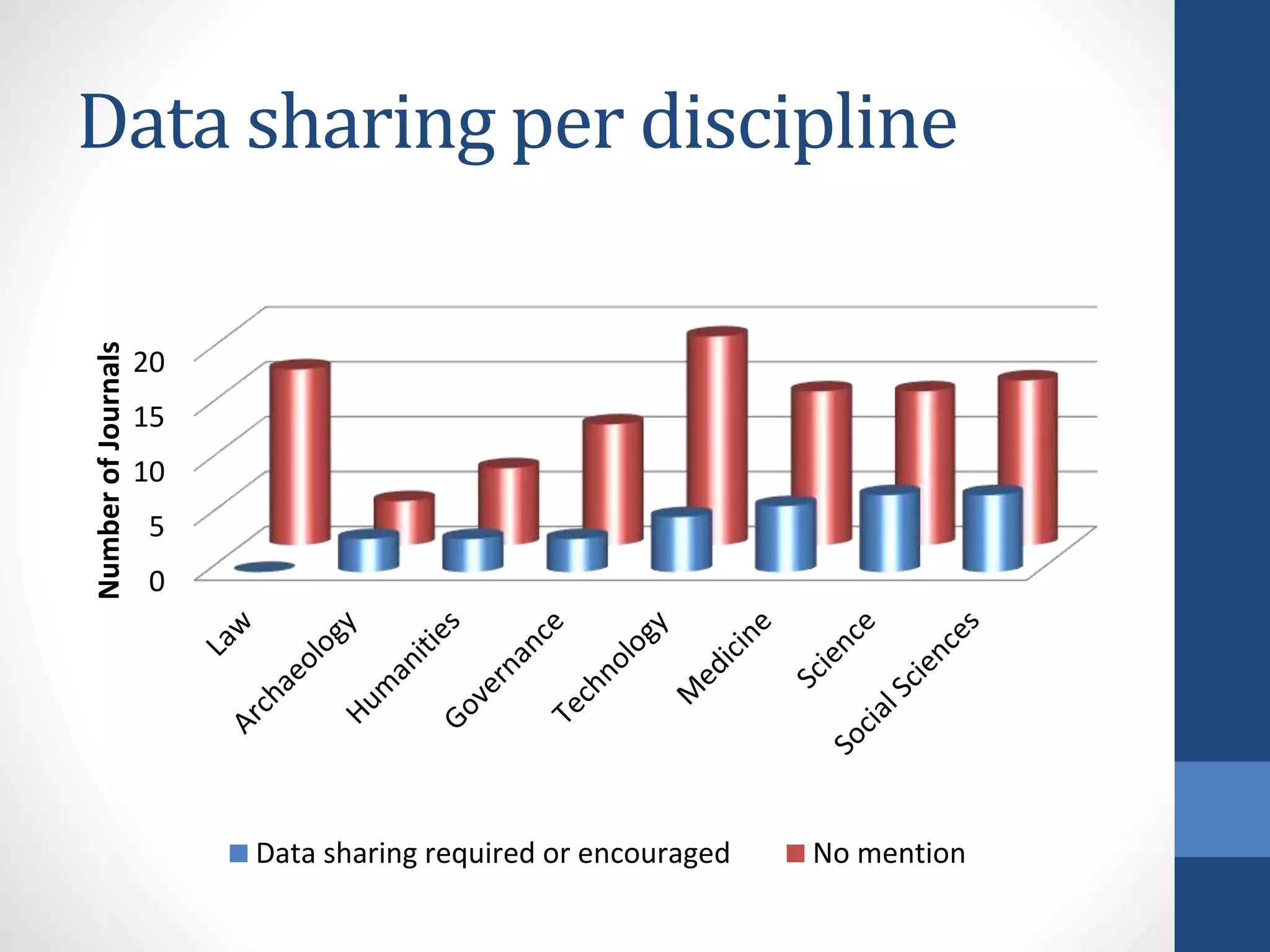
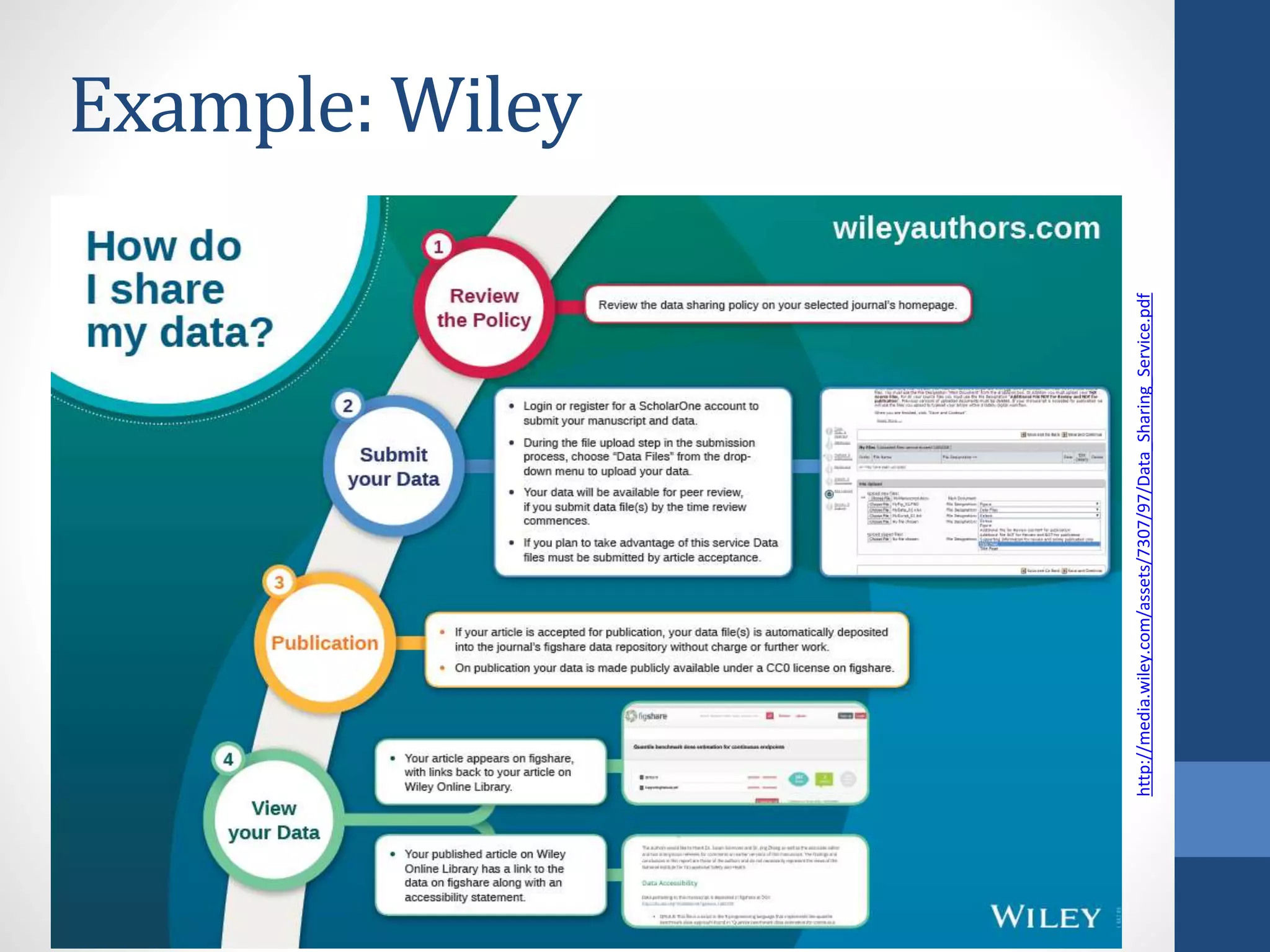
The document discusses the current state of research data management policies among Dutch publishers and highlights the need for improved data availability practices. It critiques the existence of 'type zero' policies, where many journals lack any data-sharing guidelines, and calls for a harmonization of standards. Recommendations are provided for publishers, data archives, and libraries to enhance data sharing and availability for research quality.