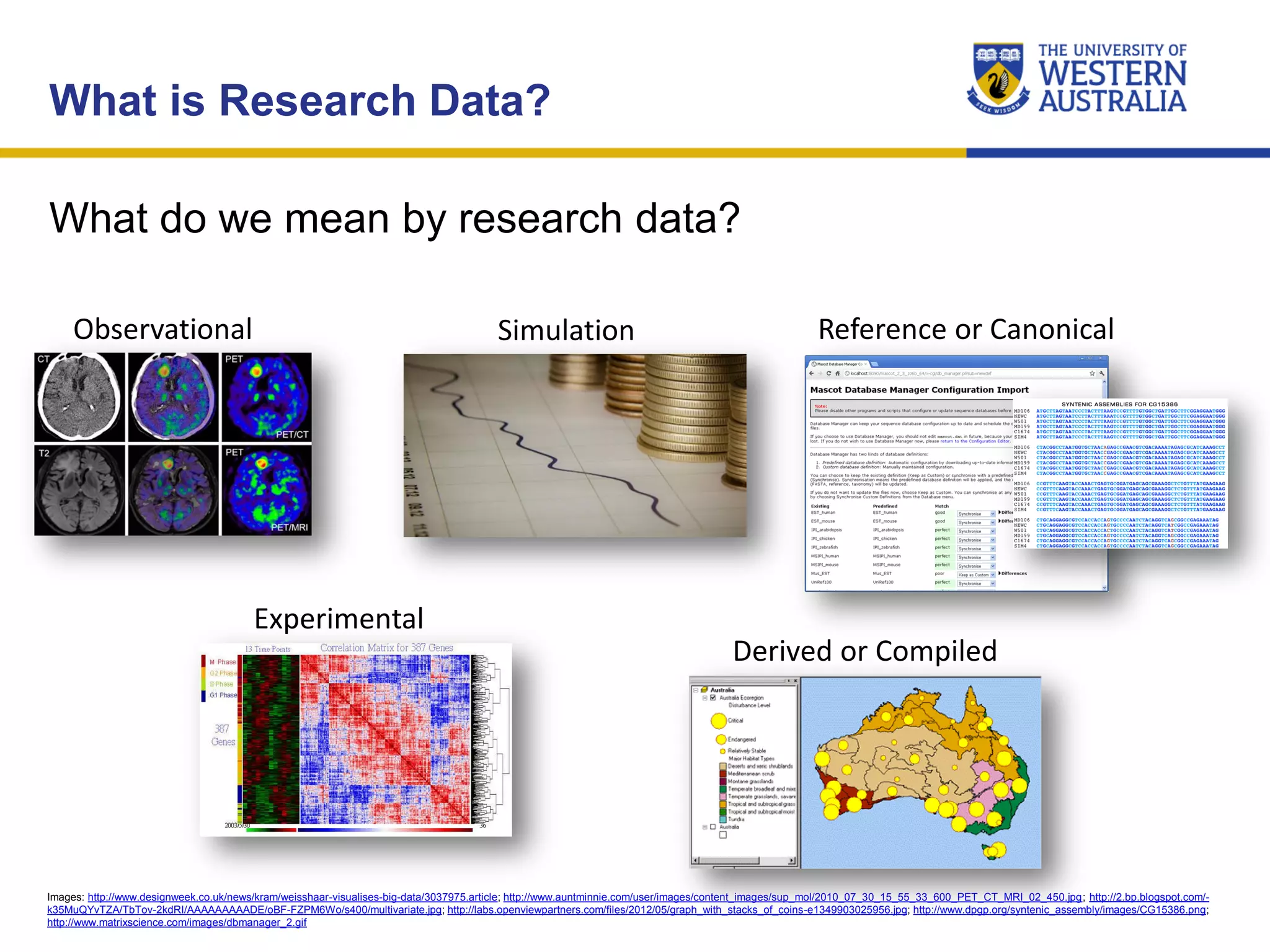
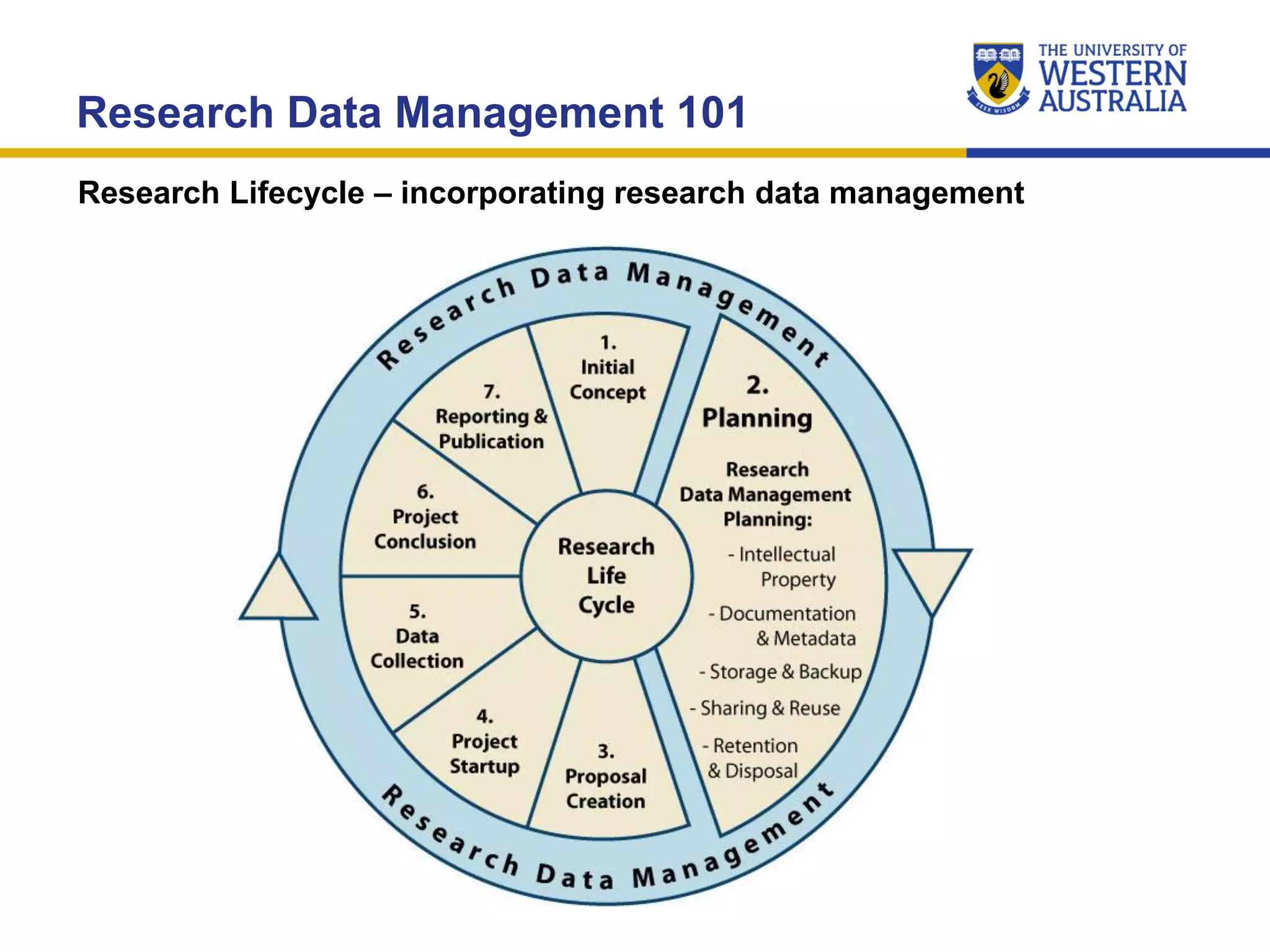
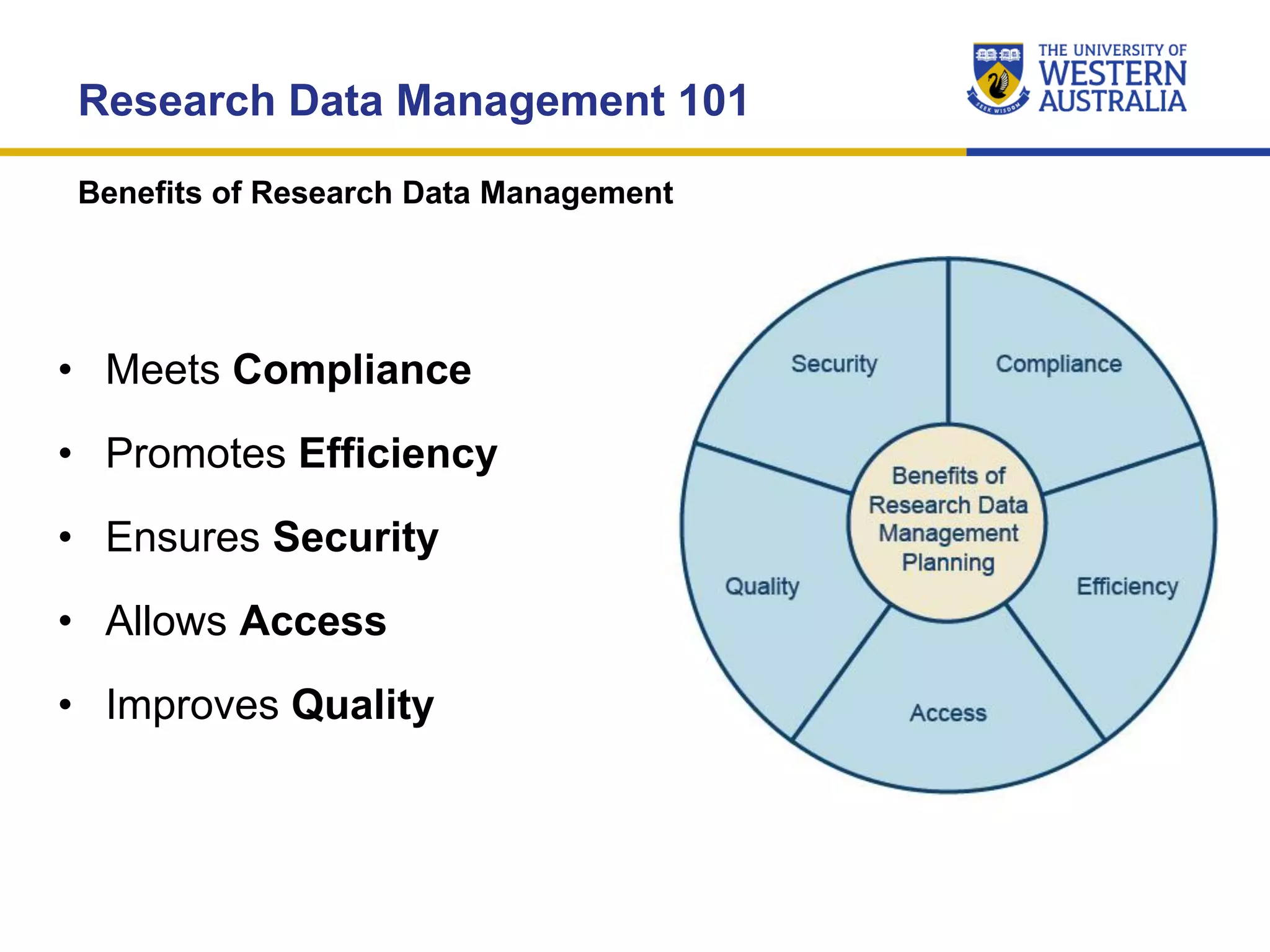
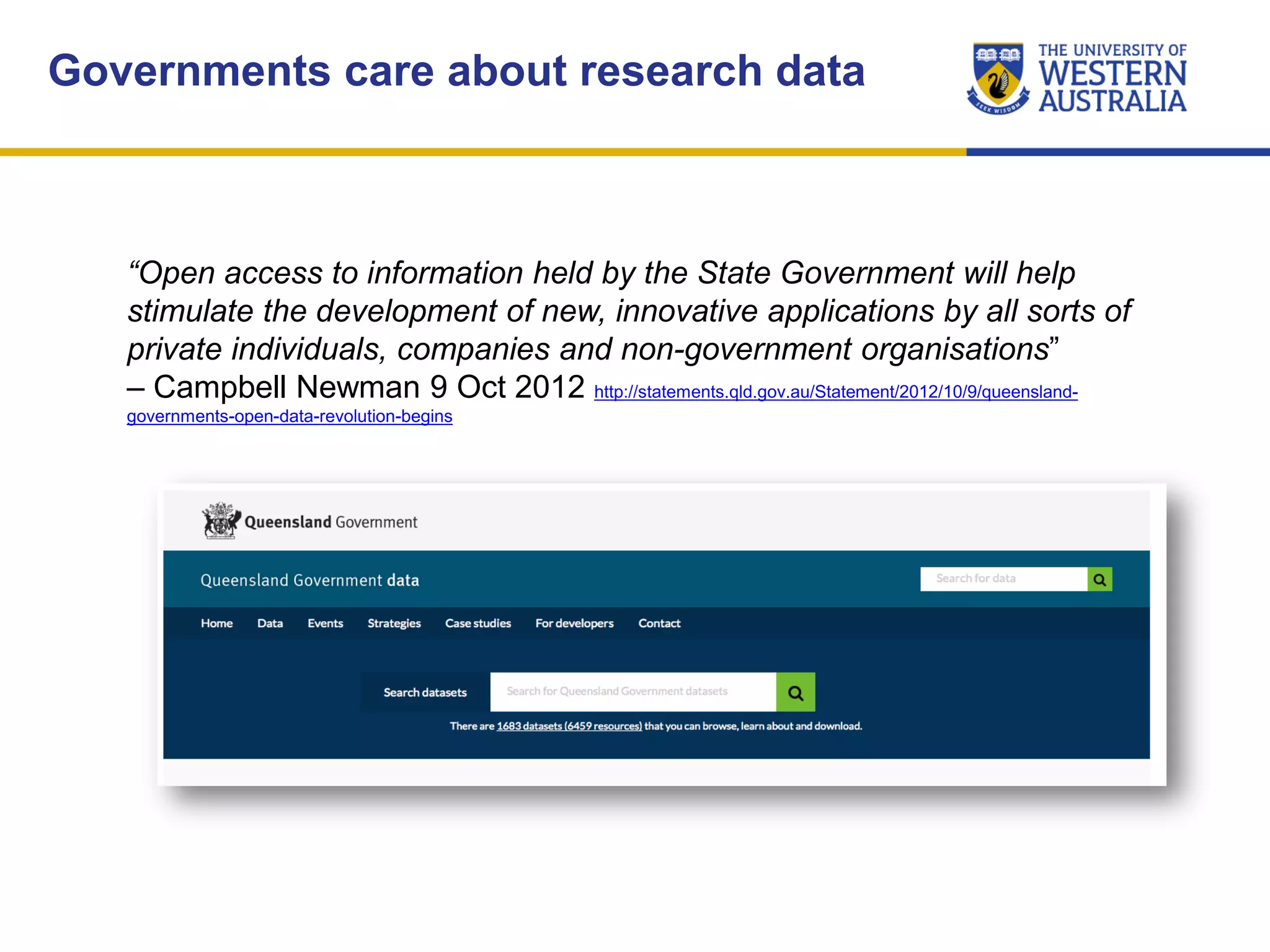
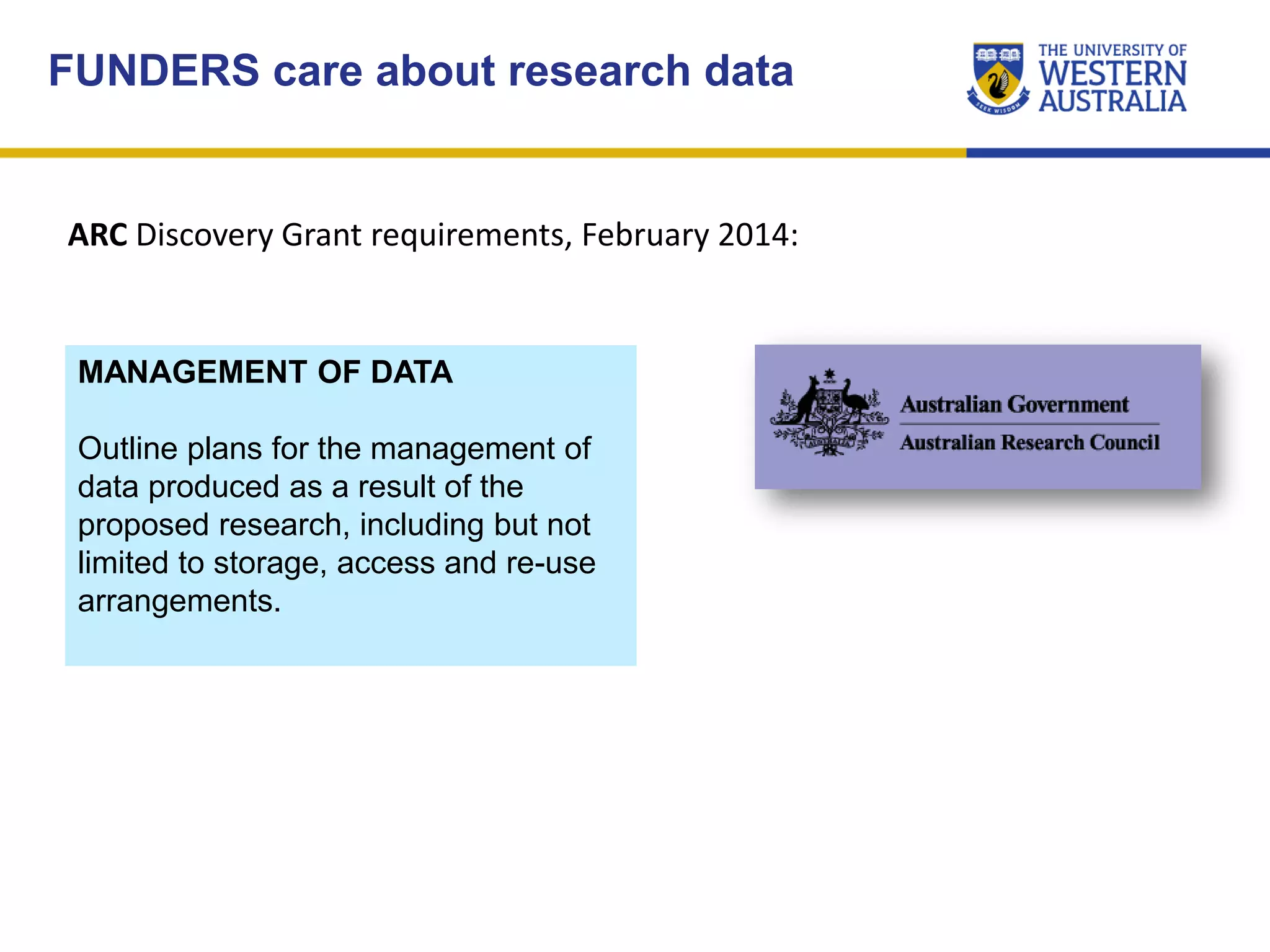
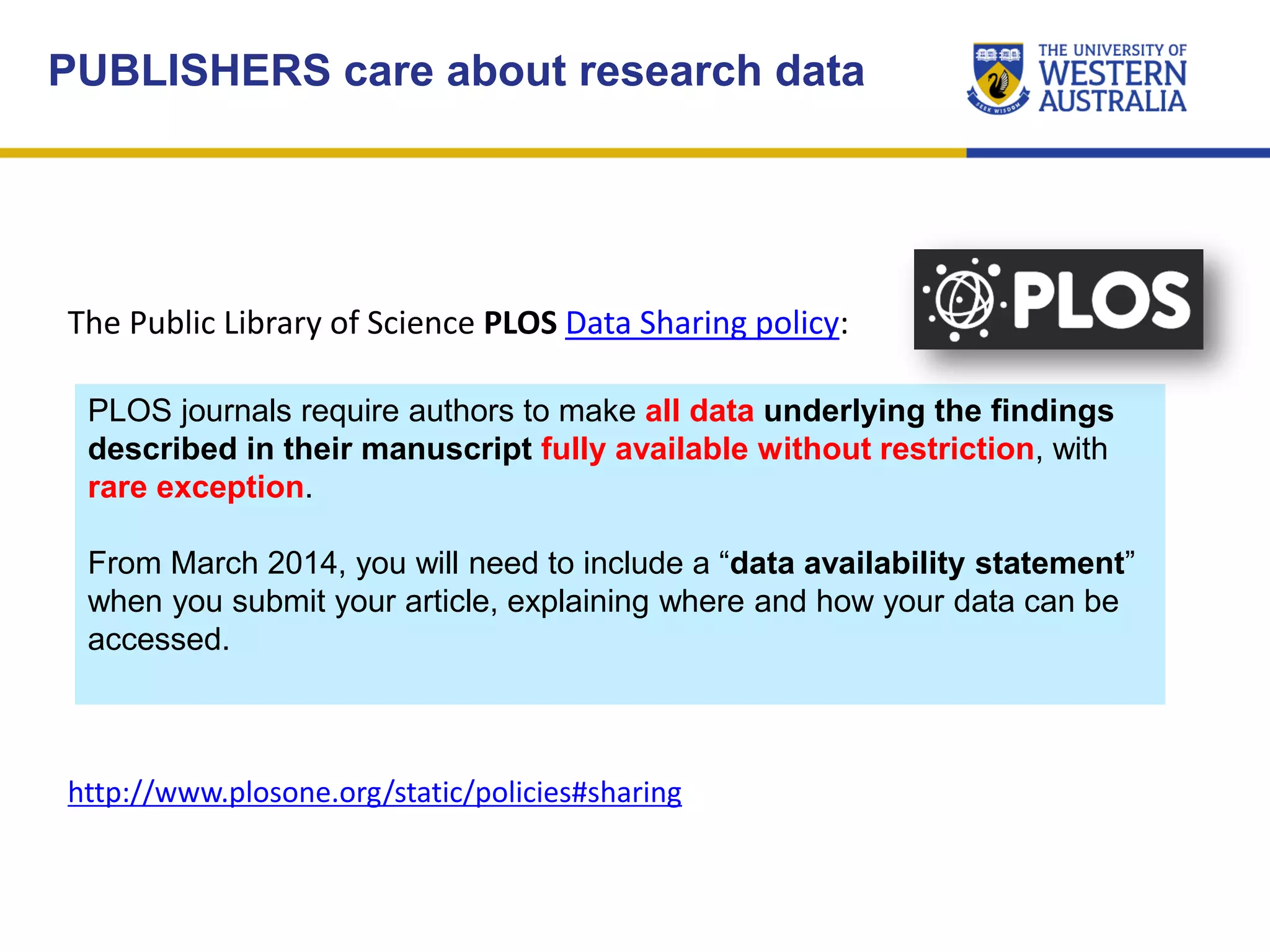
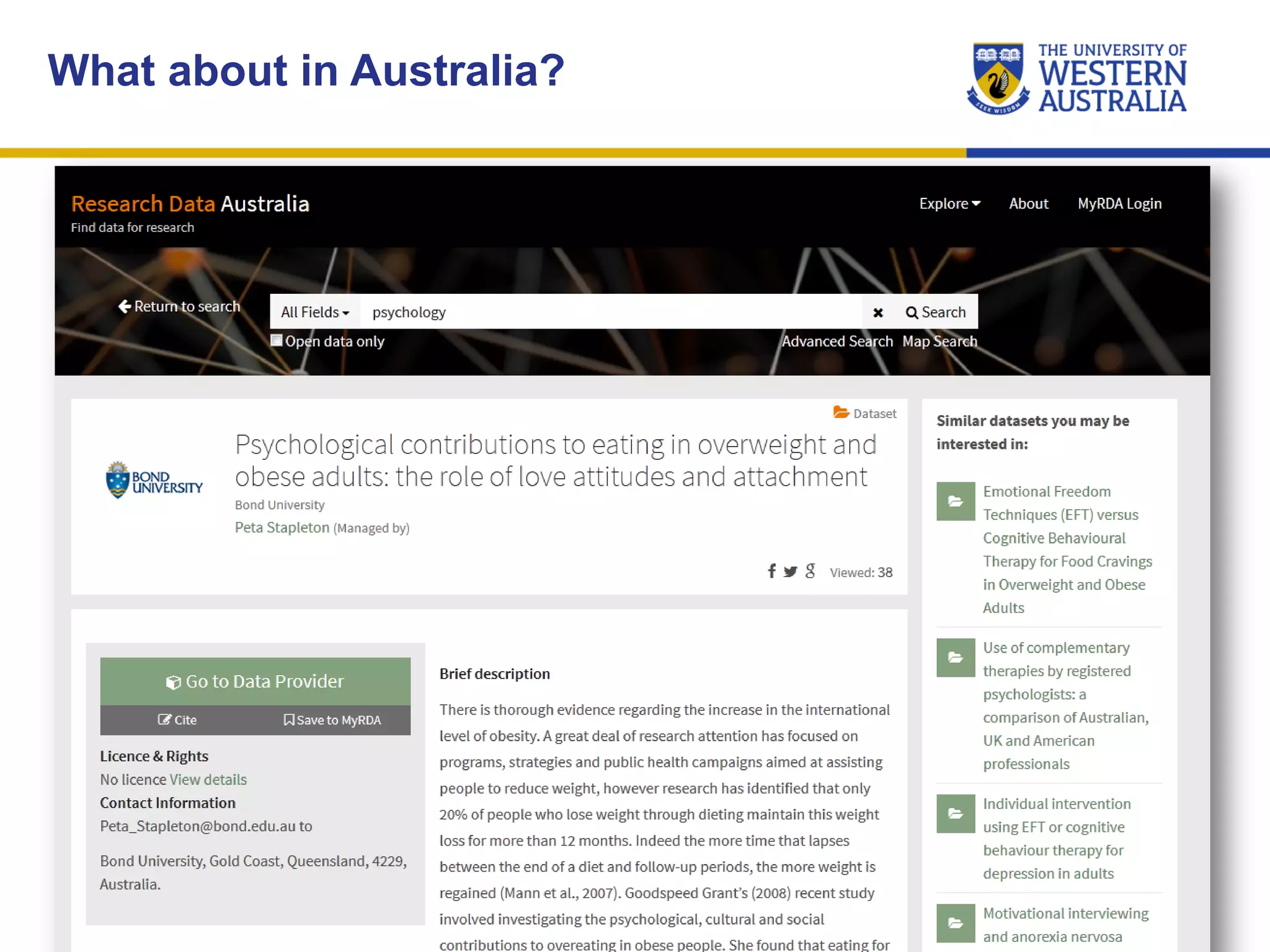
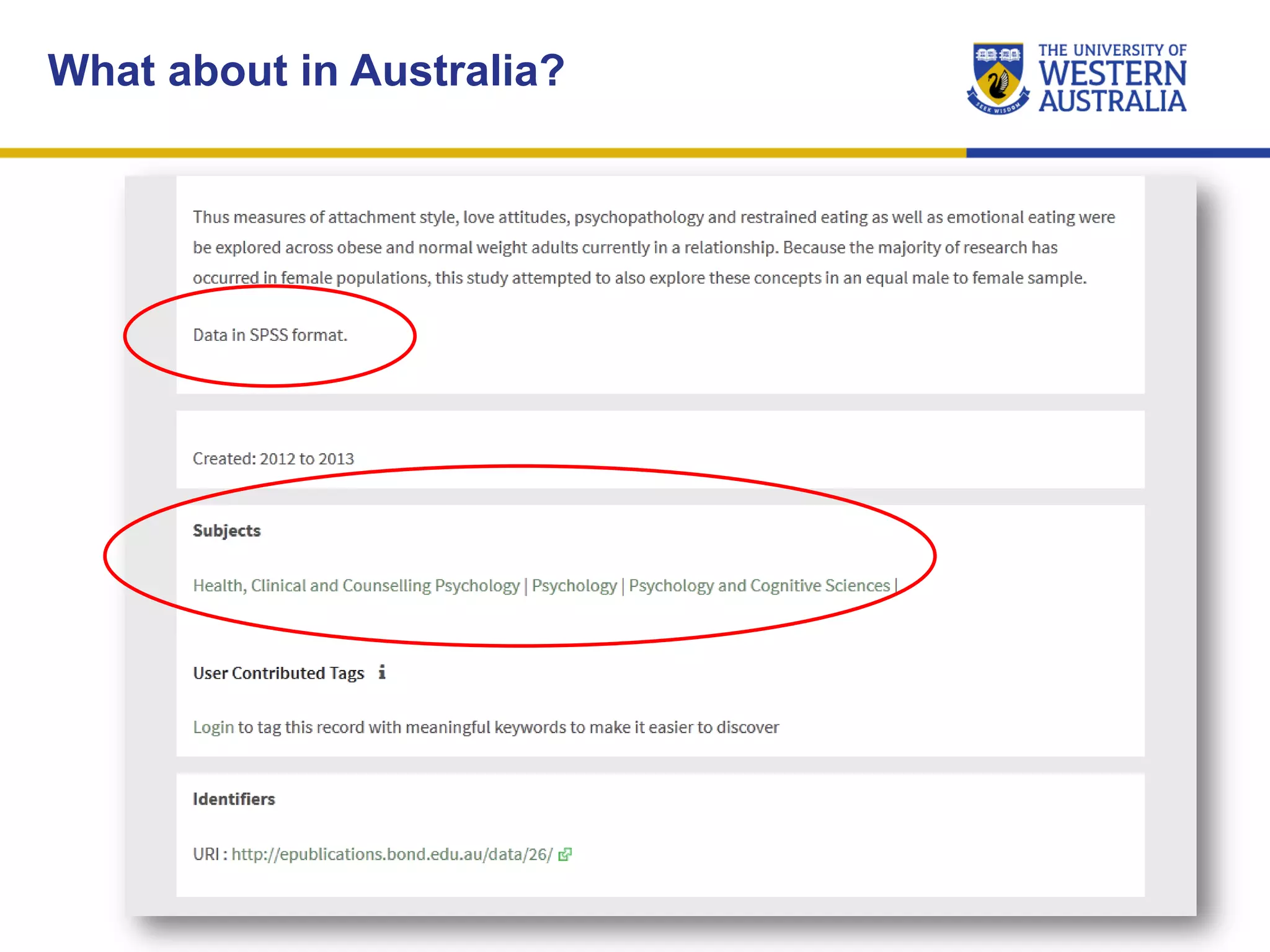
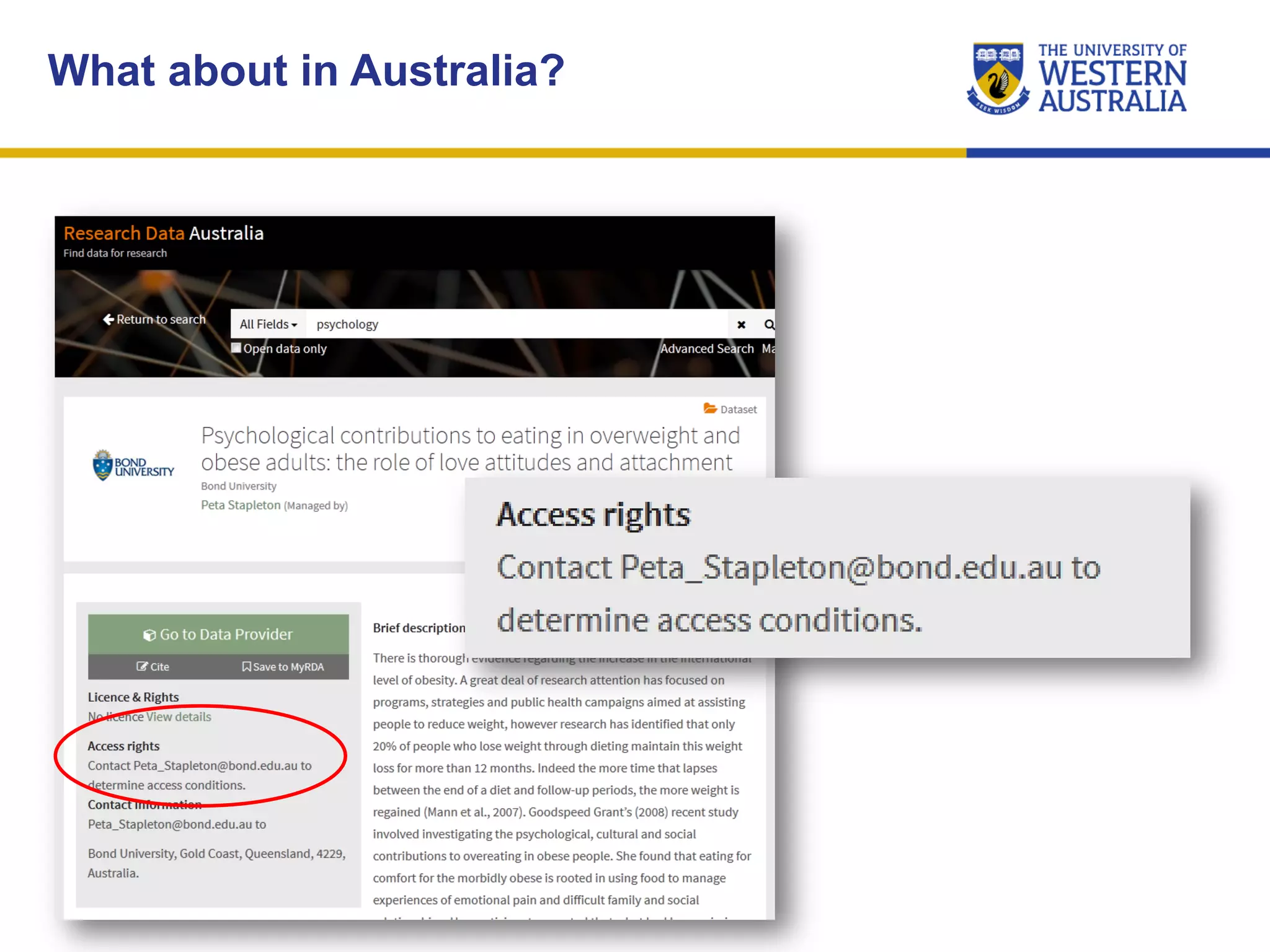
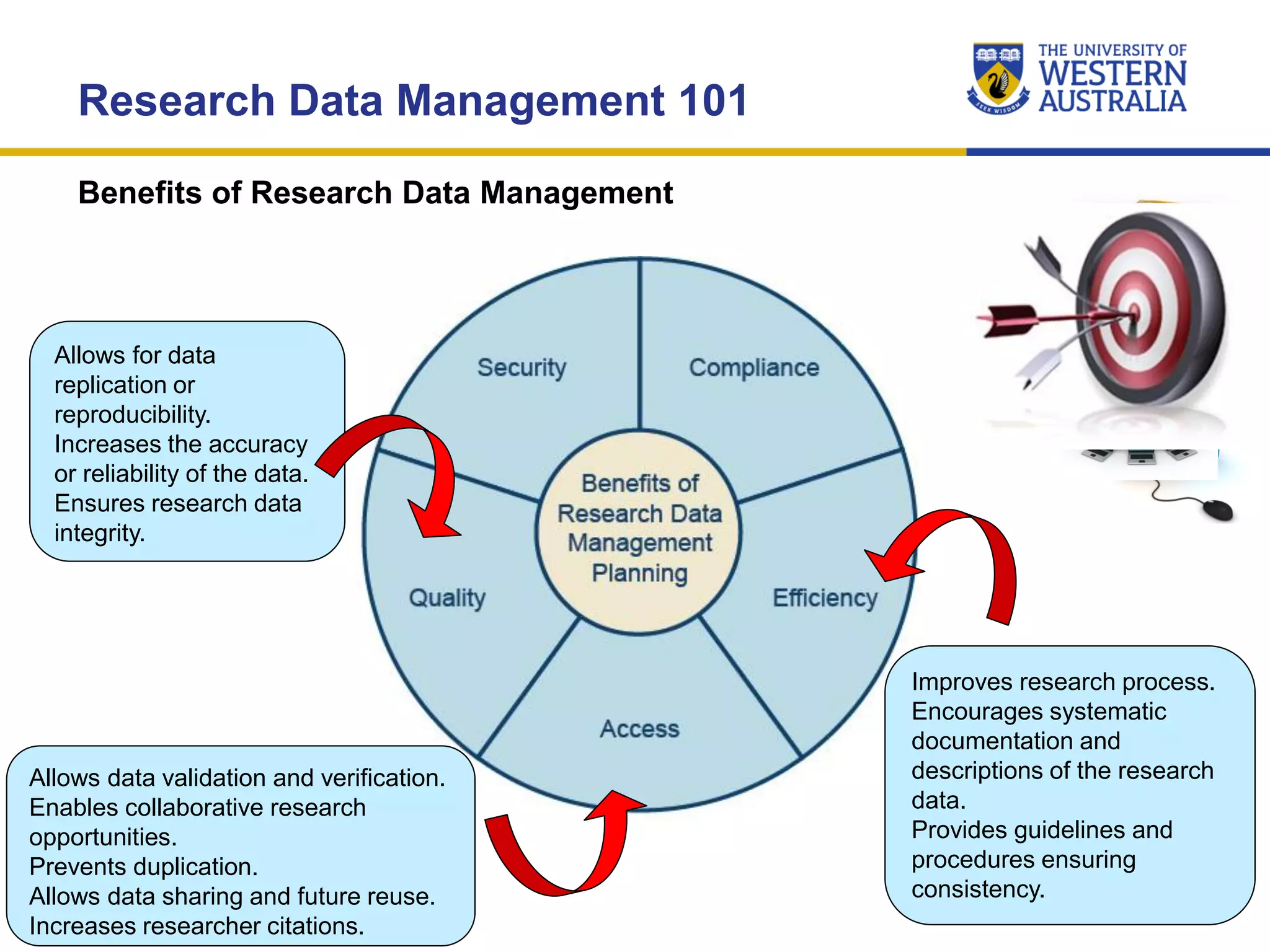
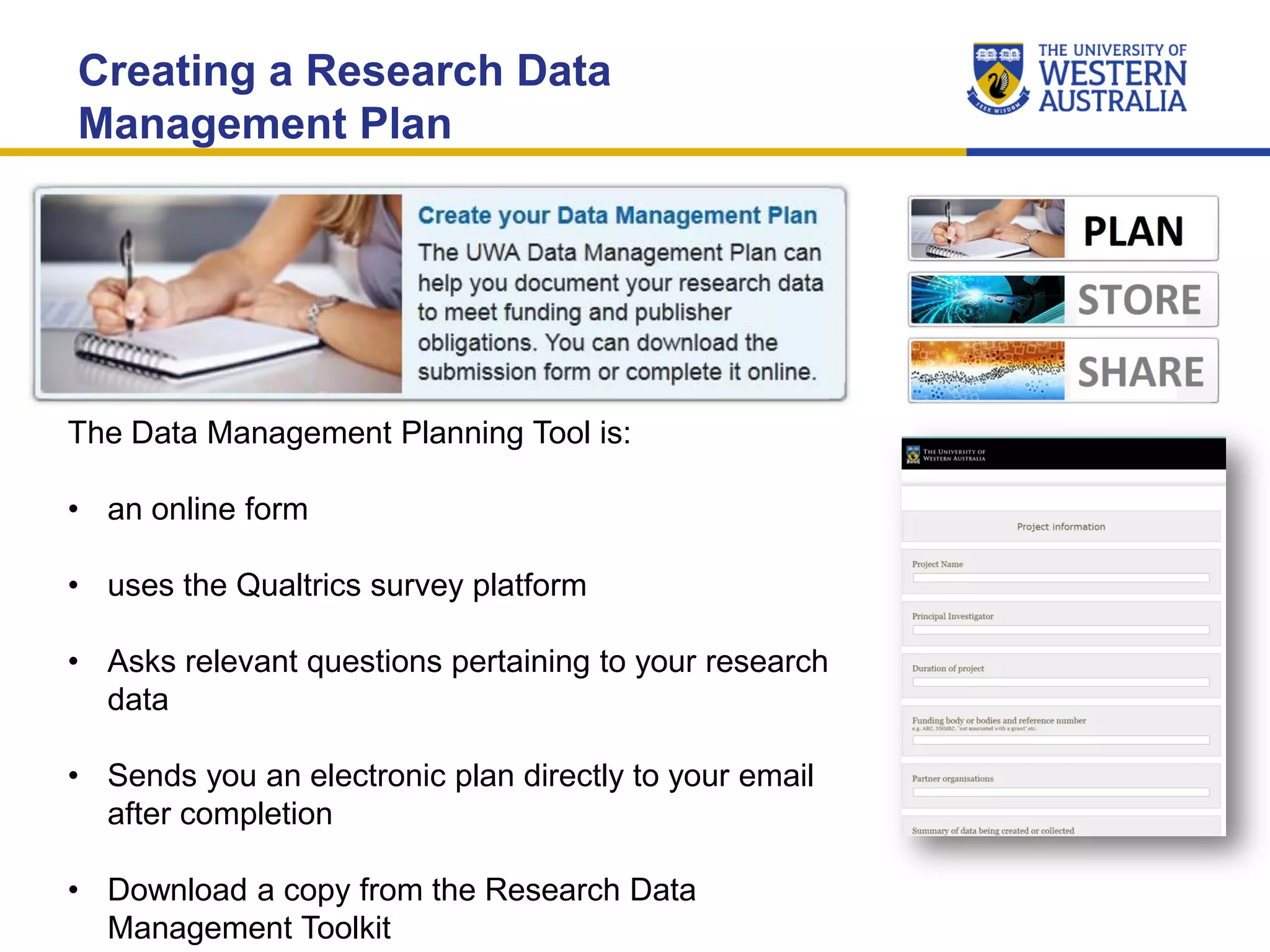
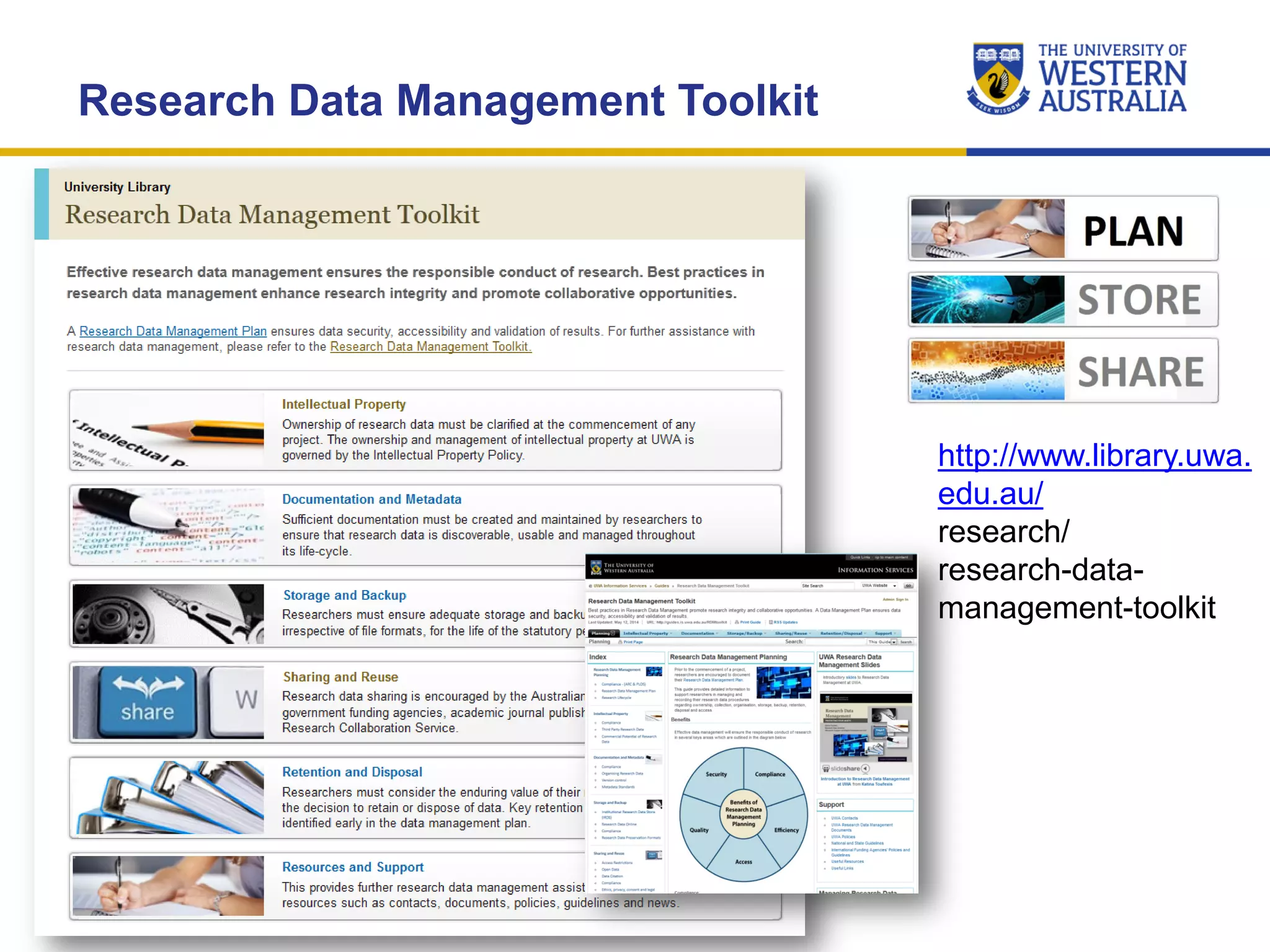
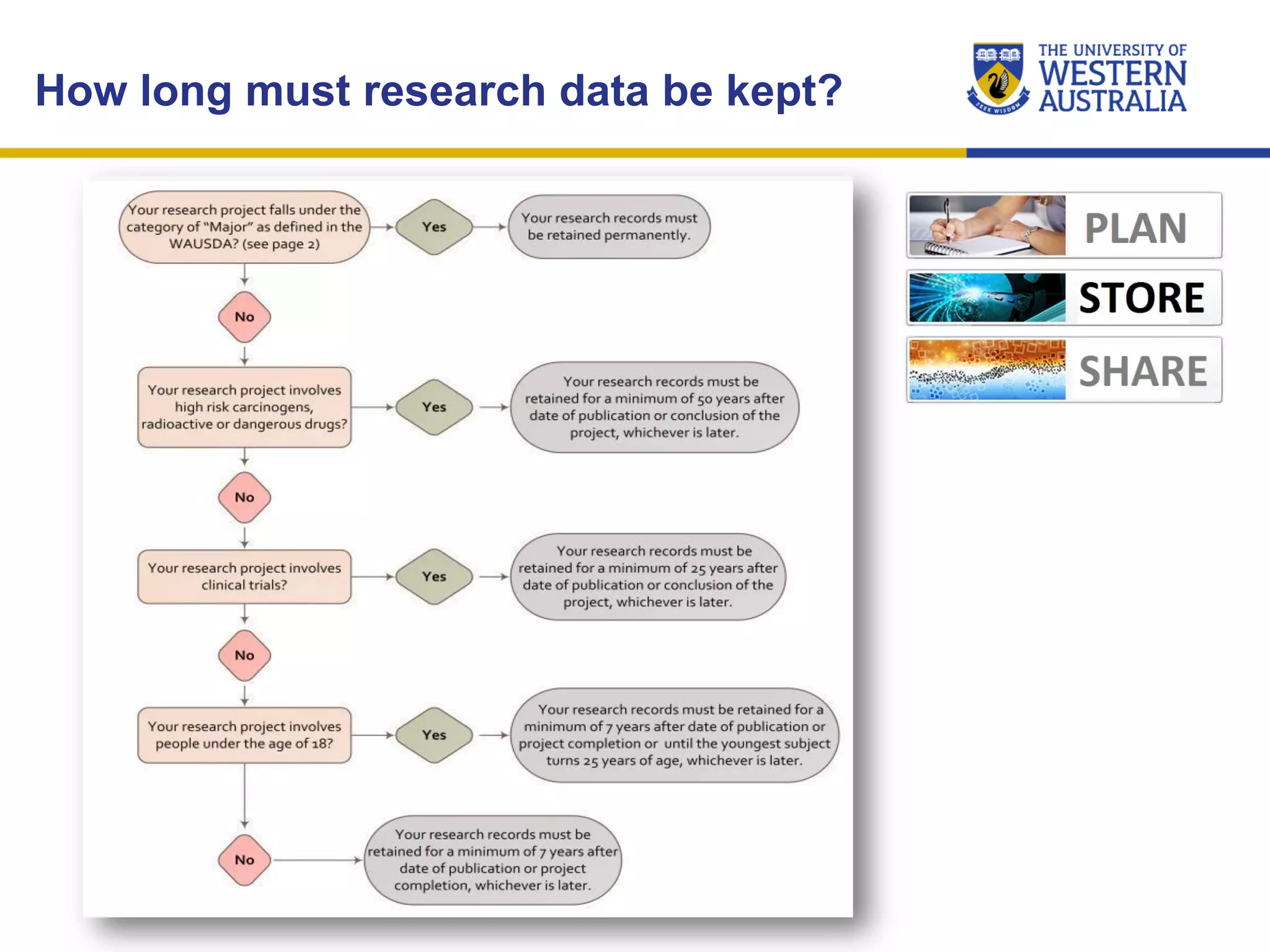
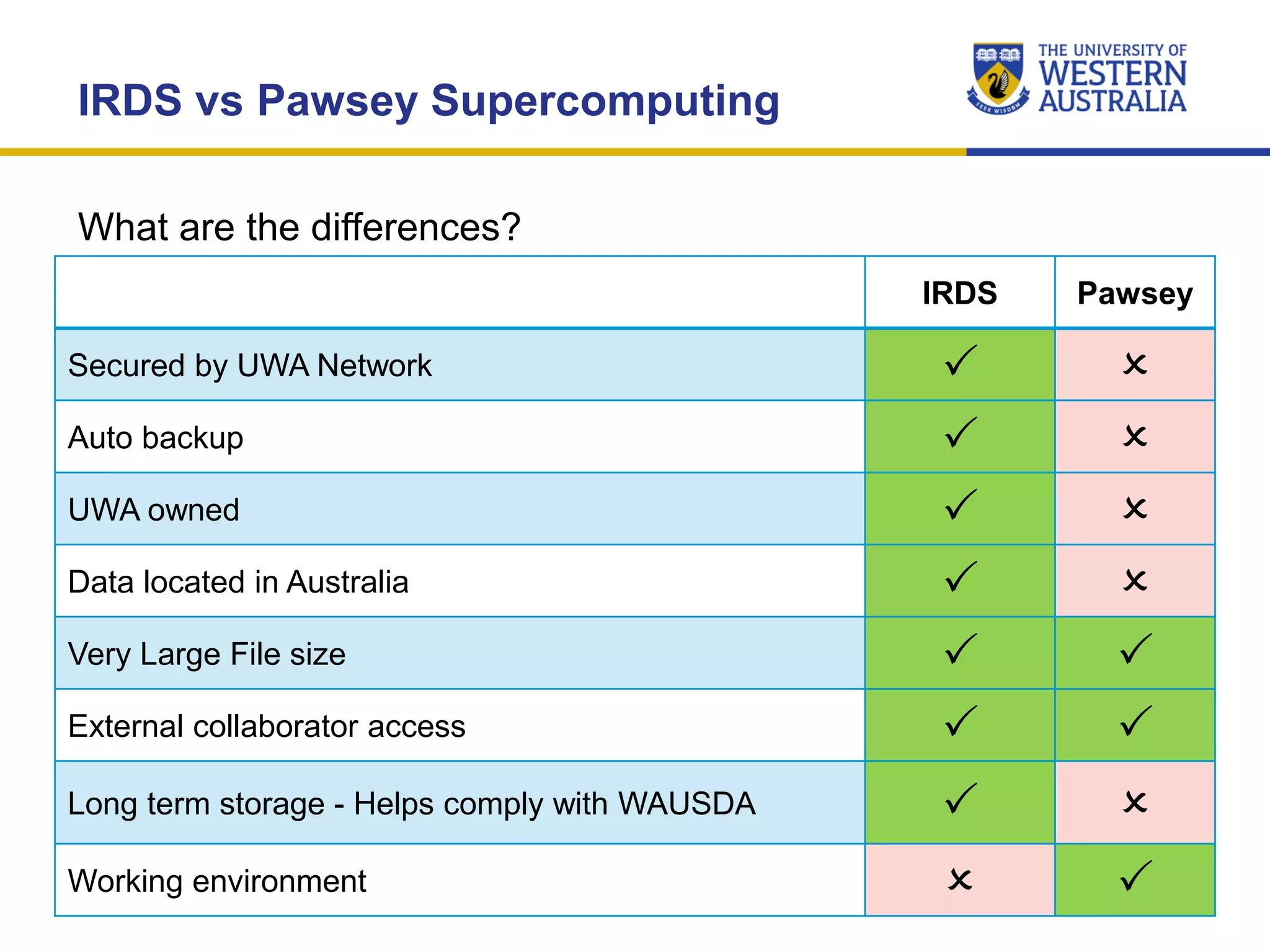
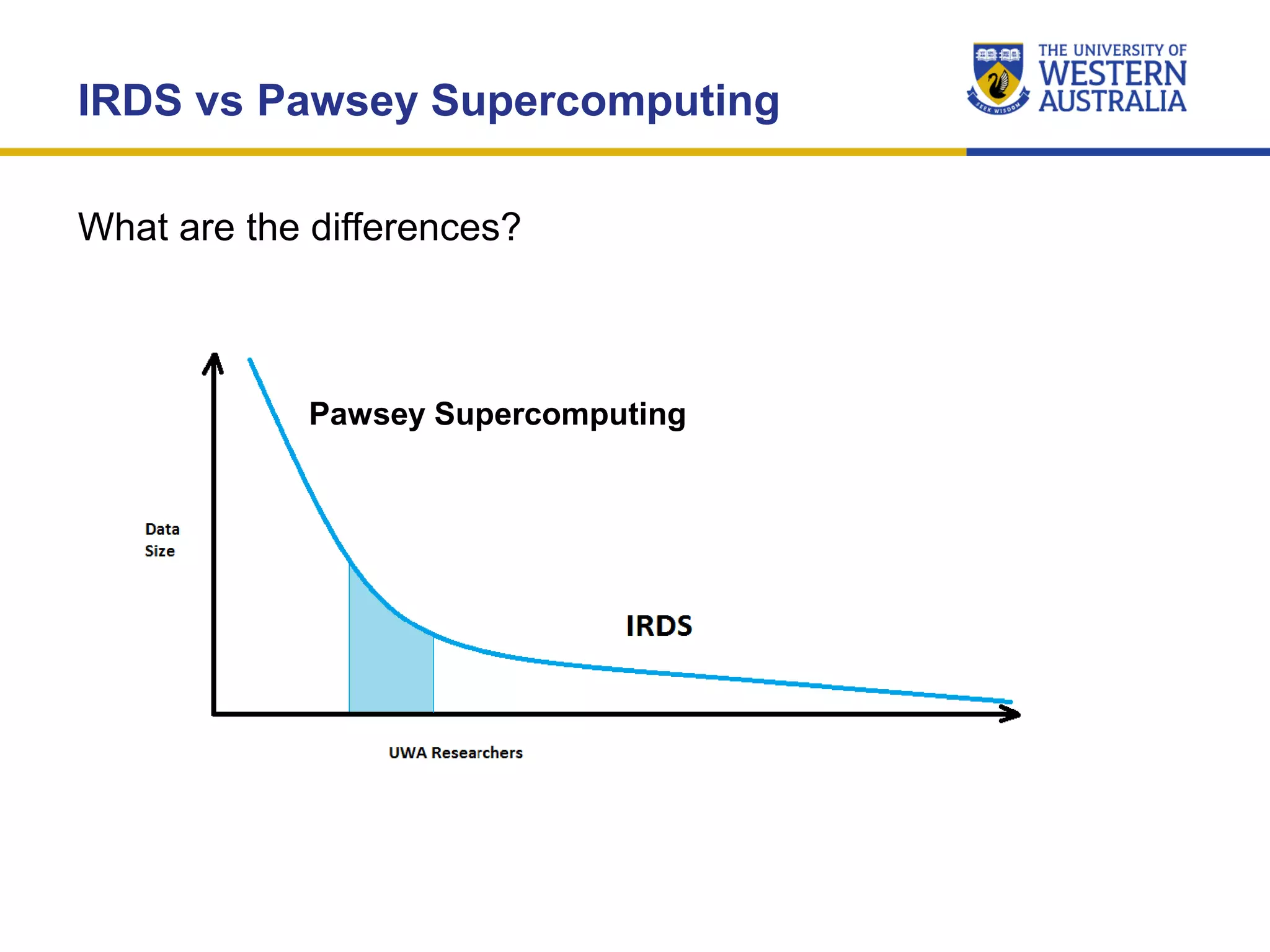
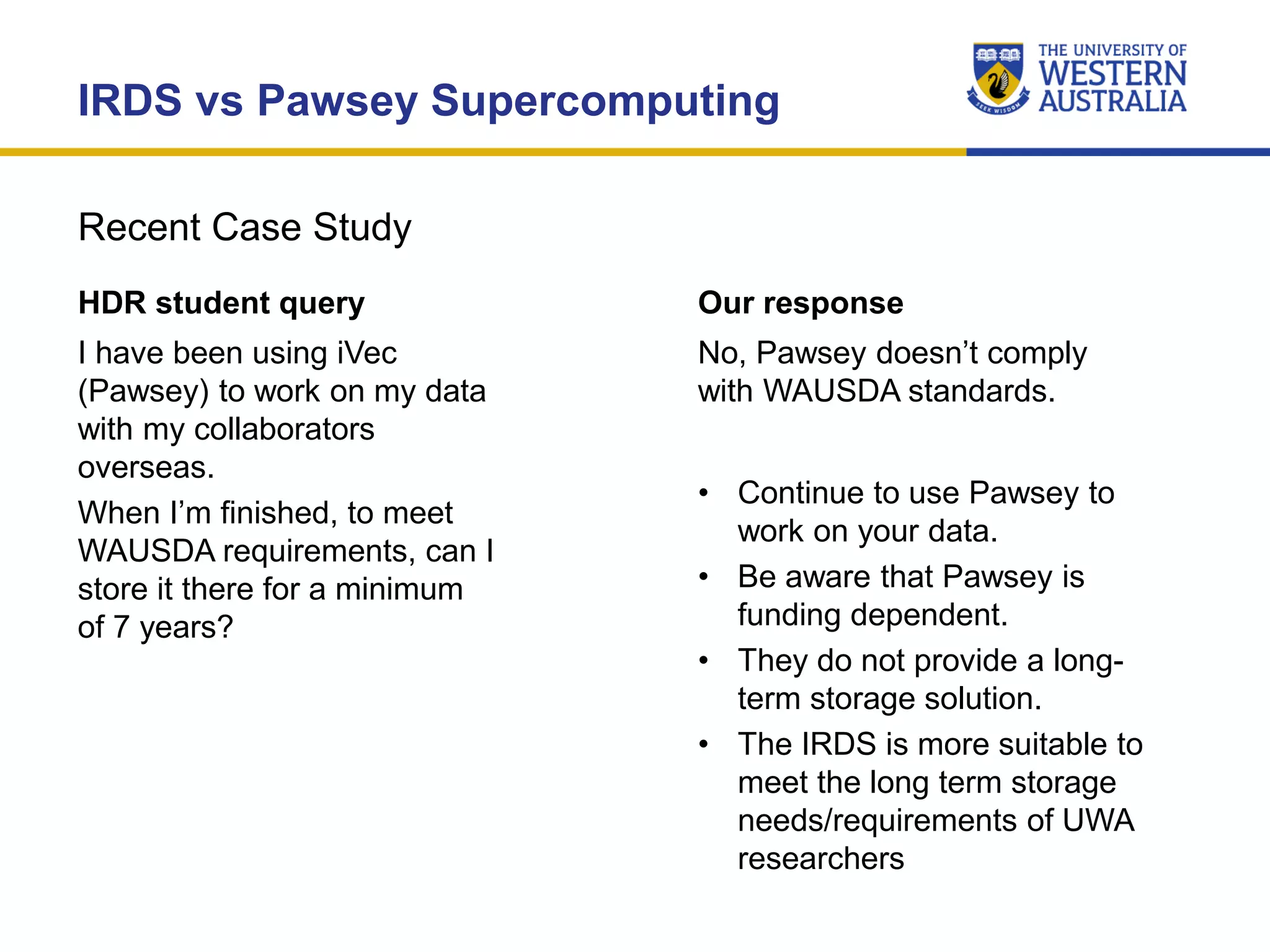
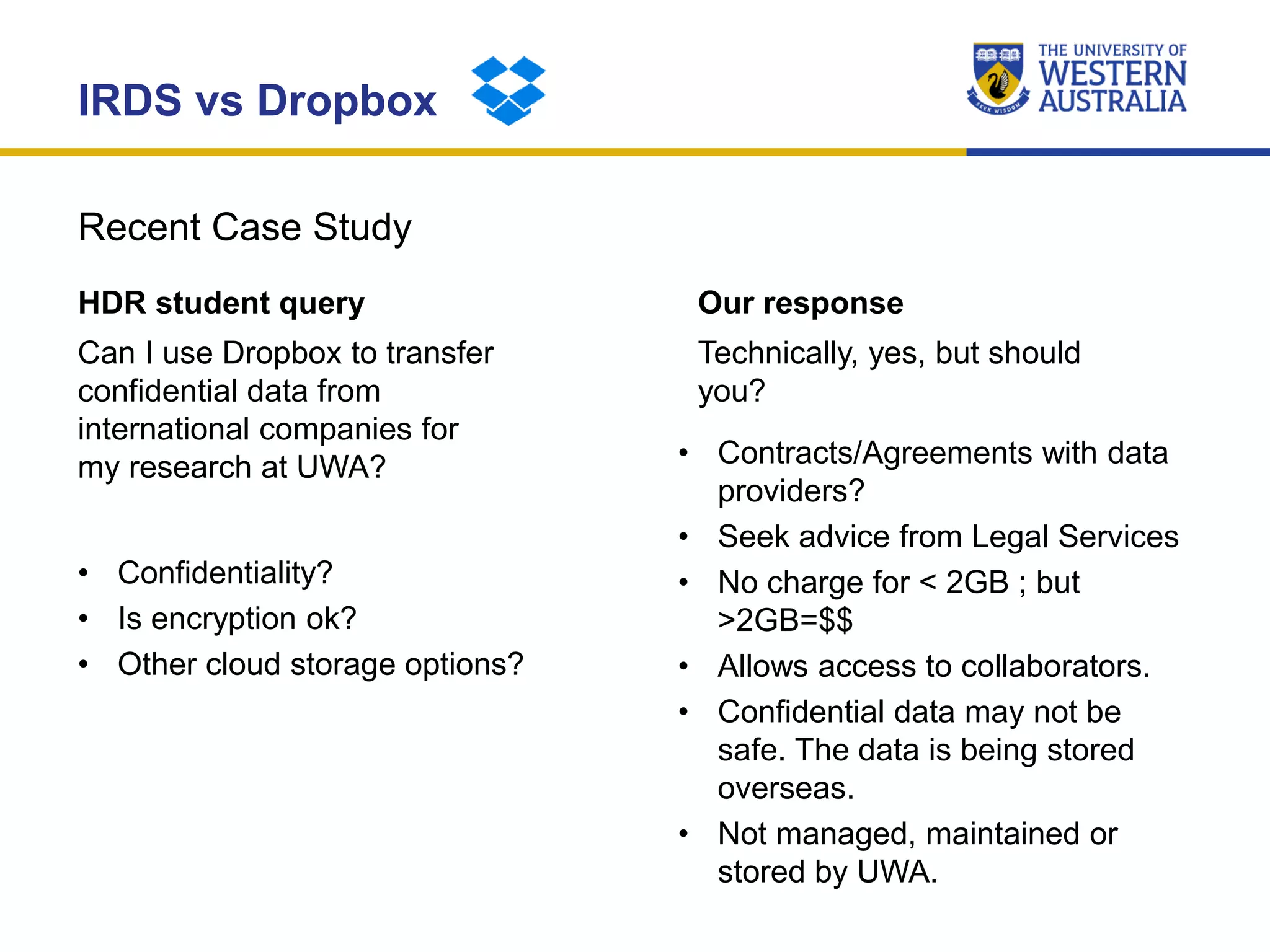
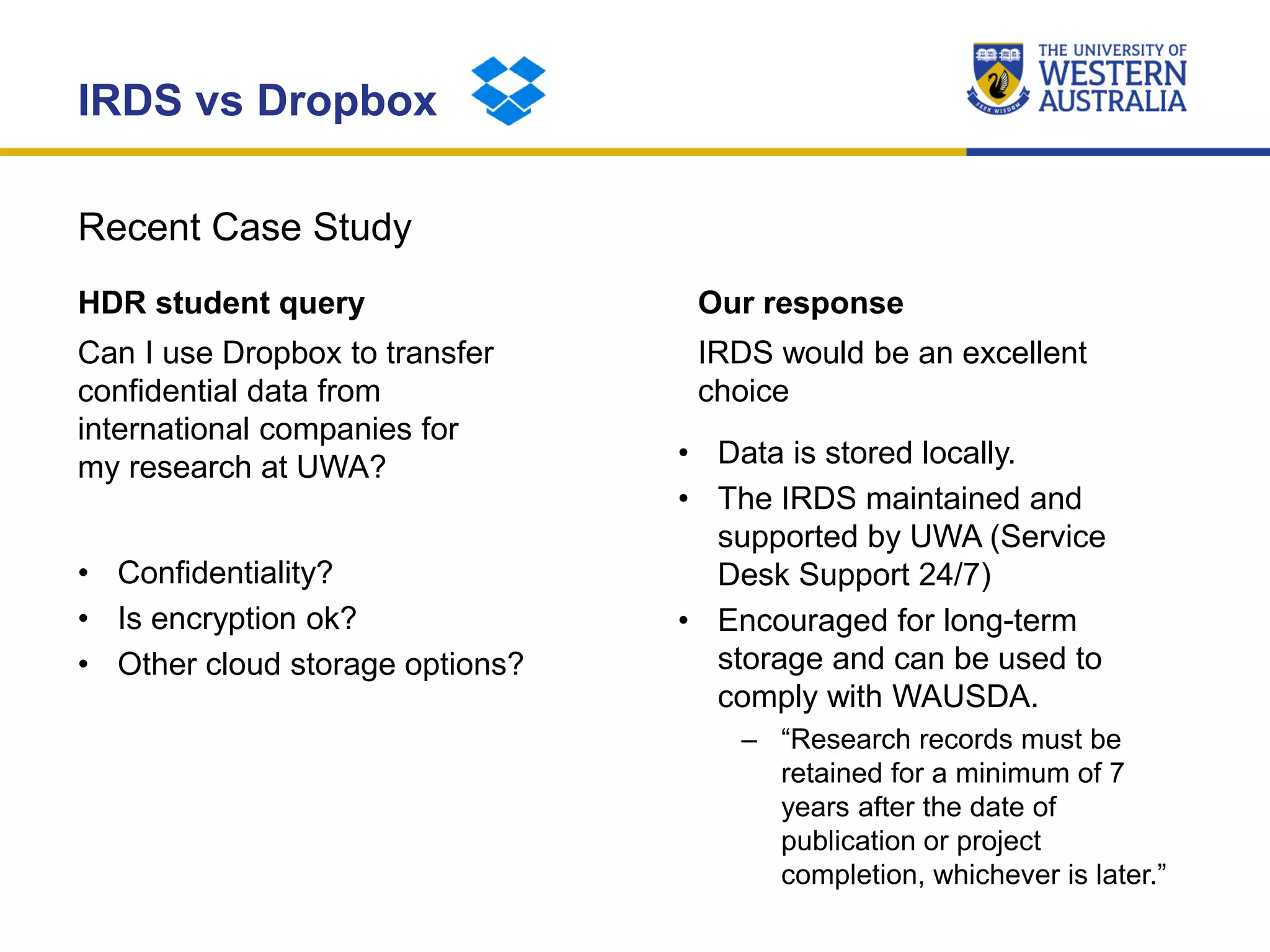
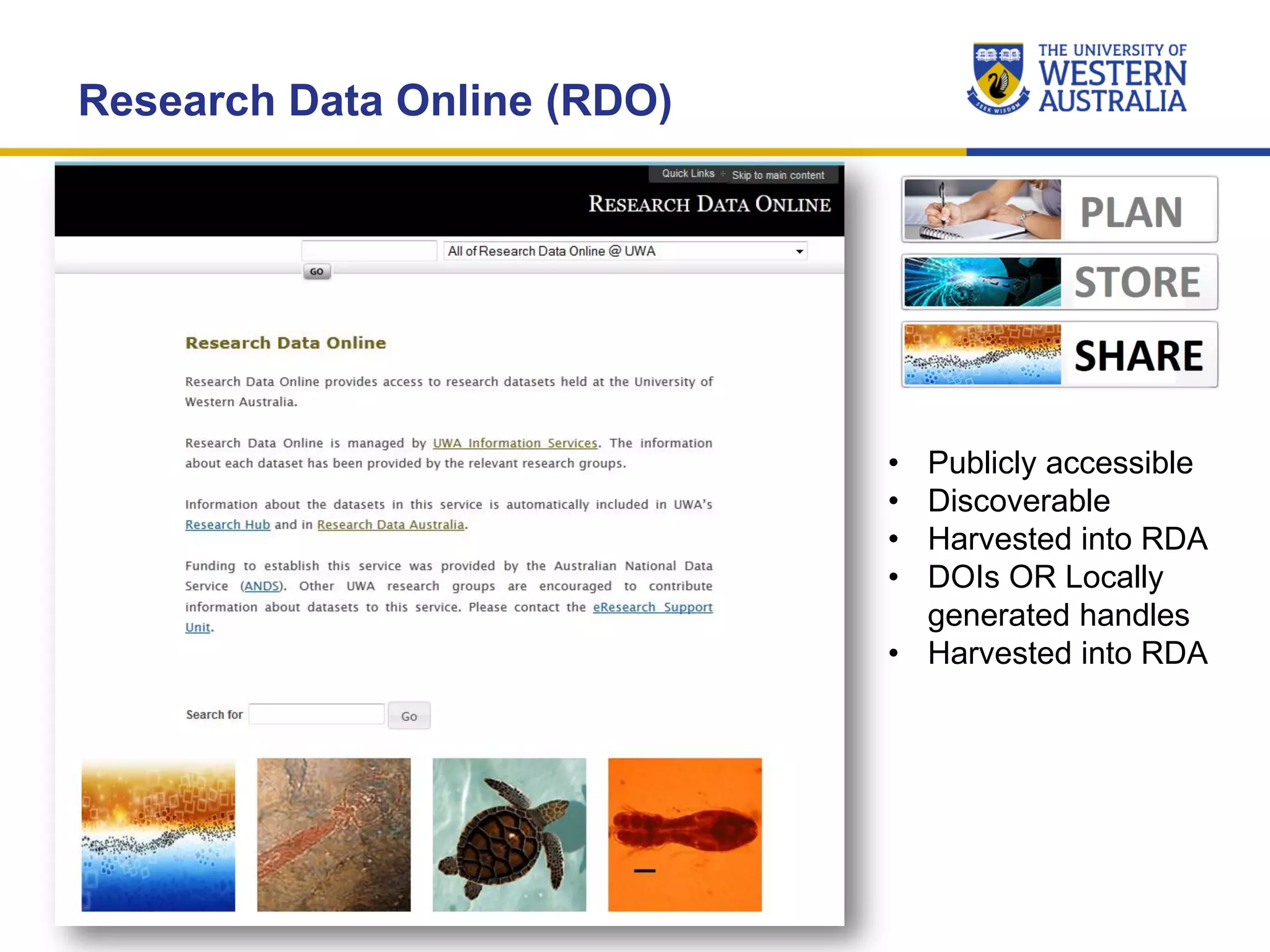
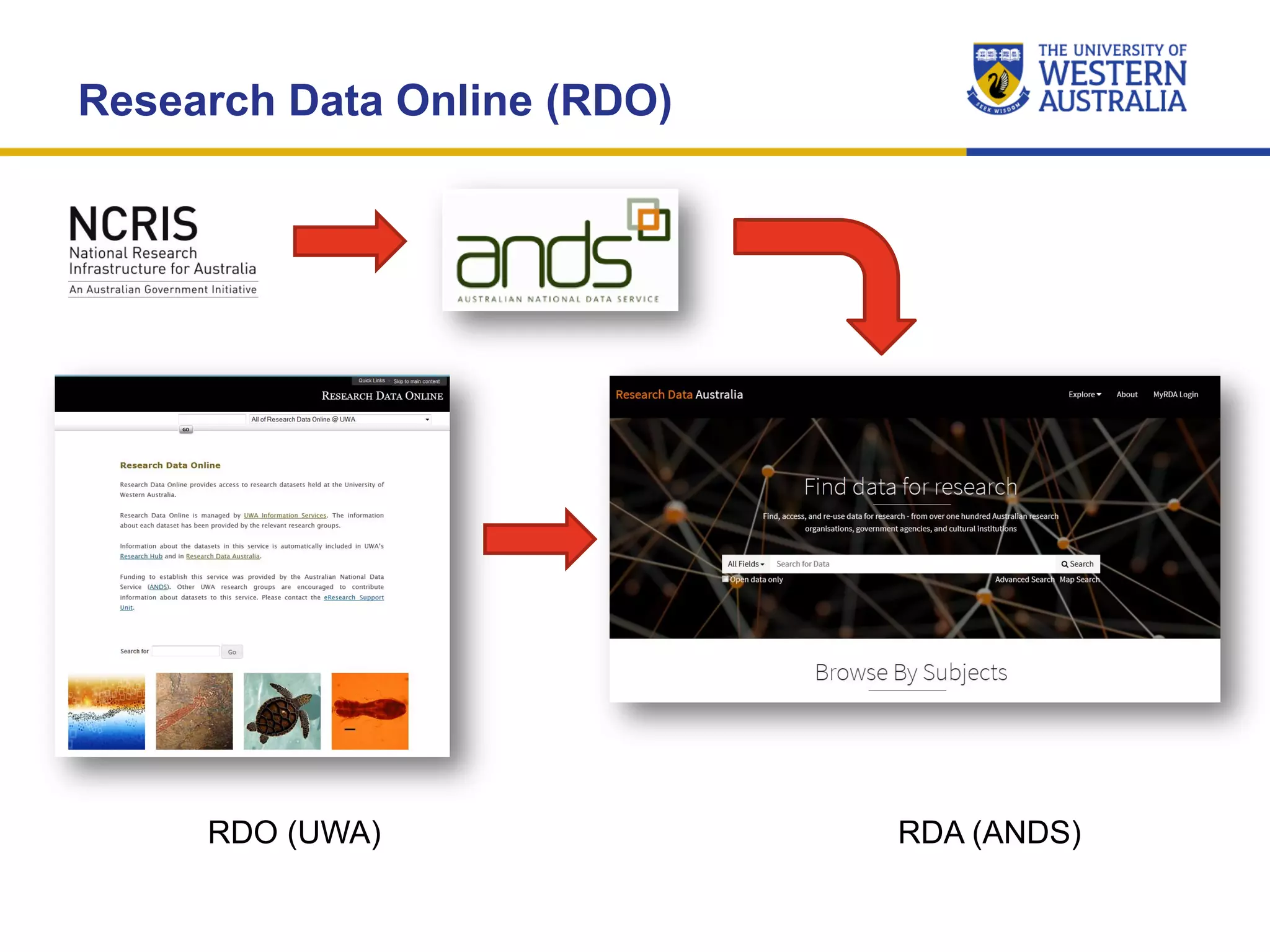
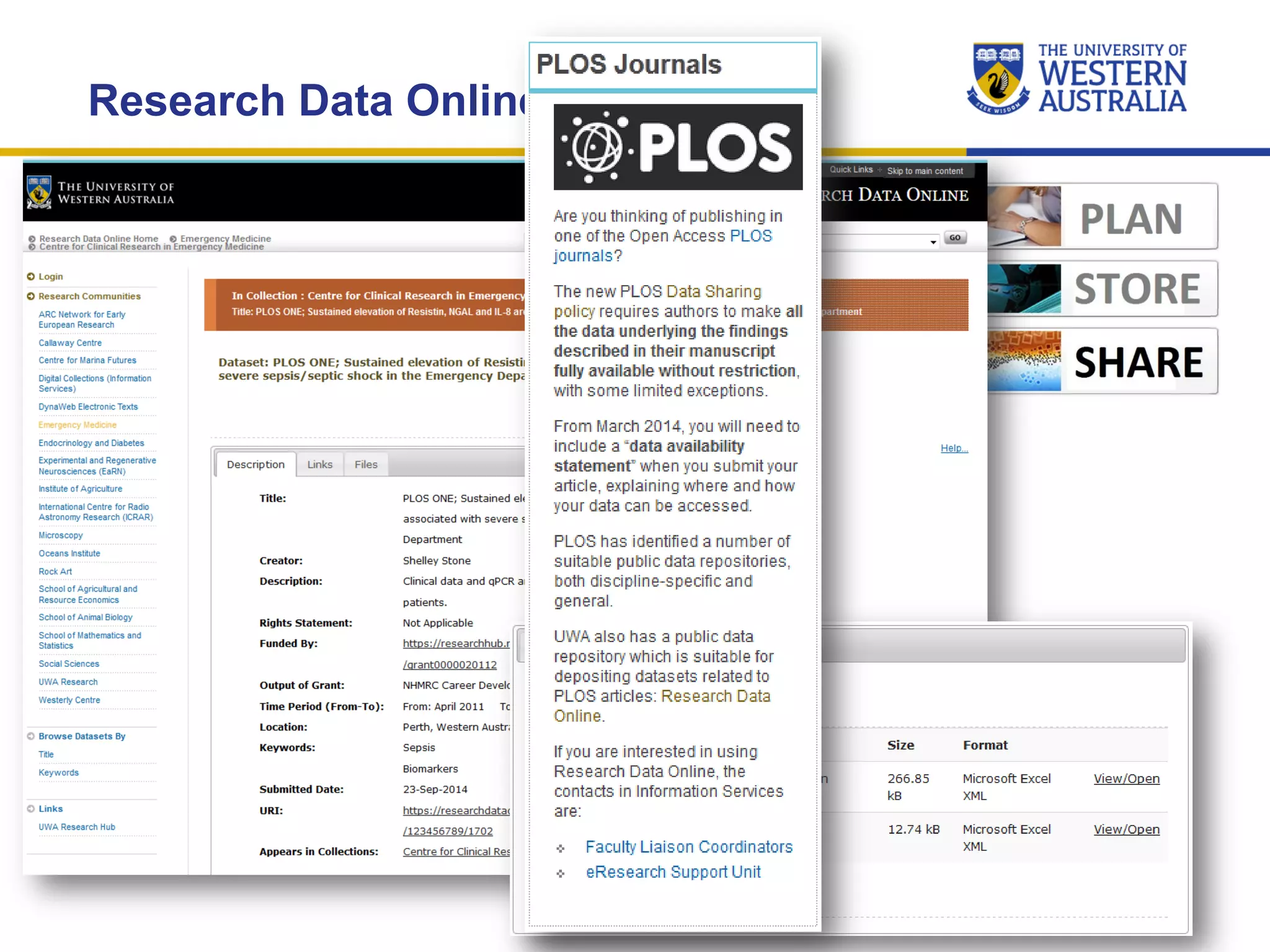
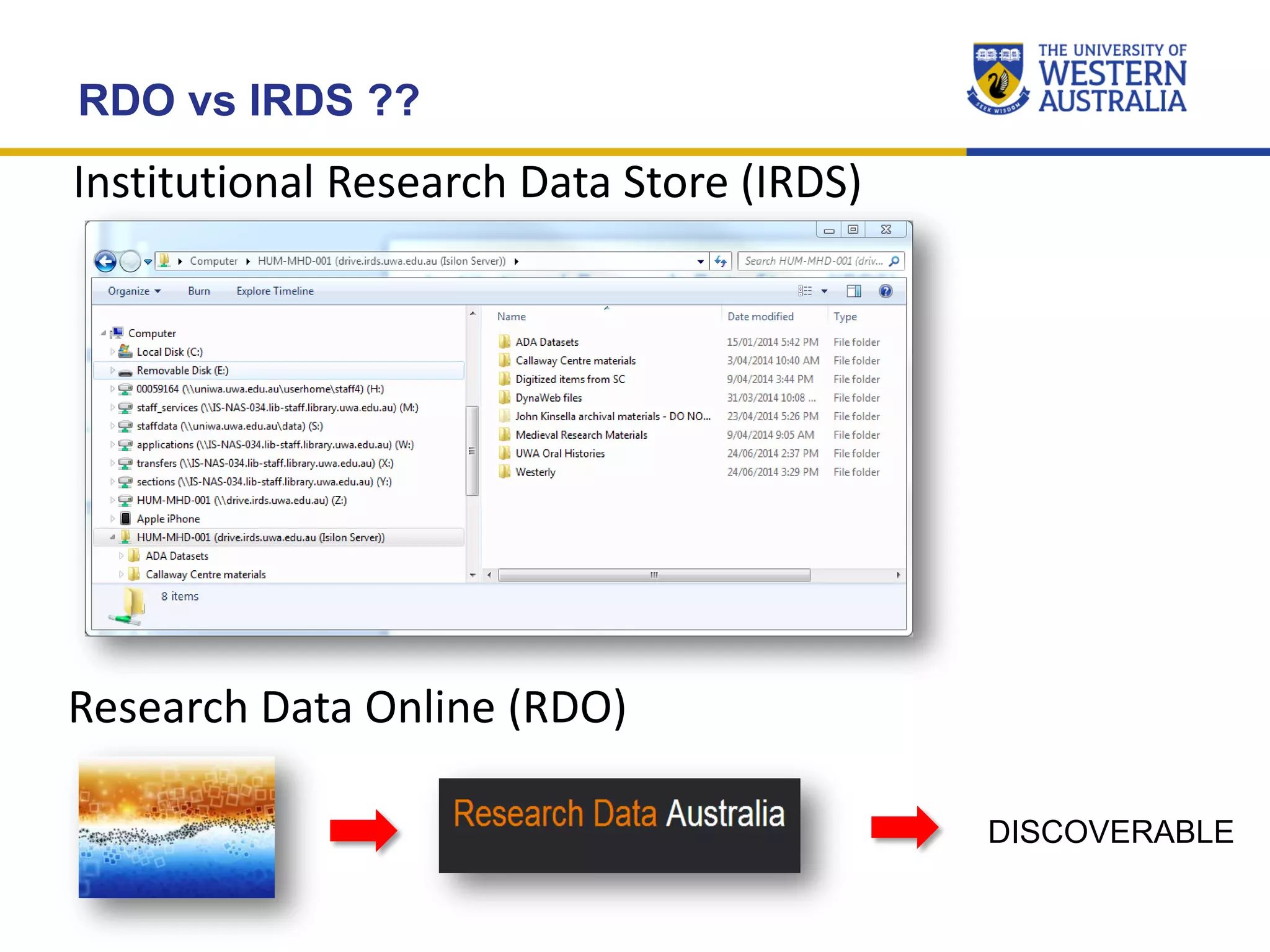
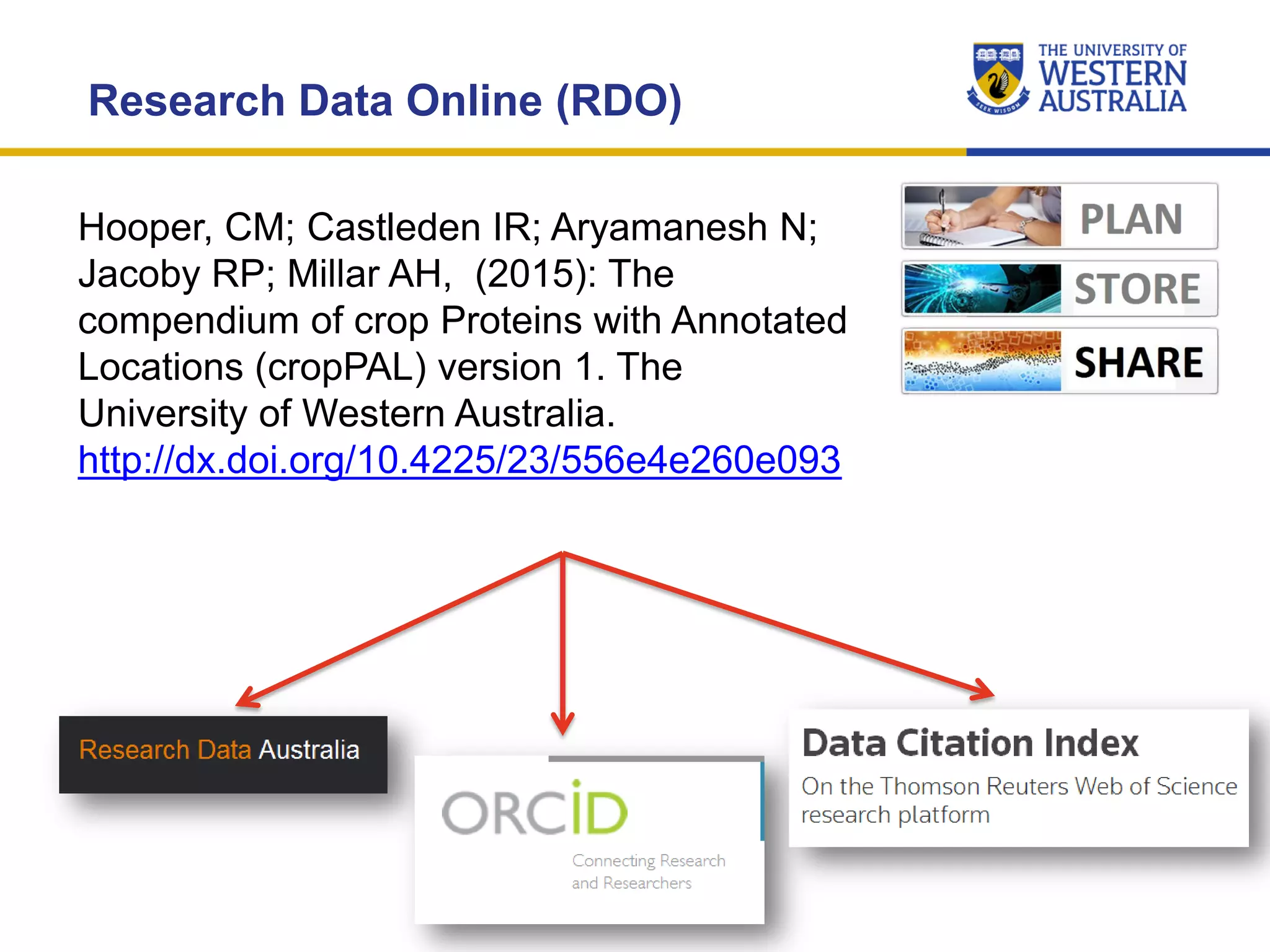
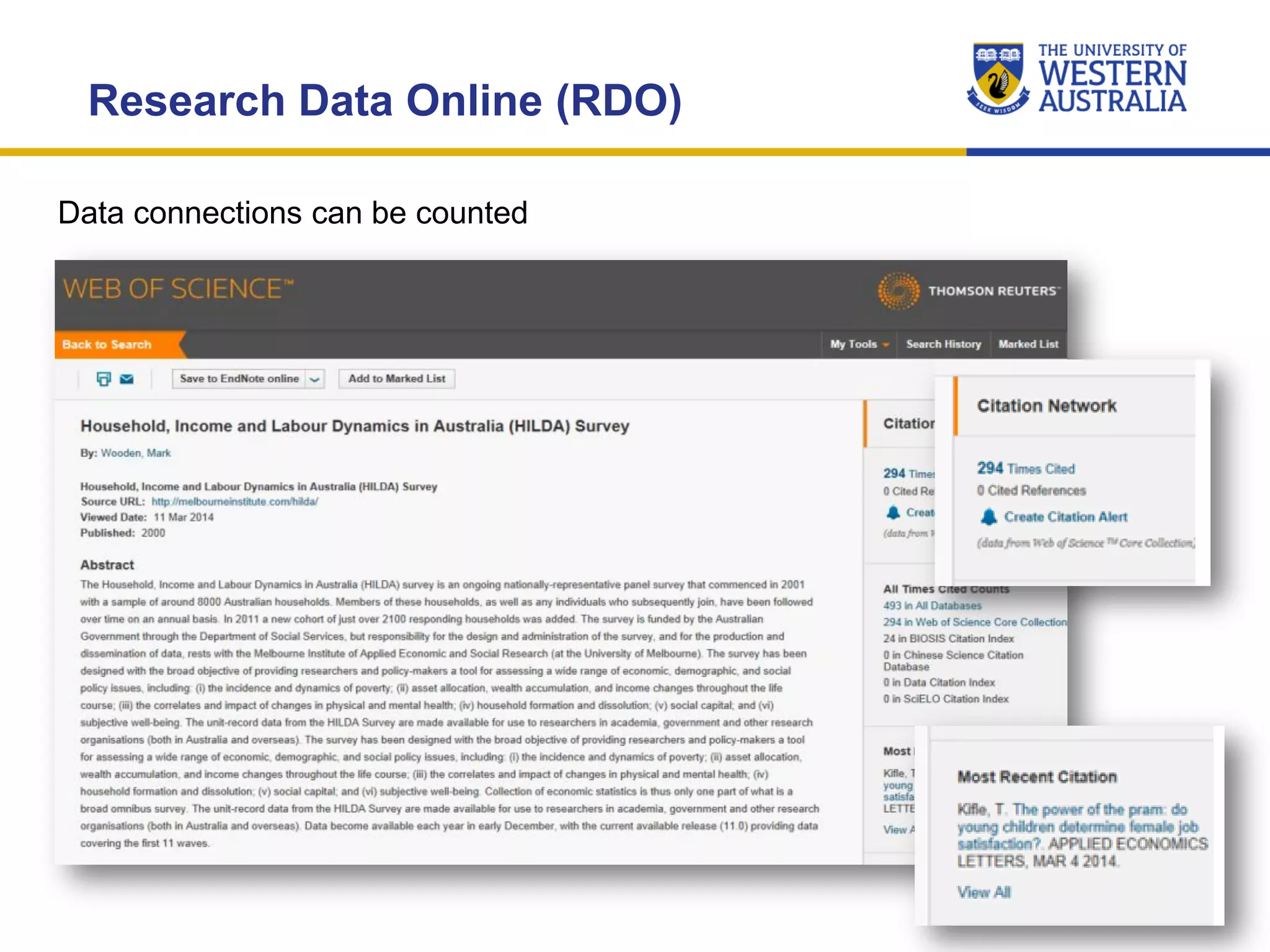
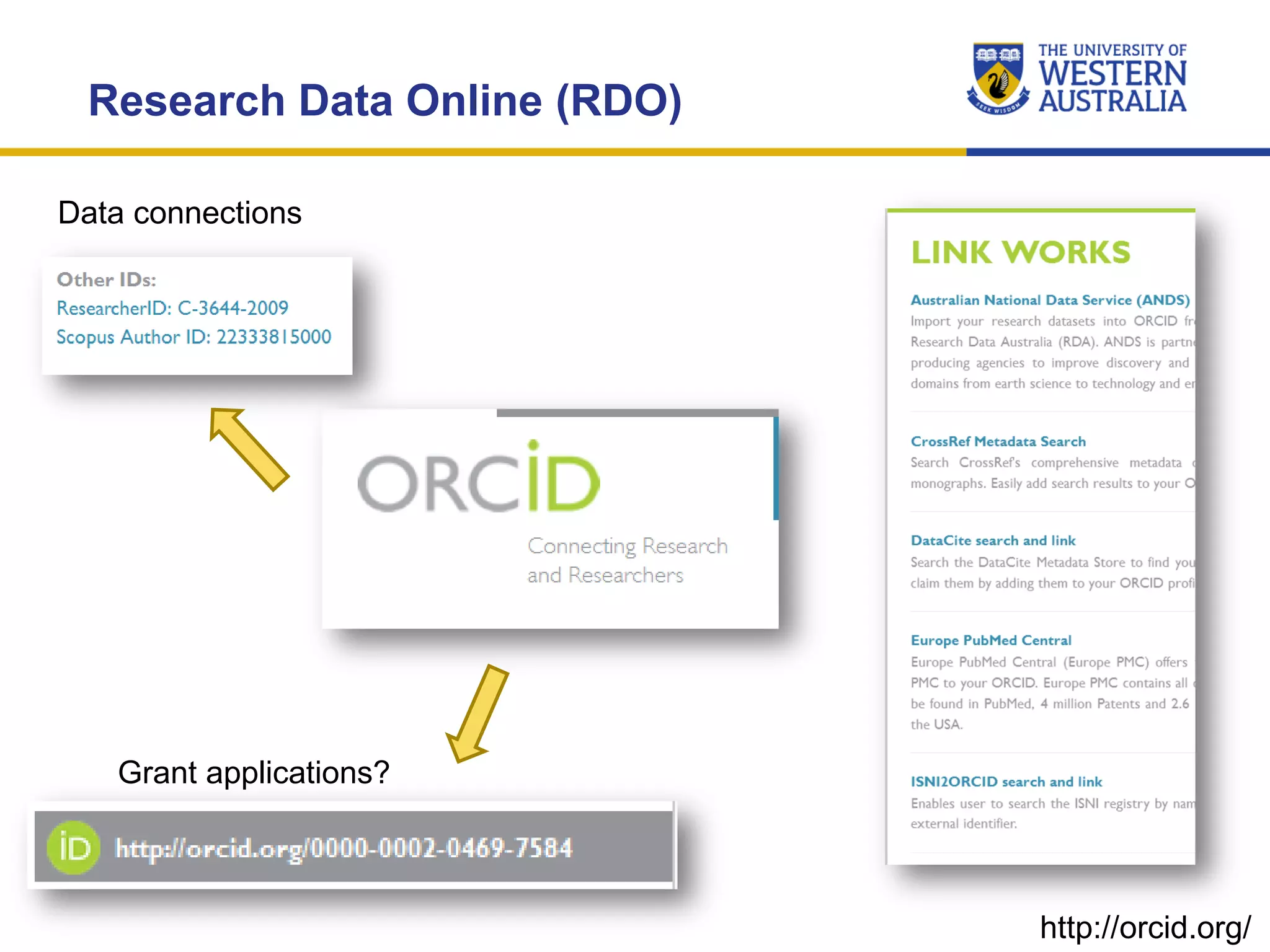
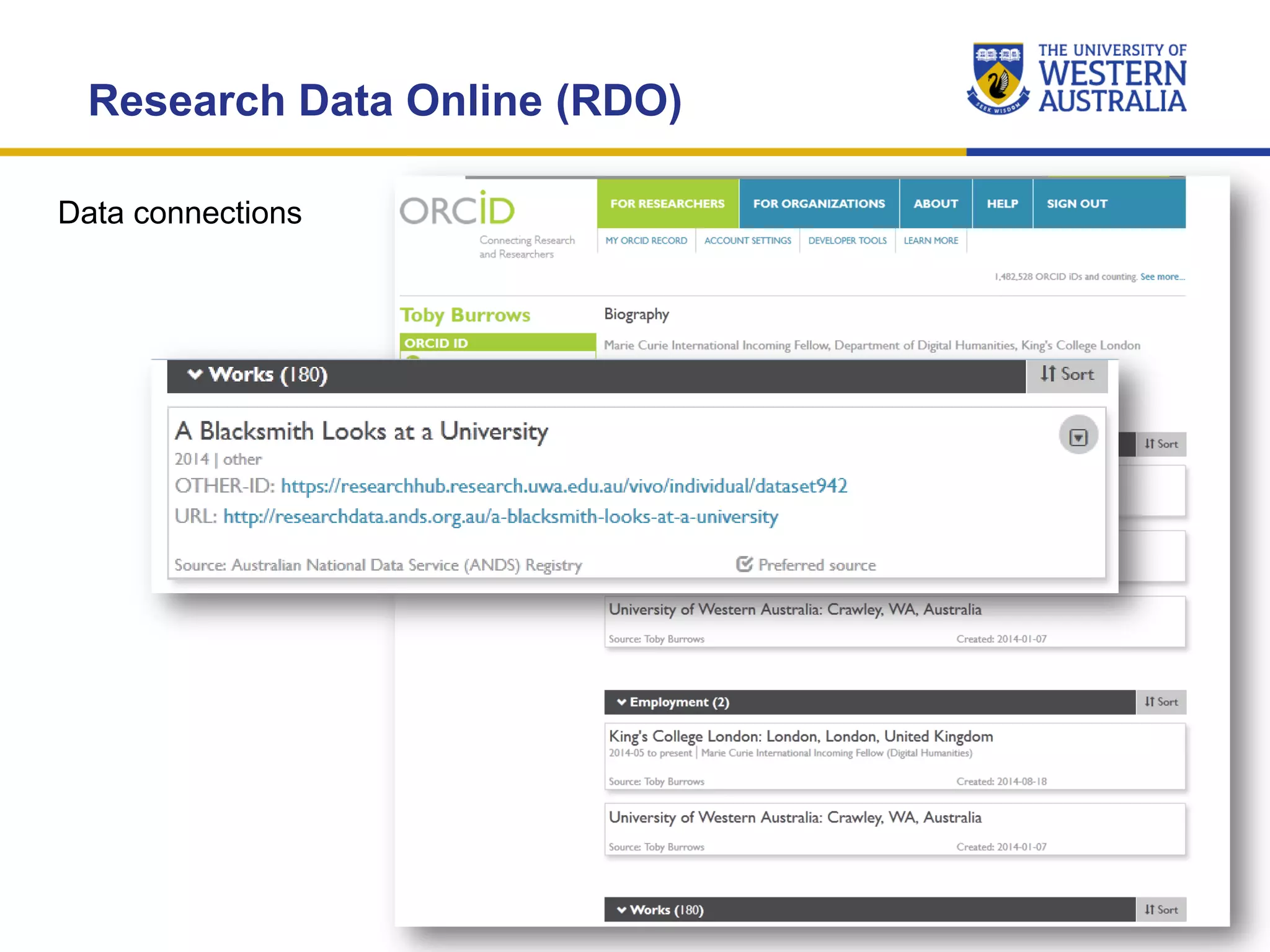
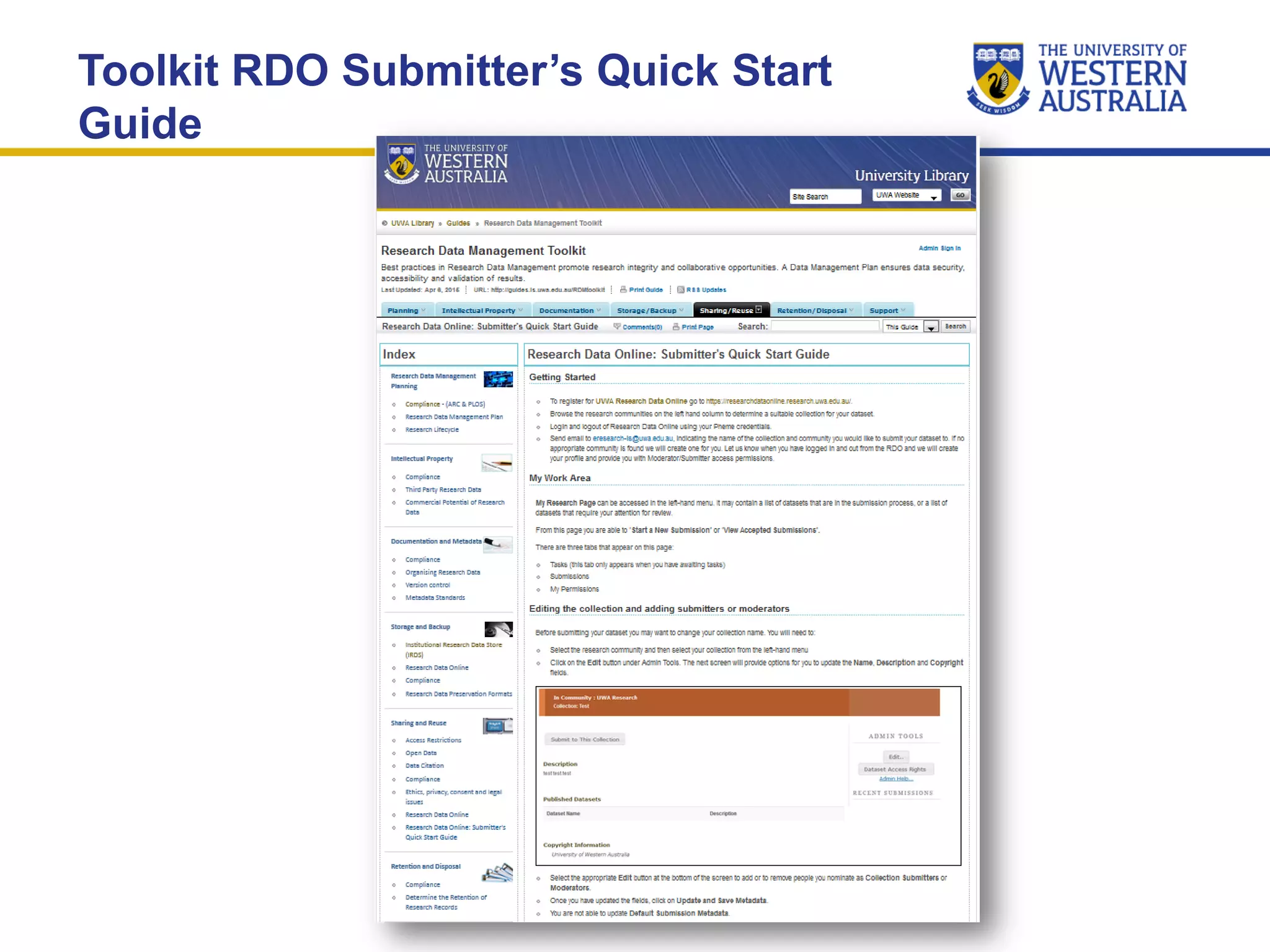
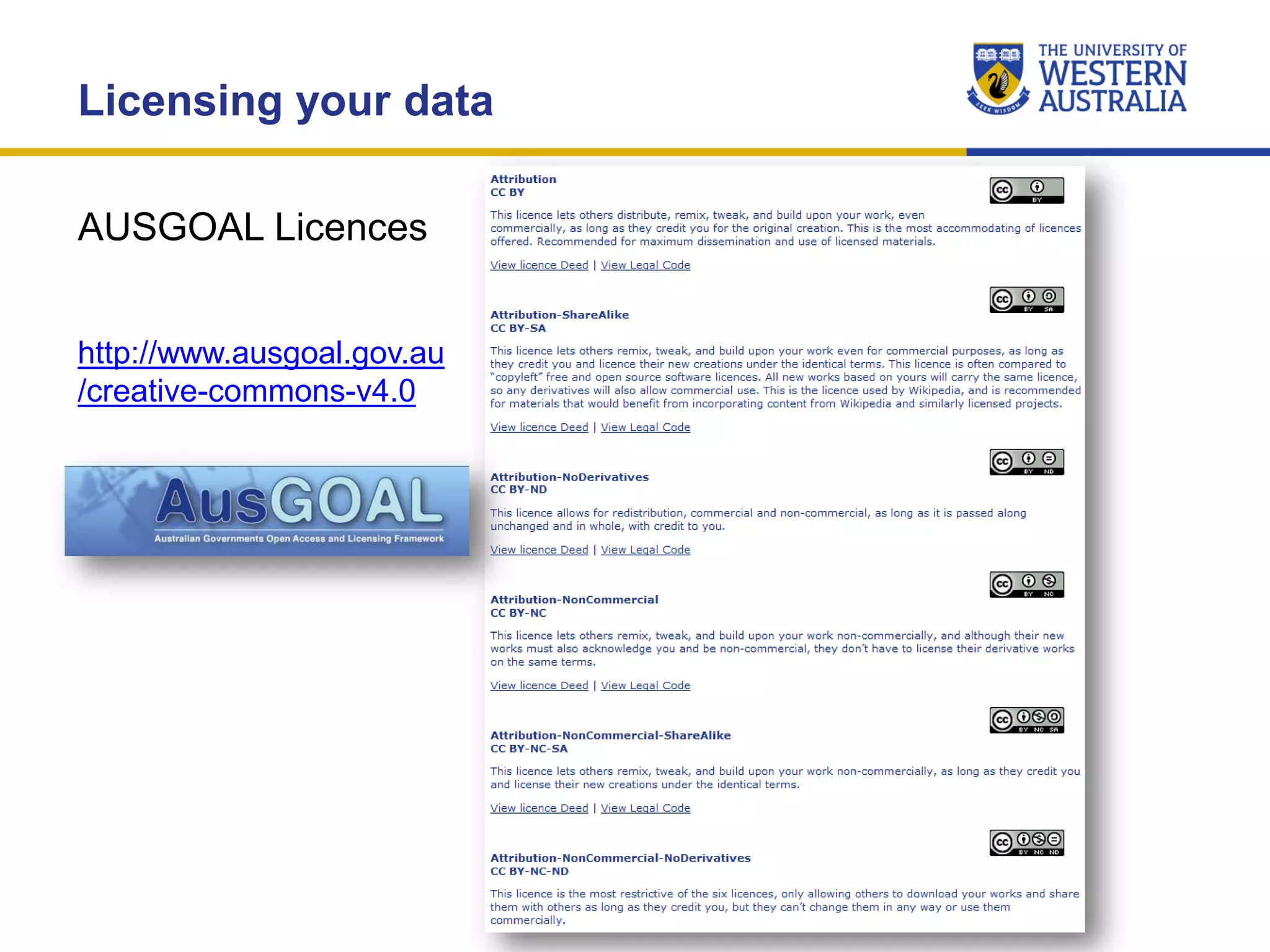
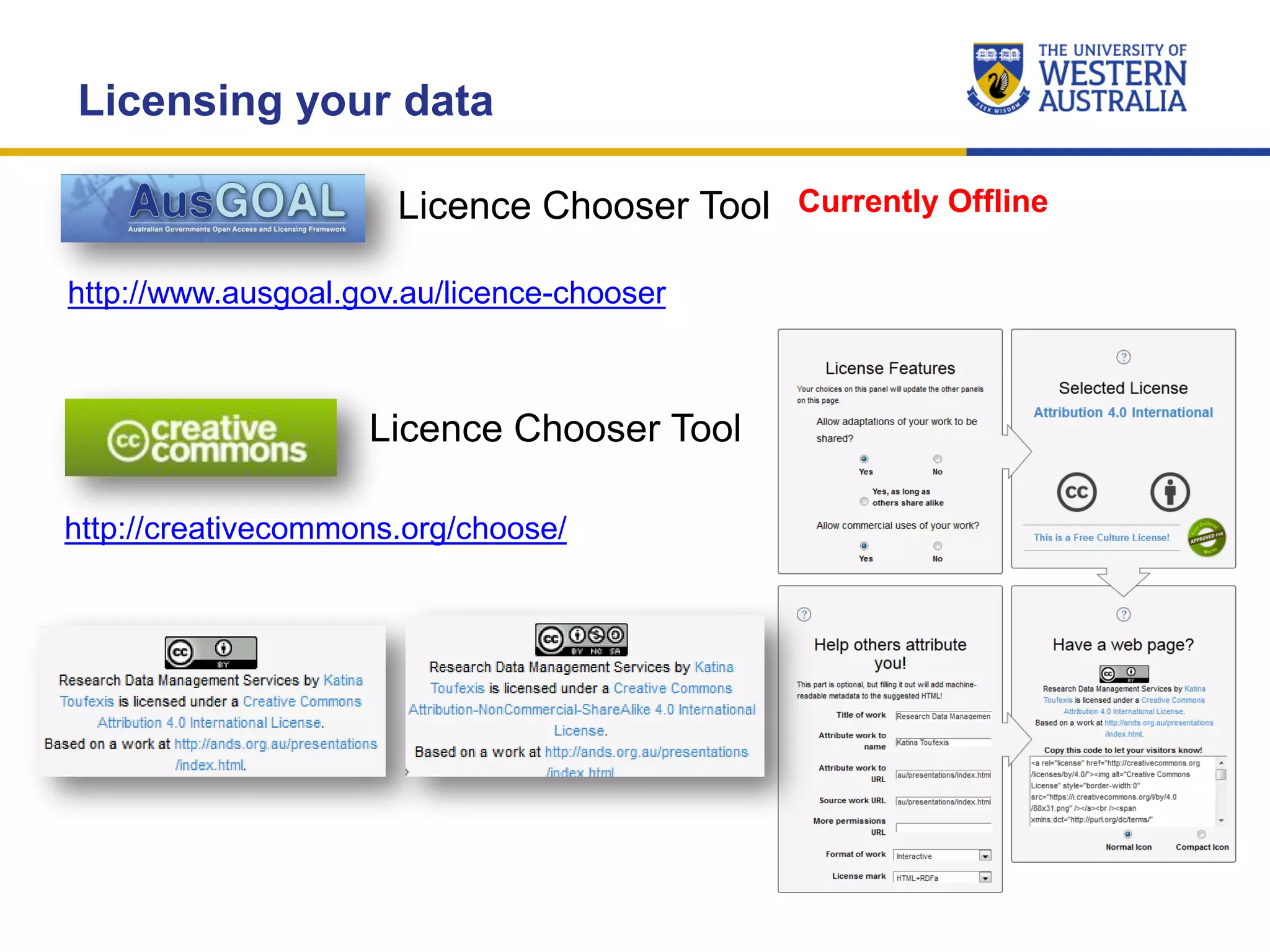
The document outlines the importance of research data management at the University of Western Australia (UWA), detailing its services, guidelines, and tools for managing research data effectively. Key topics include compliance, data sharing benefits, and retention policies, emphasizing the role of various stakeholders like governments and funders in promoting responsible research data practices. Additionally, it discusses the resources available at UWA, such as the Institutional Research Data Store (IRDS) and online data management tools, to support researchers in managing their data securely and efficiently.