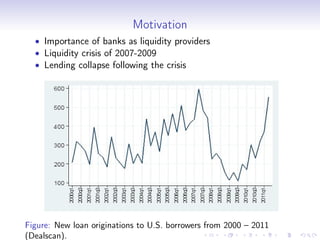
1. The author examines how shocks to bank health during the 2007-2009 financial crisis affected bank lending and economic activity in the U.S. using loan-level data.
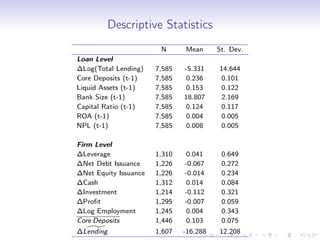
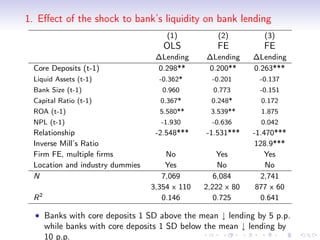
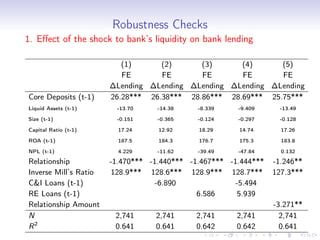
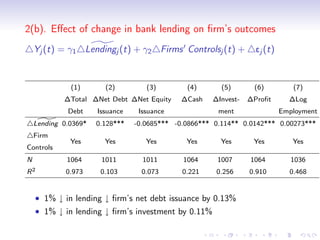
2. The results show that banks with higher levels of core deposits, a stable source of funding, reduced lending by less than banks with lower core deposit levels after the crisis, indicating that liquidity shocks to banks negatively impacted bank lending.
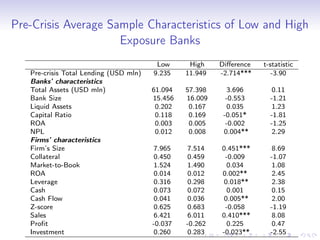
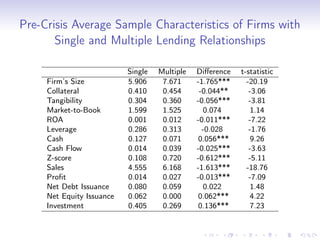
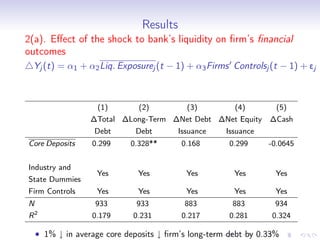
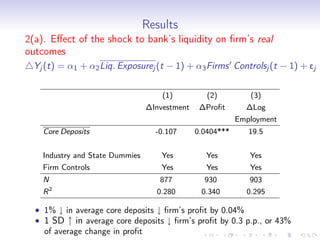
3. Further analysis finds that shocks to bank liquidity and reductions in bank lending were both associated with worse financial and economic outcomes for borrower firms, such as higher leverage, less investment, and lower profits, providing evidence that liquidity problems in the banking sector can transmit stress to the




![Methodology
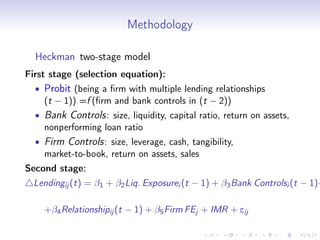
1. Does shock to bank health affect bank lending?
[based on Gan, 2007; Khwaja and Mian, 2008]
Lendingij (t) = β1 + β2 Liq. Exposurei (t − 1) + β3 Bank Controlsi (t − 1)+
+β4 Relationshipij (t − 1) + β5 Firm FEj + eij
Pre-crisis period (t − 1): 2005 q3 - 2007 q2
Post-crisis period (t): 2009 q3 - 2011 q2
• Lendingij : change in log of total credit provided by bank i to firm
j between the post-crisis and the pre-crisis periods
• Liquidity Exposurei : is the share of core deposits to banks’ total
assets measured in the pre-crisis period
• Bank Controlsi : bank size, liquid assets, equity to assets ratio,
non-performing loan ratio, return on assets
• Relationshipij : is the number of years when firm j had a positive
loan amount from bank i in past 10 years (1995-2004)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paper1presentationv-4-130305053235-phpapp02/85/Tamara-Presentation-7-320.jpg)
![Methodology
2a. Does shock to bank health affect the real economy?
[based on Gan, 2007; Khwaja and Mian, 2008]
Yj (t) = α1 + α2 Liq. Exposurej (t − 1) + α3 Firms Controlsj (t − 1) + ej
• Yj (t): change in firms’ financial and performance measures
between two periods
• Yj : leverage, net debt and equity issuance, cash holdings,
investment rate, profit and employment
• Liquidity Exposurej : is, for each firm j, the weighted average level of
exposure of the banks that are lending to the firm in the pre-crisis
period; bank liquidity exposure is measured by a share of core
deposits to bank’s total assets
• Firms Controlsj : industry and state dummies, firm size, collateral,
interest coverage, market-to-book ratio, return on assets, cash
holdings, cash flow, leverage, sales, net worth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paper1presentationv-4-130305053235-phpapp02/85/Tamara-Presentation-9-320.jpg)