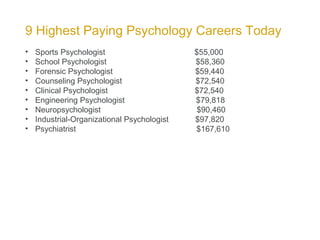
Psychologists evaluate and study behavior and mental processes, requiring a minimum of a master's degree. There are many types of psychologists depending on their area of specialization, such as educational, environmental, or forensic psychologists. Practicing psychologists receive professional training and clinical skills to help people solve life issues and mental health problems using various therapeutic techniques tailored to individual client needs and circumstances. They are trained through doctoral programs involving coursework, internships, supervised practice, and examinations. Psychologists work in a variety of settings like healthcare facilities, schools, and private practices. Their job duties involve assessing clients, providing therapy, and assisting clients with problems like depression, addictions, or chronic illnesses. The median salary for psychologists in the US is