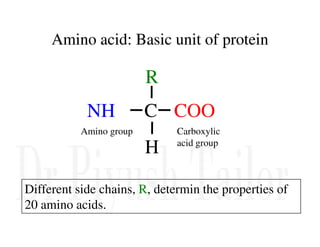
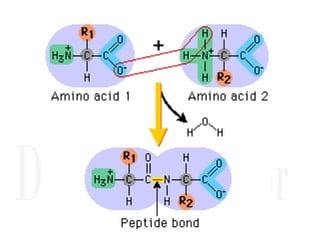
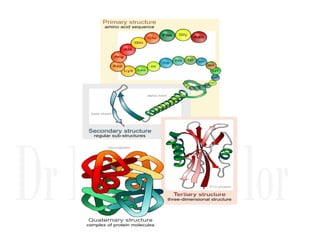
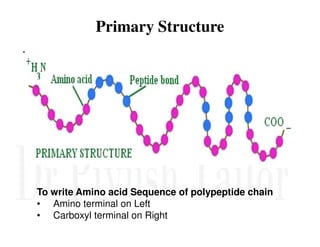
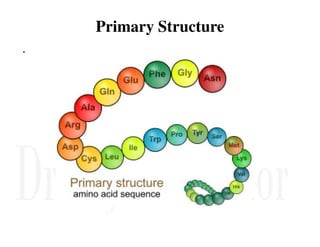
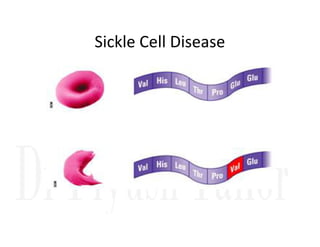
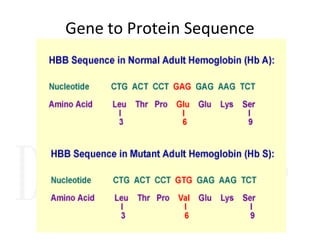
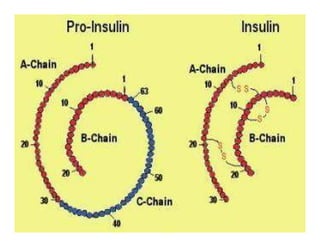
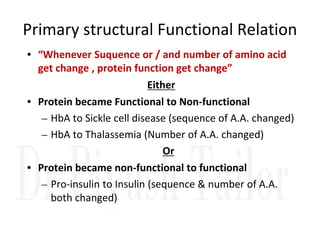
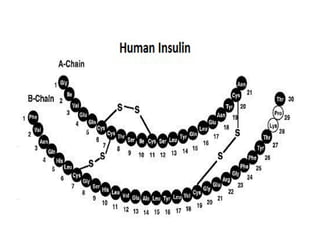
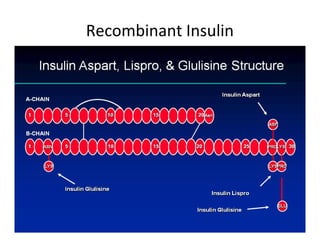
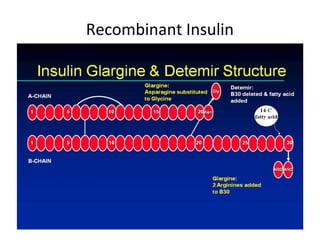
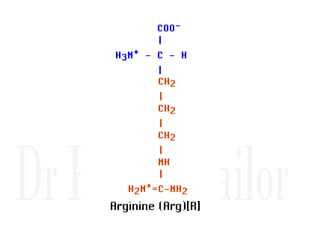
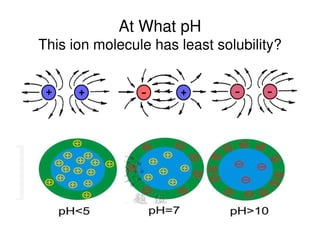
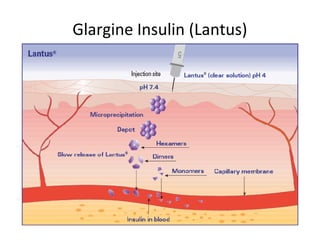
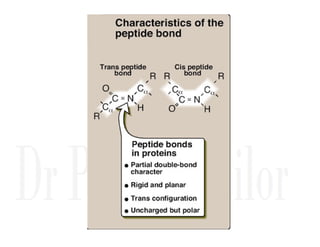
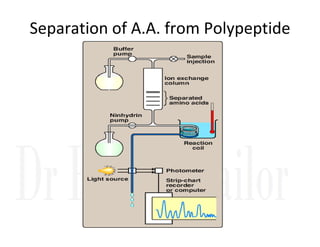
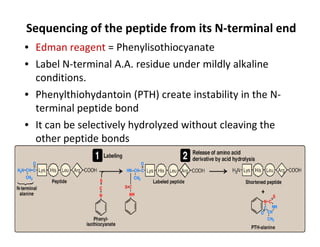
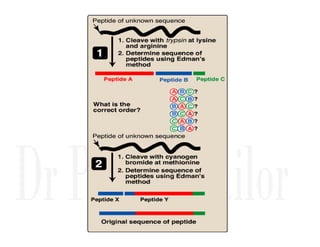
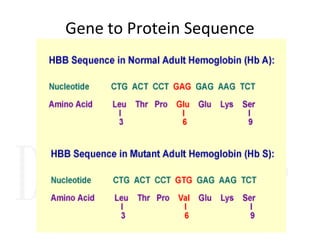
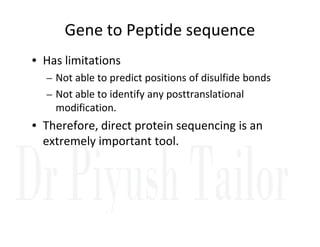
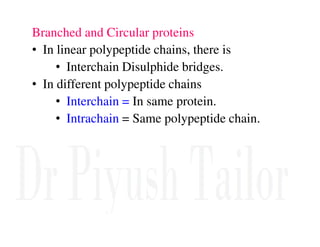
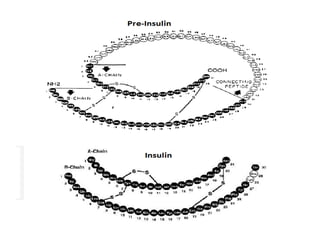
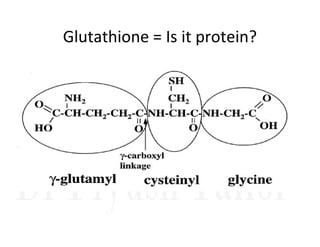
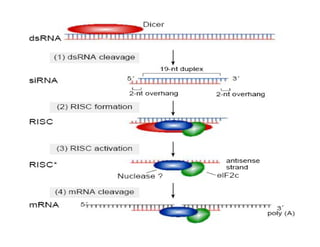
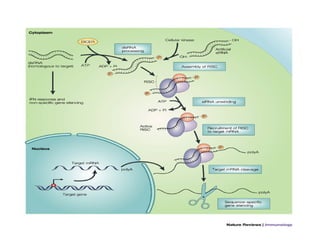
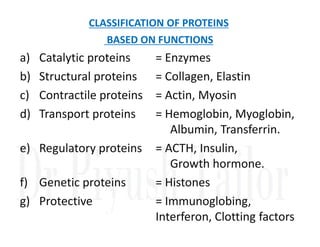
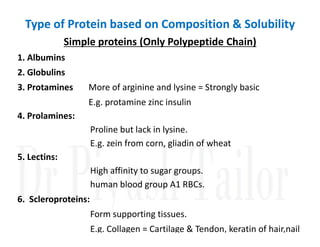
1. Proteins are polymers of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Changes to the primary structure, including the sequence or number of amino acids, can alter a protein's function.
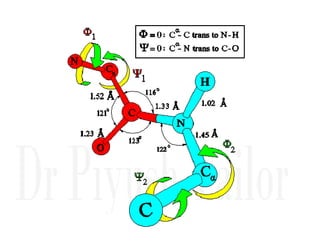
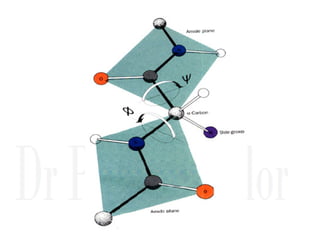
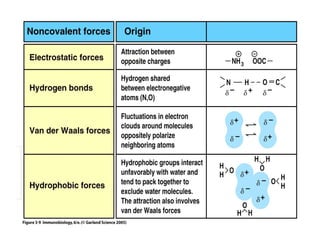
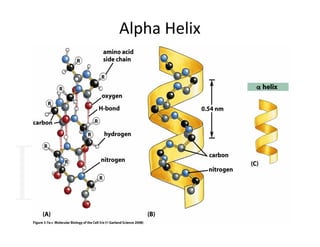
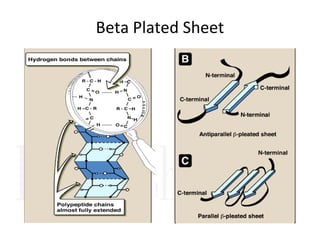
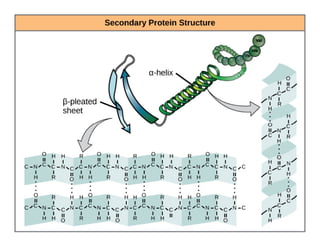
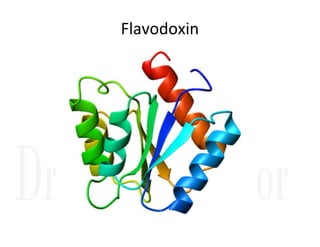
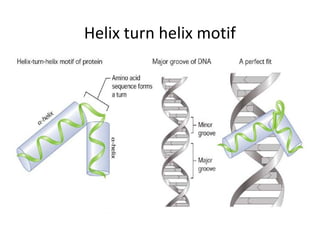
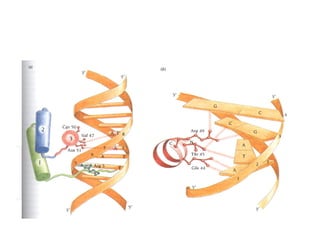
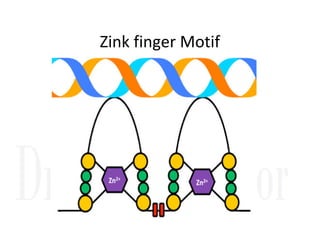
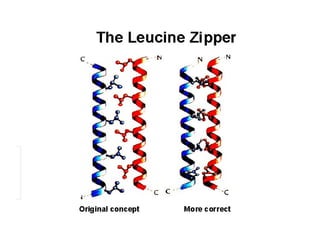
2. Secondary structure forms due to interactions between residues that are near each other in the primary structure. Common secondary structures include alpha helices and beta sheets.
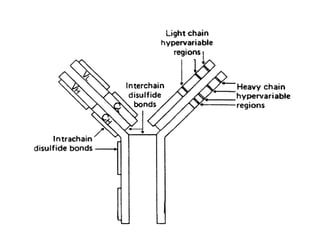
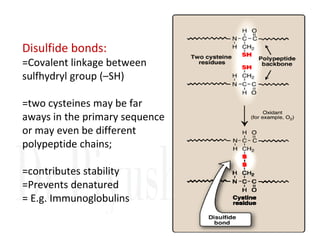
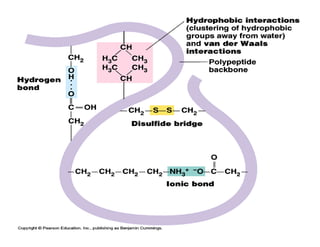
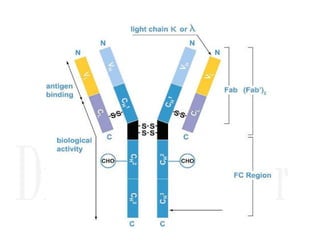
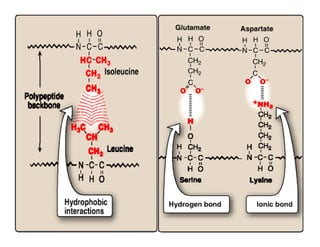
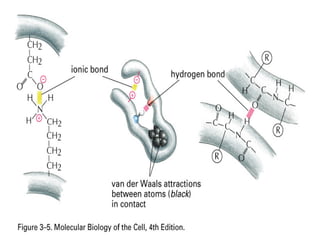
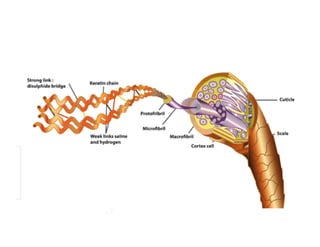
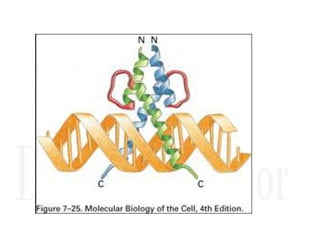
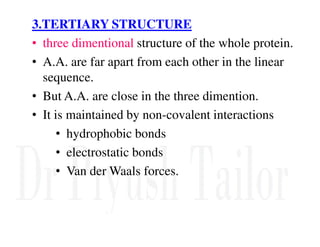
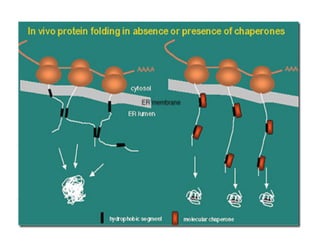
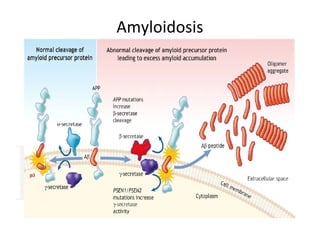
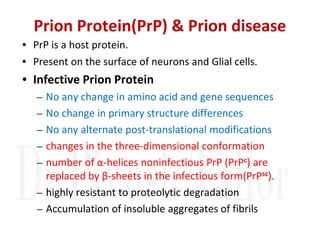
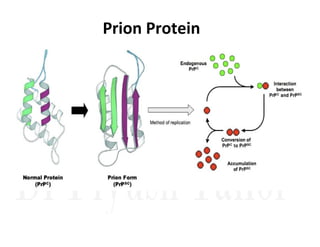
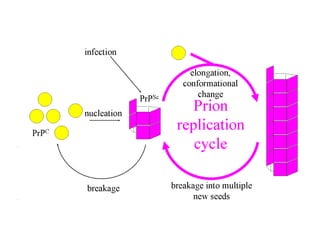
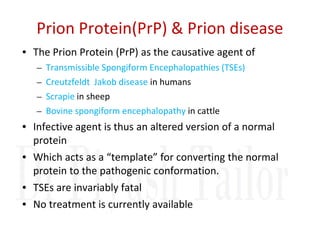
3. Tertiary structure describes the three-dimensional structure of the whole protein, influenced by interactions between residues far apart in the primary structure. Misfolded proteins can cause diseases like amyloidosis.