Chemical Forms of Vitamin A
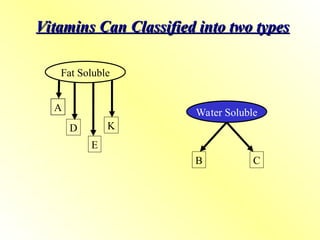
Vitamin A refers to a group of fat-soluble retinoids, including:
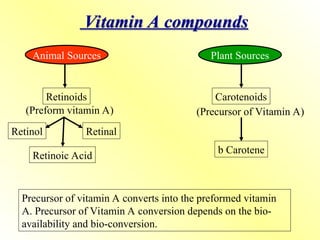
1.1 Preformed Vitamin A (Active forms)
Retinol (alcohol form)
Retinal (aldehyde form)
Retinoic acid (acid form)
Retinyl esters (storage form)
These are found in animal-derived foods.
1.2 Provitamin A (Precursors)
Carotenoids, especially beta-carotene, from plant sources.
Must be converted to retinol in the body.
---
2. Absorption and Metabolism
2.1 Absorption
Occurs in the small intestine.
Requires bile salts and dietary fat for micelle formation.
Retinyl esters are hydrolyzed to retinol by pancreatic lipase and intestinal enzymes.
2.2 Transport
Retinol is re-esterified in enterocytes and packaged into chylomicrons.
Transported via the lymphatic system to the liver.
2.3 Storage
Liver stores ~90% of the body's Vitamin A as retinyl esters in hepatic stellate (Ito) cells.
2.4 Mobilization and Circulation
When needed, retinol is released from the liver bound to retinol-binding protein (RBP) and transthyretin.
2.5 Cellular Uptake
Target cells take up the retinol-RBP complex via specific receptors.
Inside cells, retinol is converted to retinoic acid, the active form that regulates gene expression.
---
3. Physiological Roles
3.1 Vision
11-cis-retinal is a component of rhodopsin, essential for low-light (scotopic) vision.
Light converts 11-cis-retinal to all-trans-retinal, triggering a neural signal.
3.2 Gene Expression
Retinoic acid binds to nuclear receptors (RAR and RXR) and regulates gene transcription.
Important in cell differentiation, especially epithelial cells and immune cells.
3.3 Immunity
Supports T-cell differentiation, mucosal integrity, and antibody production.
3.4 Reproduction and Development
Crucial for embryogenesis and spermatogenesis.
Controls limb patterning and organogenesis.
3.5 Skin and Mucosa
Promotes epithelial differentiation, inhibits keratinization.
Used topically in acne and psoriasis (e.g., tretinoin, isotretinoin).
---
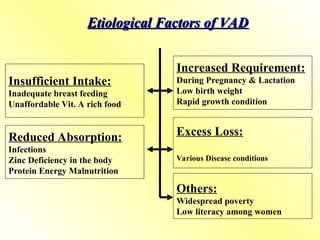
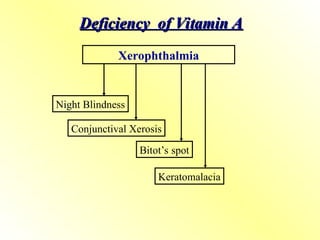
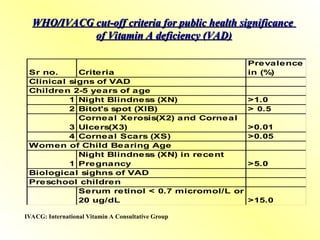
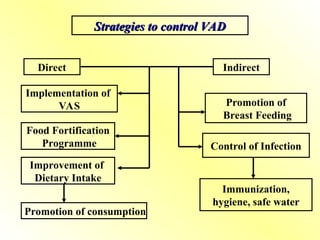
4. Deficiency of Vitamin A
Causes
Malnutrition
Fat malabsorption syndromes (e.g., celiac disease, cystic fibrosis)
Liver disorders
Symptoms
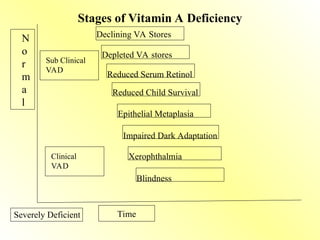
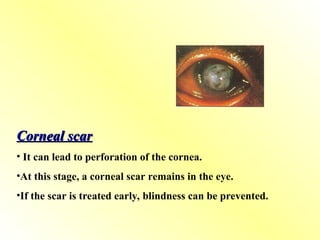
Night blindness (nyctalopia) – early sign
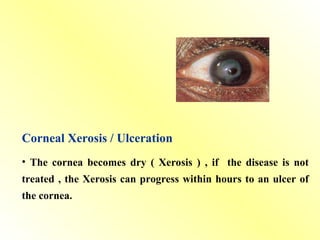
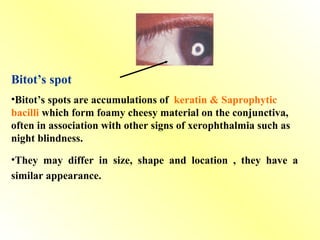
Xerophthalmia – dryness, Bitot’s spots, keratomalacia
Increased infections – especially respiratory and gastrointestinal
.