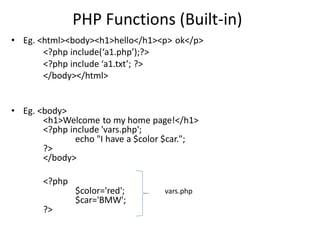
The document discusses PHP functions, highlighting their role as organized code blocks that can be called when needed. It categorizes functions into built-in and user-defined, detailing various built-in PHP functions and providing examples for their usage. Additionally, it explains concepts like dynamic function calls and variable scope within functions.