Recommended
PPT
PPT
PPTX
PPT
Bhel inventory management singh begun yeh
PPT
Process Design and Layouts of fundamental of apreations and managemant.ppt
PPT
Layout Class different type and Advantages
PPT
PPT
PPT
Product service -profiling
PPTX
Operations and Supply Chain Management Wednesday -W3 - 68G.pptx
PPTX
Mba ii pmom_unit-2.3 facility layout a
PPTX
Plant Layout basic idea and classification.pptx
PPTX
plant layout ( Operation Research )
PPT
Process Selection & Facility Layout.ppt
PPT
Meenakshi mam Types of plant layout video.ppt
PPT
PPT
PPT
Chapter VI-chapter 6 dt-2024-11-20 10-38-54.ppt
PPT
PPTX
understanding of industrial facility layout.pptx
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
DOC
PPTX
PDF
Why Projects Fail – The Need to “Do the Right Project” and “Do the Project Ri...
PPTX
Chapter 1 - Introduction to Business Research.pptx
More Related Content
PPT
PPT
PPTX
PPT
Bhel inventory management singh begun yeh
PPT
Process Design and Layouts of fundamental of apreations and managemant.ppt
PPT
Layout Class different type and Advantages
PPT
PPT
Similar to Process_Choices_Layout_Decisions_and_Space_Utilization.pptx
PPT
Product service -profiling
PPTX
Operations and Supply Chain Management Wednesday -W3 - 68G.pptx
PPTX
Mba ii pmom_unit-2.3 facility layout a
PPTX
Plant Layout basic idea and classification.pptx
PPTX
plant layout ( Operation Research )
PPT
Process Selection & Facility Layout.ppt
PPT
Meenakshi mam Types of plant layout video.ppt
PPT
PPT
PPT
Chapter VI-chapter 6 dt-2024-11-20 10-38-54.ppt
PPT
PPTX
understanding of industrial facility layout.pptx
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
DOC
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PDF
Why Projects Fail – The Need to “Do the Right Project” and “Do the Project Ri...
PPTX
Chapter 1 - Introduction to Business Research.pptx
PPTX
Master of Punjabi Short Story "kartar singh duggal
PPTX
How Physician Assistants in the USA Earn CME Credits Online.pptx
PPTX
Definition of communication skills and it's process.
PDF
West Hatch High School - GCSE Media Specification
PPTX
How to Easily Track Appraisal Analysis Report in Odoo 18 Appraisal
PDF
How to Select a Project Title for UG Zoology Projects: A Step-by-Step Guide f...
PDF
Information about Presentation strategies
PPTX
West Hatch High School - GCSE Media Studies
PPTX
West Hatch High School -- GCSE Geography
PDF
Darwinism: Theory of Natural Selection and Origin of Species
PDF
Tetracycline Class of Antibiotics: SAR, MOA and Uses
PDF
Pratishta Educational Society., Courses & Opportunities
PPTX
literary theory and criticism by Vivek p
PPTX
Guidelines for reporting social networks and personal networks data
PDF
West Hatch High School - GCSE French Specification
PPTX
West Hatch High School - GCSE Spanish Presentation
PPT
West Hatch High School - GCSE History Option
PPTX
SOLAR SYSTEM.pptx || The infinity solar system
Process_Choices_Layout_Decisions_and_Space_Utilization.pptx 1. 2. 3. Understanding Process Choices
• Process choice refers to selecting the method
used to produce goods or deliver services.
• It depends on volume, variety, and customer
requirements.
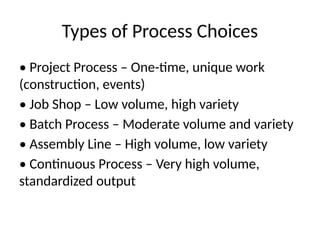
4. Types of Process Choices
• Project Process – One-time, unique work
(construction, events)
• Job Shop – Low volume, high variety
• Batch Process – Moderate volume and variety
• Assembly Line – High volume, low variety
• Continuous Process – Very high volume,
standardized output
5. Importance of Process Choice
• Impacts cost and quality
• Determines flexibility
• Affects resource utilization
• Influences customer satisfaction
6. Layout Decisions – Meaning
• Layout decision involves arranging machines,
workstations, people, and equipment within a
facility for smooth workflow.
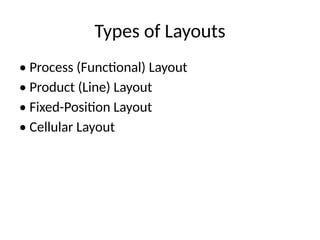
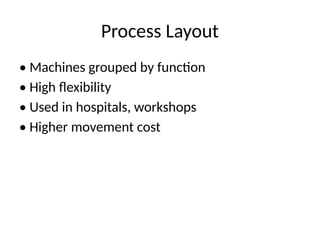
7. Types of Layouts
• Process (Functional) Layout
• Product (Line) Layout
• Fixed-Position Layout
• Cellular Layout
8. 9. 10. Fixed Position Layout
• Product remains at one place
• Resources move around it
• Used in shipbuilding, construction
11. 12. Space Utilization – Meaning
• Space utilization refers to effective use of
available space to support operations, safety,
and comfort.
13. Importance of Space Utilization
• Reduces congestion
• Improves workflow
• Enhances safety
• Improves employee comfort
14. Key Factors in Layout & Space
Planning
• Space utilization
• Flexibility
• Cost
• Safety
• Comfort
15. Flexibility
• Ability of layout to adapt to changes in
demand, product, or process.
• Flexible layouts support future growth.
16. 17. 18. Comfort & Ergonomics
• Proper seating and workspace
• Ventilation and lighting
• Noise control
• Comfort improves productivity and morale.
19.