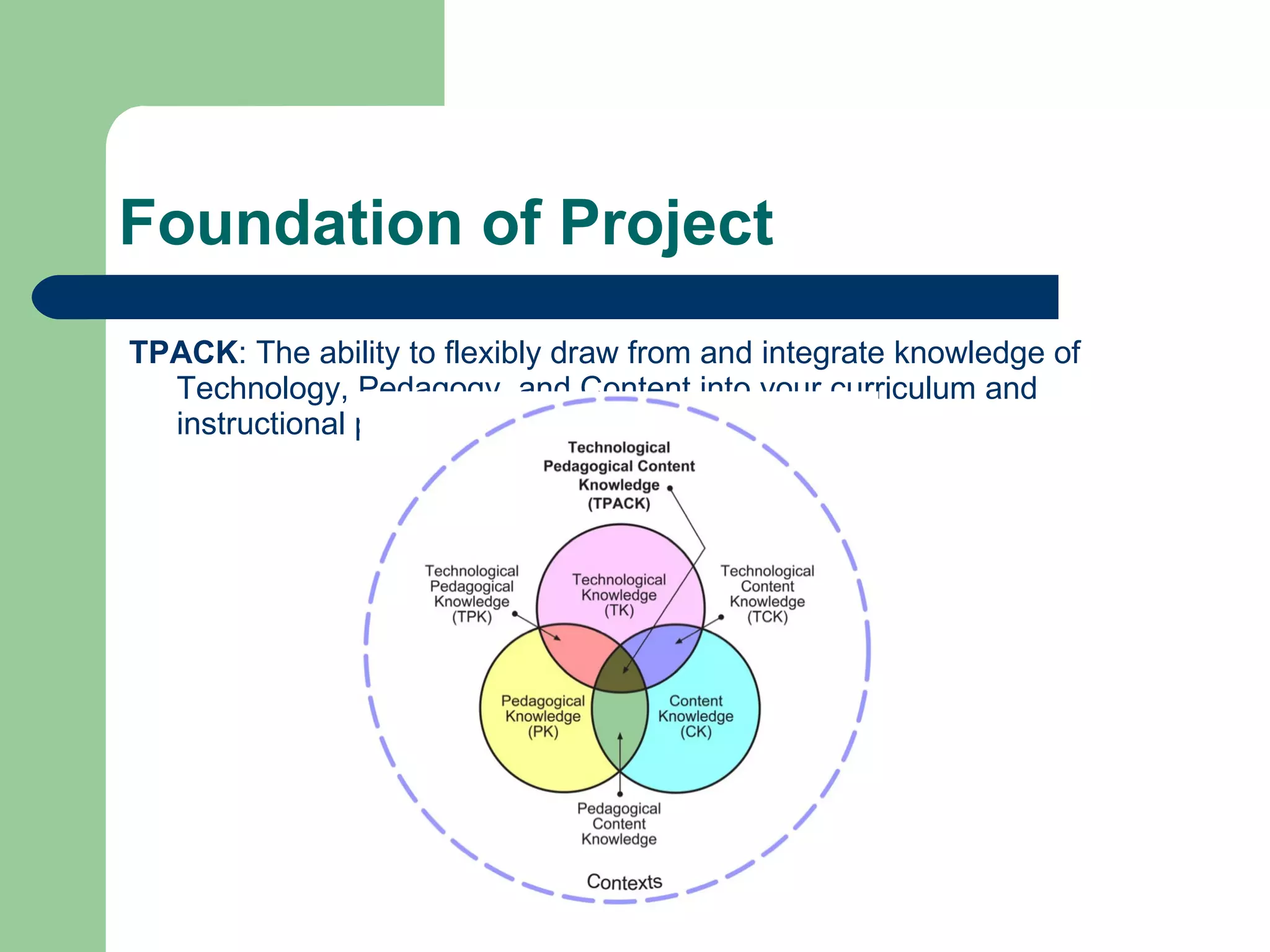
This document outlines a curriculum project focused on problem solving. It discusses the foundation of applying technology, pedagogy and content knowledge (TPACK) to curriculum and instruction. The essential question is about the role of problem solving in society's evolution. Standards for technology literacy and mathematical practice involving problem solving are presented. Objectives are to apply and demonstrate a four-step problem solving process by creating a multimedia presentation. Assessment involves a multimodal project showing the problem solving process.