This document introduces key concepts in probability:
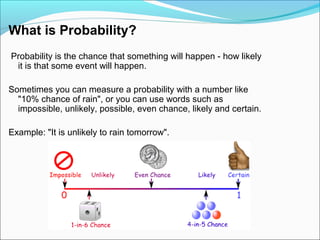
1. Probability is the likelihood of an event occurring, which can be expressed as a number or words like "impossible" or "likely".
2. Events can be classified as exhaustive, favorable, mutually exclusive, equally likely, complementary, and independent.
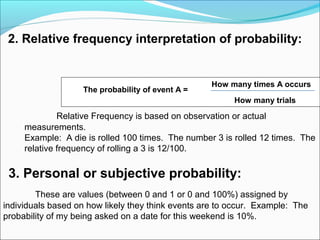
3. There are three approaches to defining probability: classical, frequency, and axiomatic. The classical approach defines probability as the number of favorable outcomes over the total number of possible outcomes. The frequency approach defines it as the limit of favorable outcomes over total trials. The axiomatic approach uses axioms like probabilities being between 0 and 1.
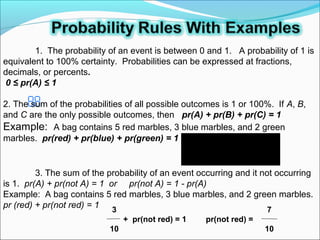
4. Several properties of probability are described, like the sum