Embed presentation
Download to read offline



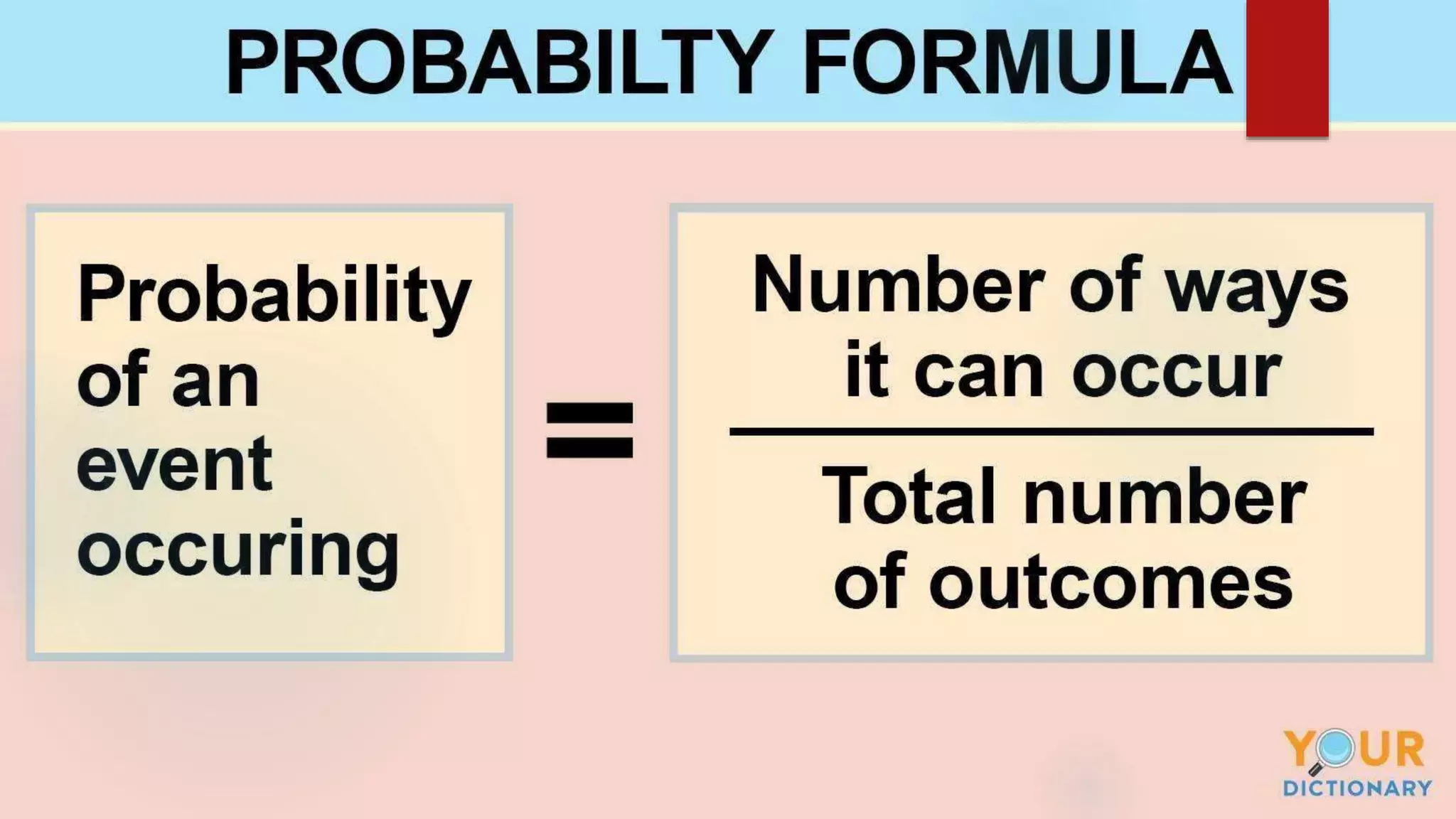






Probability is the likelihood that an event will occur, which is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes. There are three types of probability: theoretical, experimental, and axiomatic. Theoretical probability is defined as the ratio of favorable to possible outcomes and can be demonstrated using examples like selecting letters from a word. Experimental probability is determined by repeated experiments or simulations. Axiomatic probability aims to precisely measure the chance of an event occurring using probability assignments.









