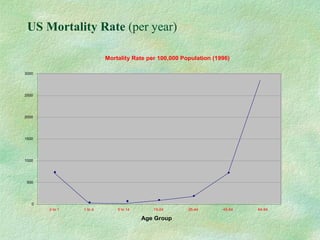
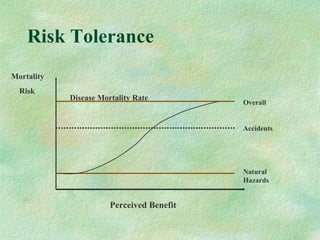
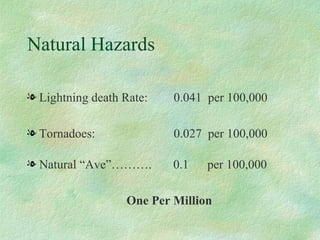
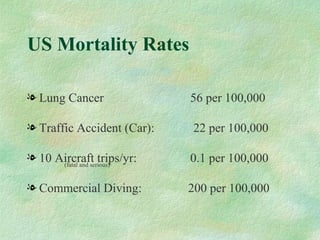
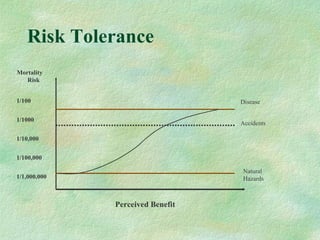
This document discusses probabilistic risk assessment and factors that influence risk tolerance. It addresses the classification of probability and severity of hazardous events. It also examines different types of risks, including voluntary and involuntary risks. Mortality rates from various causes such as accidents, diseases, and natural hazards are presented to illustrate perceptions of risk tolerance.