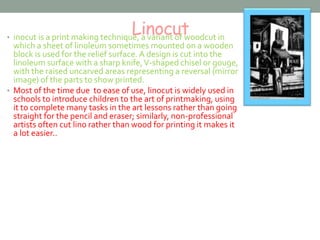
This document provides an overview of various printmaking techniques including etching, linocut, screen printing, woodcut, lithography, mechanical printing, letterpress printing, gravure, digital printing, photocopying, laser printing, inkjet printing, and desktop publishing. It describes the basic processes of each technique such as how etchings are made using acid to cut into metal plates and how linocuts involve cutting designs into linoleum. The document also explains differences between techniques like how screen printing uses mesh screens to apply ink versus relief printing which involves carving or etching images.