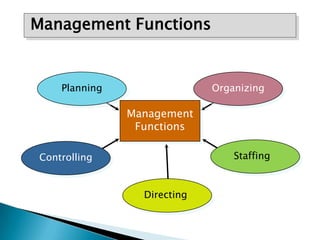
1. The document discusses several concepts in management including definitions of management provided by Koontz and Fayol, characteristics of management, and principles of management.
2. It also summarizes the Hawthorne experiments which studied the impact of workplace conditions on productivity and found social factors to be important motivators.
3. Major management thinkers discussed include Frederick Taylor with his scientific management principles, Fayol's administrative management principles, and Max Weber's bureaucracy model.