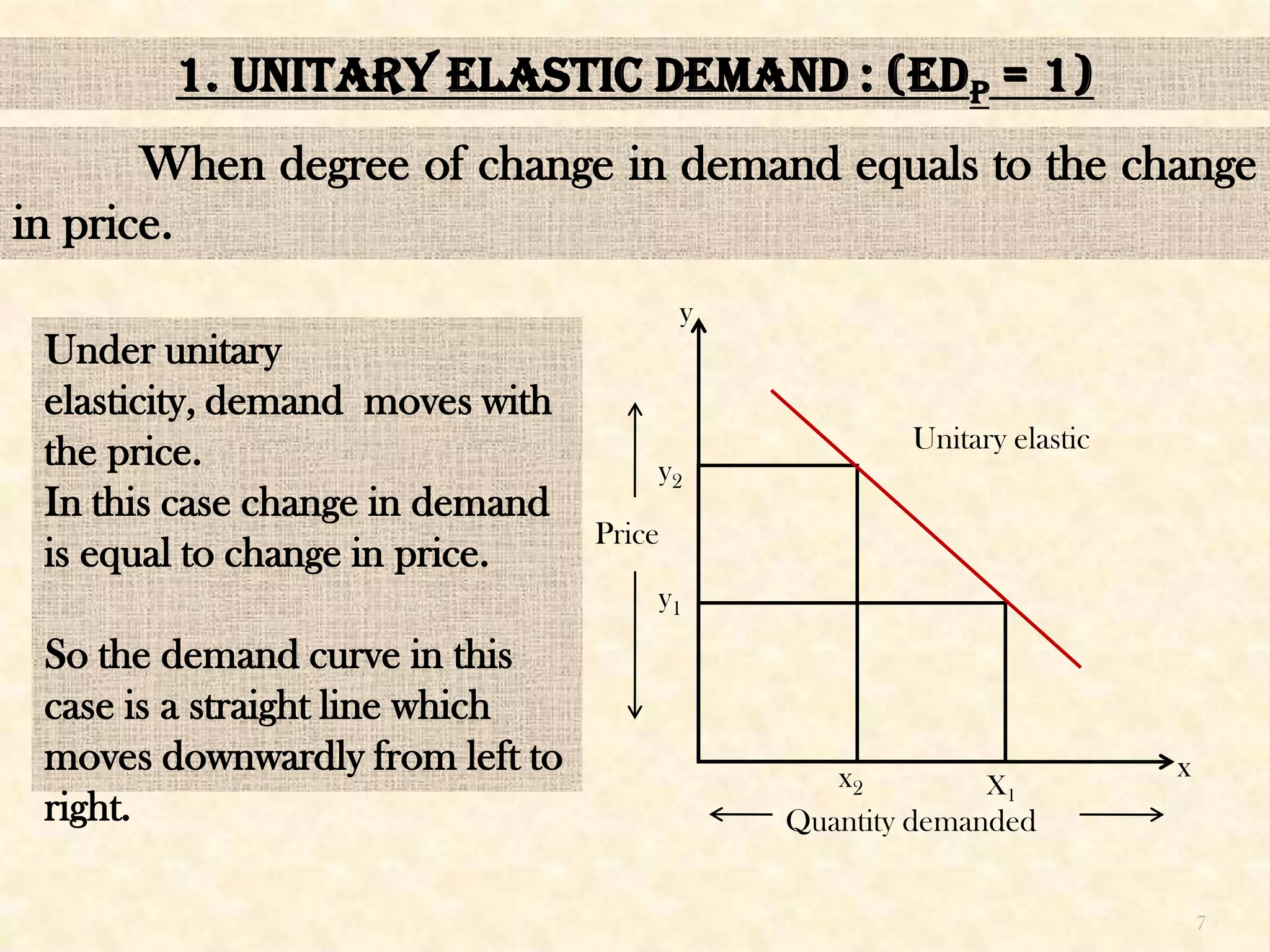
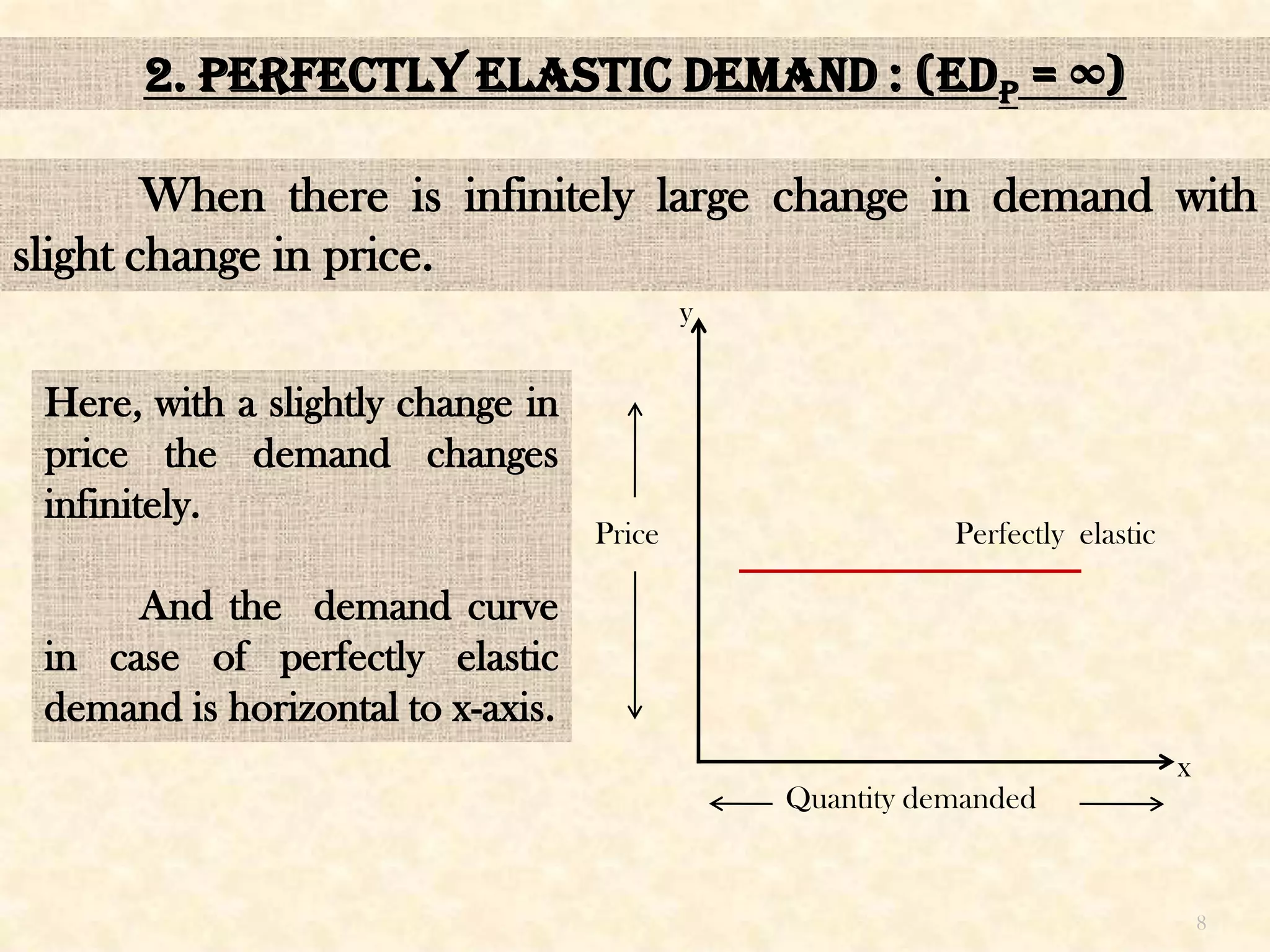
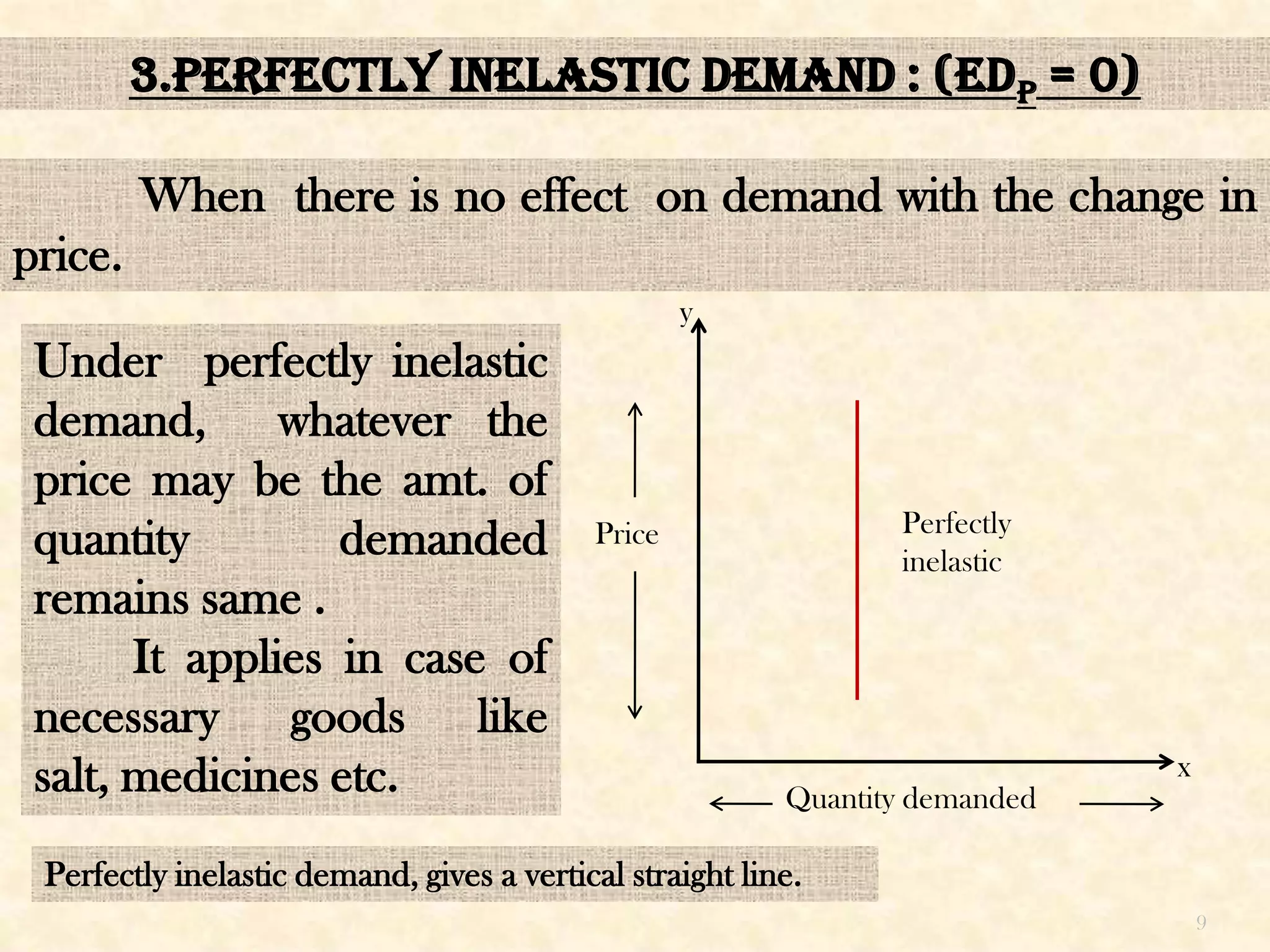
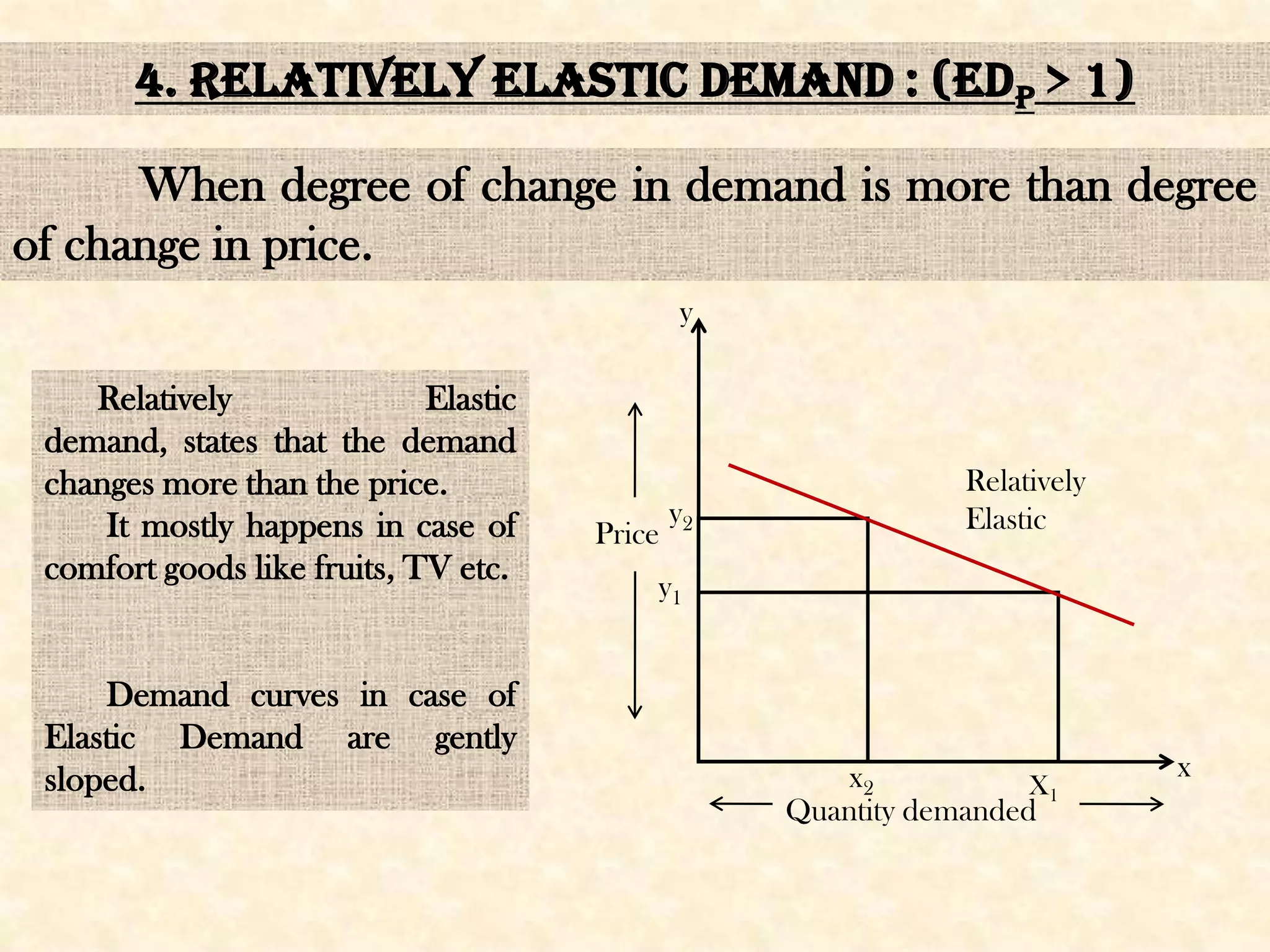
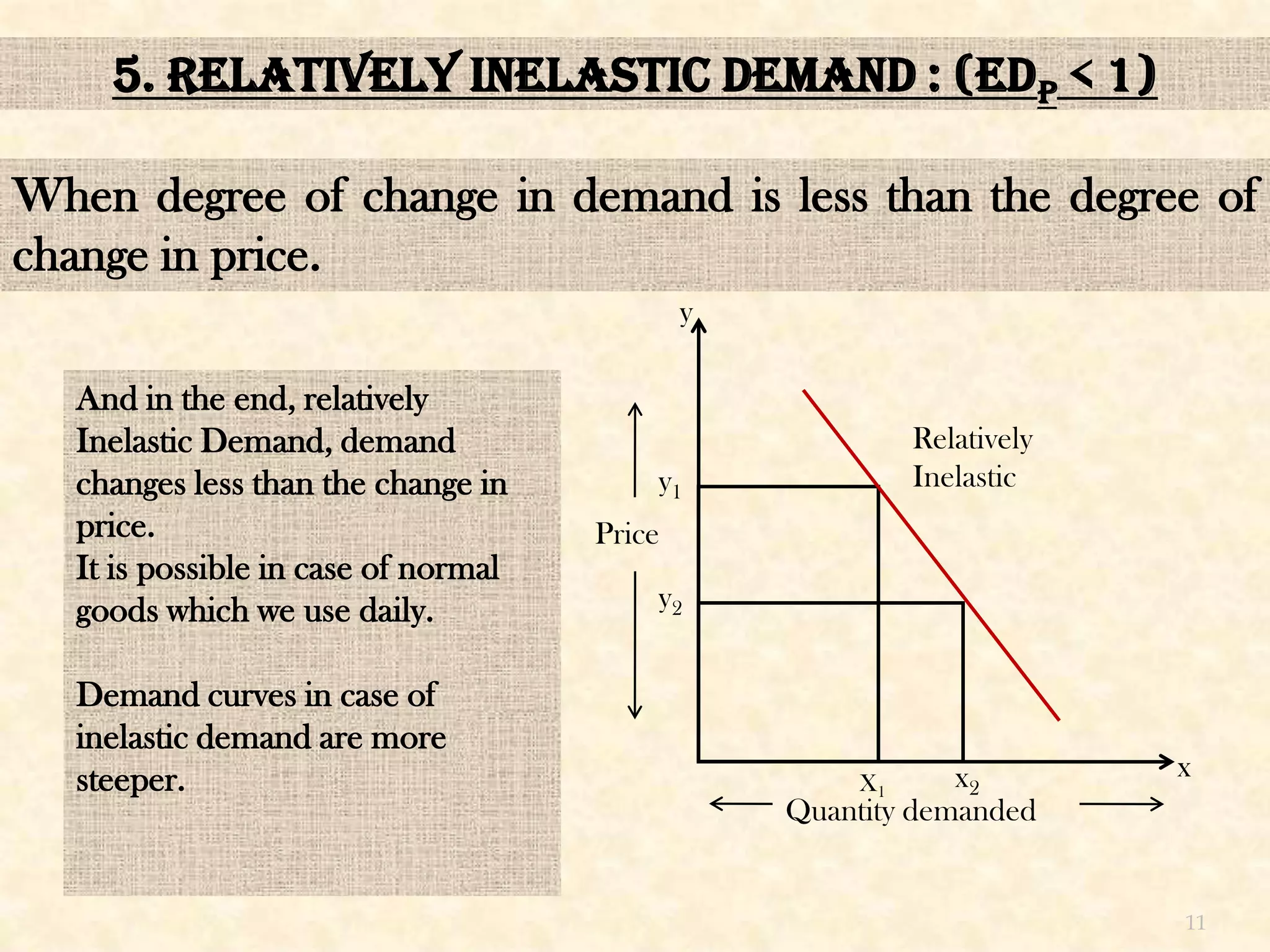
This seminar presentation discusses price elasticity of demand. It begins by defining price elasticity of demand as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. It then outlines the five degrees of price elasticity: [1] Unitary elastic demand (edp=1) where changes in demand equal changes in price; [2] Perfectly elastic demand (edp=∞) where small price changes cause large demand changes; [3] Perfectly inelastic demand (edp=0) where demand is unchanged by price changes; [4] Relatively elastic demand (edp>1) where demand changes more than price; and [5] Relatively inelastic demand (edp